Concrete is ubiquitous in our world, as is concern about carbon emissions. The creation of concrete is a major source of carbon emissions, because the calcium-based substances that make it up are heated at high temperatures to form the cement.
But scientists at MIT may have found a way to decrease the carbon emissions that result from concrete production: reducing the ratio of calcium to the silicate-rich clay.
Normally, concrete is made by mixing gravel, water, sand, and cement, Gizmag reports. The cement is produced by heating calcium-rich materials (e.g., limestone) at temperatures up to 2,732 F, and researchers say that this part of the process produces the majority of the carbon emissions.
The MIT research team examined the makeup of the concrete, and found that a calcium to silica ratio of 1.5 is the optimal mix for reducing emissions and producing quality concrete. In the industry, these ratios can vary from 1.2 to 2.2, though 1.7 is the cement production standard. Changing the standard ratio to 1.5, researchers say, could reduce carbon emissions by as much as 60%.
This mix of concrete was also shown to have a higher resistance to fractures. According to Gizmag, the researchers claim that "this is due to the molecular structure transforming from a tightly ordered crystalline to a disordered glassy structure." Regardless of the reason why, the 1.5 ratio concrete has twice the mechanical resistance to fractures of normal cement.
Because the analysis of this concrete mix was carried out on a molecular level, it remains to be seen whether or not these results will remain the same in engineering-scale applications. This research was published in the journal Nature Communications.
Related Stories
Concrete | May 18, 2021
GCP Applied Technologies Partners with Athena Sustainable Materials Institute
GCP Applied Technologies, a leading global provider of construction products technologies, is pleased to announce a partnership with Athena Sustainable Materials Institute, a nonprofit research collaborative bringing life cycle assessment to the construction sector.
Steel Buildings | Apr 17, 2021
Speed Core wall system is used for the second time in office building in San Jose
The construction method is expected to knock off three months from the project’s schedule.
Concrete | Apr 1, 2021
Fabcon acquires Michigan's Kerkstra Precast
Minneapolis-based Fabcon Precast, a leading provider of structural precast wall panels, announced today that, effective March 31st, it has acquired Kerkstra Precast, a Michigan corporation.
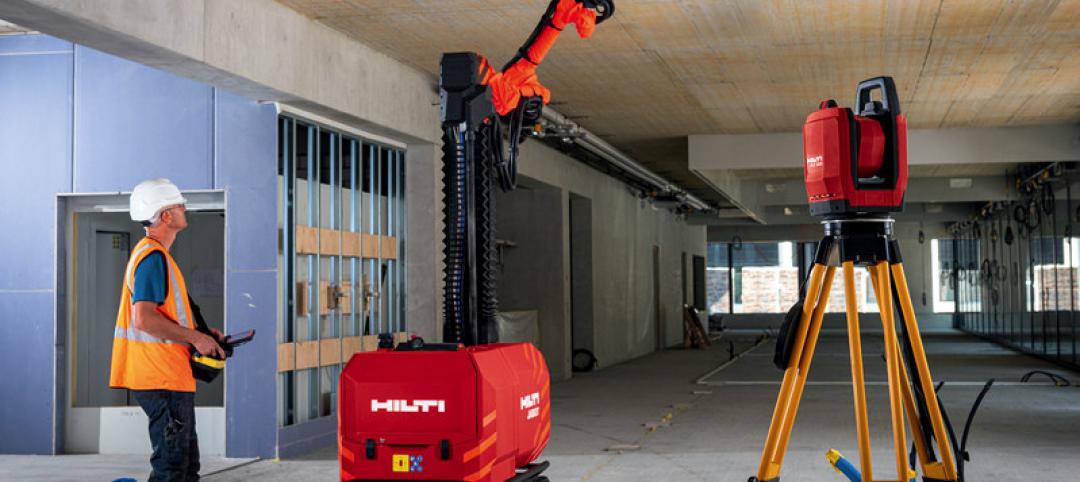
AEC Tech | Oct 28, 2020
Meet Jaibot, Hilti's new construction robot
The semi-autonomous robot is designed to assist MEP contractors with ceiling-drilling applications.
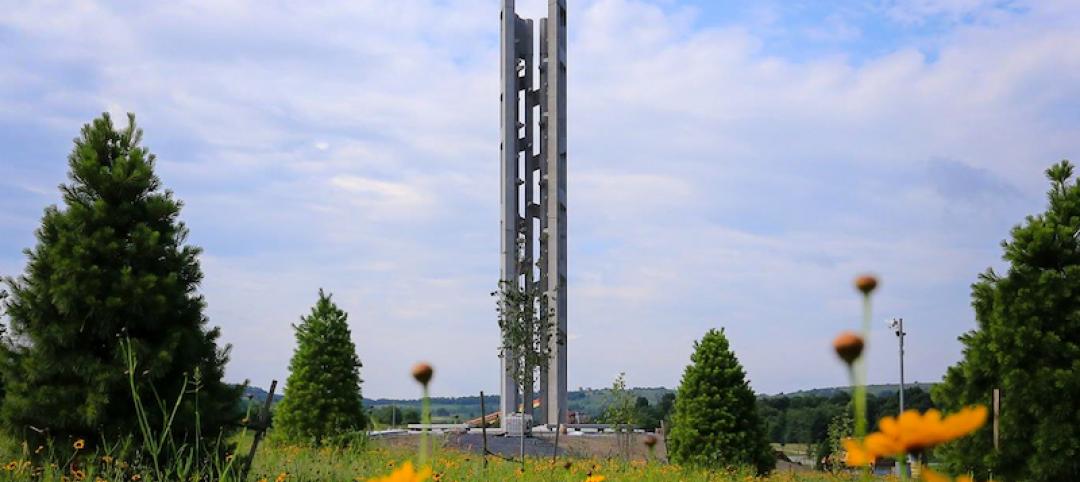
Concrete | Sep 2, 2020
Precast concrete tower honors victims of United Airlines Flight 93
Paul Murdoch Architects designed the project.
75 Top Building Products | Dec 16, 2019
Top Structural Products for 2019
Inpro’s Fireline 140 fire barrier and Owens Corning’s Foamglas cellular glass insulation are among the 10 structural products to make Building Design+Construction's 2019 101 Top Products report.
75 Top Building Products | Dec 16, 2019
101 Top Products for 2019
Building Design+Construction readers and editors select their top building products for the past 12 months in the fourth-annual 101 Top Products report.
Codes and Standards | Sep 9, 2019
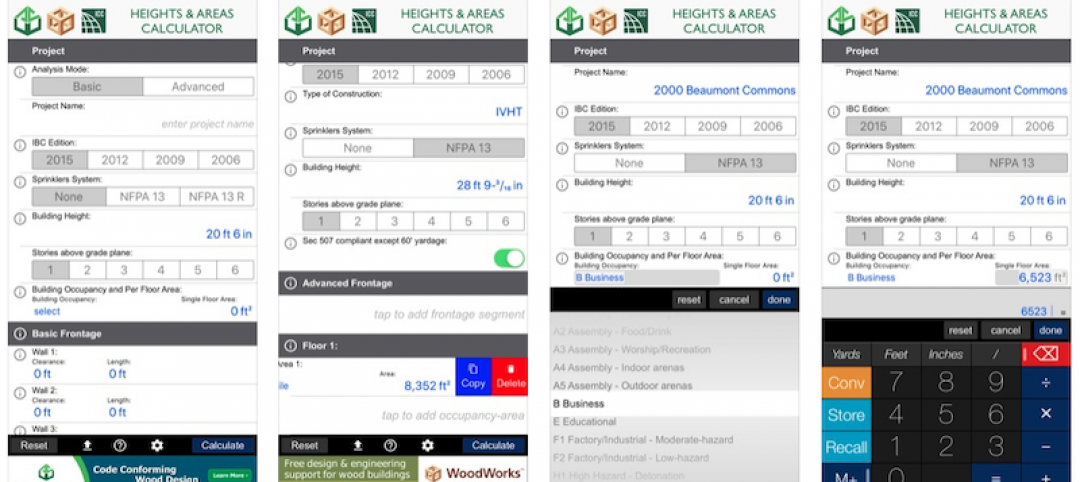
Free app calculates maximum allowable heights and areas for buildings
A free app that calculates the maximum allowable heights and areas for buildings of various occupancy classifications and types of construction has been released.
Concrete | Jul 8, 2019
Concrete repair code requirements released
American Concrete Institute offers guidance on assessment, repair, rehab of existing concrete structures.