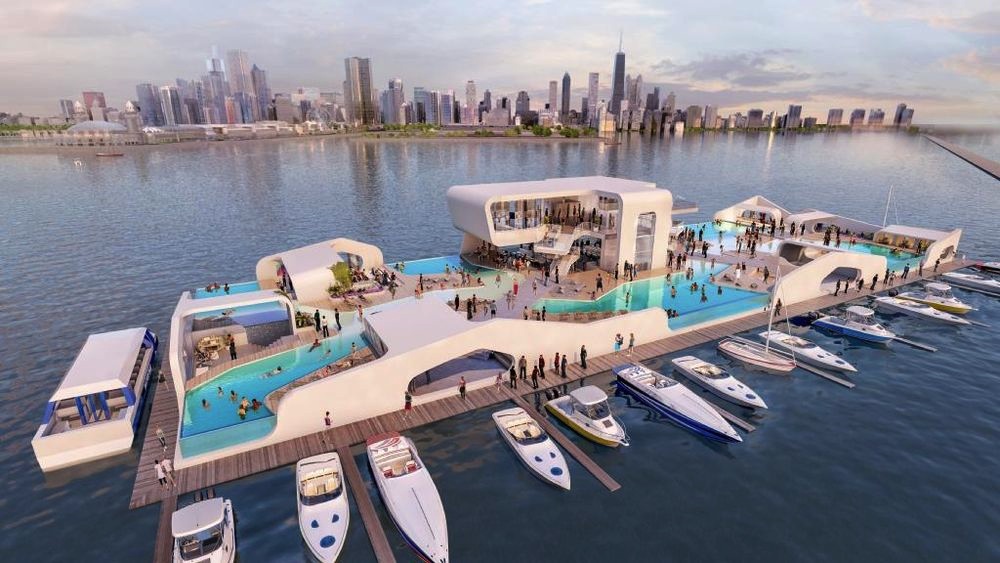
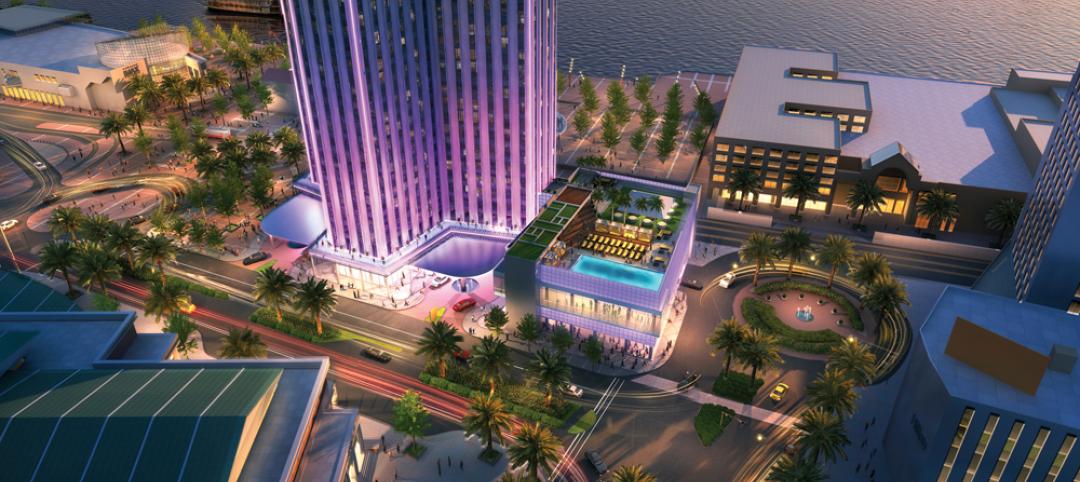
A floating resort barge is luxurious enough, but how about one with a lazy river? Breakwater Chicago is a proposed 300x100-foot party vessel that will be anchored on Lake Michigan, a little more than a mile off Chicago’s shoreline. Breakwater has been sharing renderings of its project across social media channels this month.
We're sure you've all envisioned hanging out on Breakwater on a summer day. If you haven't, let us help you out.. pic.twitter.com/0LOA4oPXhx
— Breakwater Chicago (@BreakwaterCHI) March 8, 2016
The resort will have three restaurants, a swimming pool, and spa. The vessel’s open-air structures are defined by their rounded shapes and smooth, modern appearance. Boats and water taxis can dock on its piers. Though it's only the size of a football field, Breakwater will be able to hold more than 2,000 people.
Ever thought about what it would look like as soon as you step foot onto Breakwater? pic.twitter.com/YkYlfph04s
— Breakwater Chicago (@BreakwaterCHI) March 4, 2016
It will even be operable in the winter. Breakwater will be towed to the coast and enclosed in a clear dome during the colder months.
While the project is rich with ambitious concepts, specific details on construction and clearance have not been released.
The project, which was announced in 2014, is led by Chicago area native Beau D’Arcy, a lifelong sailor and Harvard Business School graduate. D’Arcy estimates that it will cost $23 million to fund Breakwater. A Kickstarter campaign raised more than $60,000.
Related Stories
| Nov 26, 2013
Construction costs rise for 22nd straight month in November
Construction costs in North America rose for the 22nd consecutive month in November as labor costs continued to increase, amid growing industry concern over the tight availability of skilled workers.
| Nov 25, 2013
Building Teams need to help owners avoid 'operational stray'
"Operational stray" occurs when a building’s MEP systems don’t work the way they should. Even the most well-designed and constructed building can stray from perfection—and that can cost the owner a ton in unnecessary utility costs. But help is on the way.
| Nov 19, 2013
Top 10 green building products for 2014
Assa Abloy's power-over-ethernet access-control locks and Schüco's retrofit façade system are among the products to make BuildingGreen Inc.'s annual Top-10 Green Building Products list.
| Nov 15, 2013
Metal makes its mark on interior spaces
Beyond its long-standing role as a preferred material for a building’s structure and roof, metal is making its mark on interior spaces as well.
| Nov 13, 2013
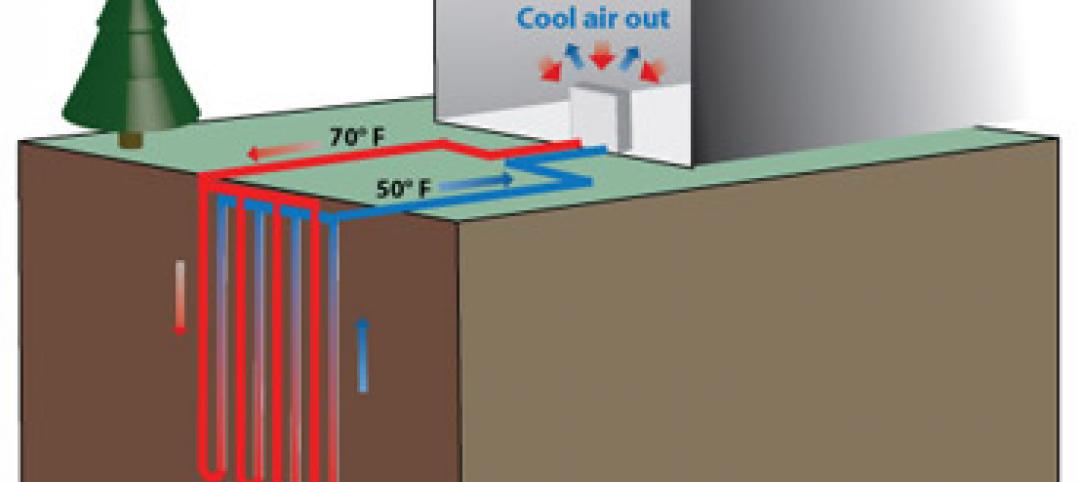
Installed capacity of geothermal heat pumps to grow by 150% by 2020, says study
The worldwide installed capacity of GHP systems will reach 127.4 gigawatts-thermal over the next seven years, growth of nearly 150%, according to a recent report from Navigant Research.
| Nov 6, 2013
Green hotel trends: Industry expands its sustainability focus beyond laundry
There’s more to creating a sustainable hotel than saving water and power by asking guests to reuse their towels.
| Oct 30, 2013
15 stellar historic preservation, adaptive reuse, and renovation projects
The winners of the 2013 Reconstruction Awards showcase the best work of distinguished Building Teams, encompassing historic preservation, adaptive reuse, and renovations and additions.
| Oct 30, 2013
11 hot BIM/VDC topics for 2013
If you like to geek out on building information modeling and virtual design and construction, you should enjoy this overview of the top BIM/VDC topics.
| Oct 28, 2013
Urban growth doesn’t have to destroy nature—it can work with it
Our collective desire to live in cities has never been stronger. According to the World Health Organization, 60% of the world’s population will live in a city by 2030. As urban populations swell, what people demand from their cities is evolving.
| Oct 18, 2013
Researchers discover tension-fusing properties of metal
When a group of MIT researchers recently discovered that stress can cause metal alloy to fuse rather than break apart, they assumed it must be a mistake. It wasn't. The surprising finding could lead to self-healing materials that repair early damage before it has a chance to spread.