Designed by Chicago architect Jarvis Hunt and constructed in 1903, Building 13 is one of 39 structures within the Great Lakes Historic District at Naval Station Great Lakes, Ill. The original boathouse, considered a “contributing structure with major significance,” reflects the Beaux Arts vocabulary and classical forms that Hunt applied to his work (1902-1911) at the Naval Station campus.
After more than a century of use, however, the building envelope, brick, terra cotta, windows, and roof were in sore need of repair, even as the Navy was seeking to expand the function of the nearly 27,000-sf boathouse to support year-round marine activity of the Great Lakes harbor with the addition of shops, classrooms, offices, toilets, and showers. However, any renovation had to be done within the strict guidelines of the Secretary of the Interior Standards for Rehabilitation, the National Historic Preservation Act, and the Base Exterior Architecture Plan (BEAP).
The design-build team, led by Chicago firm Johnson Lasky Architects, took on the structural problems more or less from top to bottom. Visual and physical inspections, materials testing (including brick and mortar analyses), and soundings on each individual terra cotta unit were conducted.
The roof was replaced with shingles over three-inch polyiso ventilated nail base insulation panels. Forty-year asphalt shingles rated for 110 mph wind loads were used to meet the BEAP’s historic requirements. New copper gutters, flashings, and terminations were installed.
At the turn of the 20th century, terra cotta was used as a mass-produced alternative to carved stone, and Hunt made extensive use of it in Building 13. Damaged terra cotta was replaced with new matching material from California manufacturer Gladding McBean. Brick was salvaged from Navy supplies of matching historic brick. Mortar was replicated based on an analysis of existing original material. New exterior doors replicated the original wood panel design. The glass transom above the main entrance door was fitted with laminated glass.
Windows were completely restored off site; missing glass was replaced with glazing that matched the original in texture, thickness, and type (“wavy”) to meet state historical preservation standards.
With the building now providing year-round use, it was necessary to upgrade the mechanical system to forced air, with an air handler, ductwork, controls, and other equipment. The Building Team solved this problem by housing a new mechanical room between two existing mezzanines on opposite sides of the building within the warehouse.
In granting the project a Gold Award, the jury praised the Building Team’s attention to detail. “They had to tackle a lot of different components: brick, terra cotta, the windows, etc.,” said K. Nam Shiu, PE, SE, VP at Walker Restoration Consultants, Elgin, Ill. “This was a labor of love. It doesn’t look like any corners were cut,” said Tom Brooks, VP, Restoration Division, Berglund Construction, Chicago. “Instead of remove and throw away, they chose to remove and restore,” said George Tuhowski III, LEED AP, Director of Sustainability and General Superintendent, Leopardo Construction, Hoffman Estates, Ill.
Judge Darlene Ebel, Director, Facility Information Management, University of Illinois at Chicago, called it “a good restoration, with good sustainability. The building still fits in with the whole area.” BD+C
* Note: Walker Johnson, FAIA, recused himself from the proceedings during the judging of this entry.
PROJECT SUMMARY
Building Team
Submitting firm: Johnson Lasky Architects (architect)
Owner: Naval Station Great Lakes
Environmental design: EDI, Inc.
Structural engineer: AHG Structural Engineering
MEP/fire protection engineer: KJWW Engineering
GC: Boaz Friedler Joint Venture
General Information
Area: 26,900 gsf
Construction cost: $5 million
Construction time: May 2007 to August 2009
Delivery method: Design-build
Related Stories
Museums | Oct 20, 2015
Frank Lloyd Wright’s Bachman Wilson House finds new home at Arkansas museum
Crystal Bridges Museum reconstructed the 61-year-old Usonian house and will open it to the public in November.
Architects | Oct 20, 2015
Four building material innovations from the Chicago Architecture Biennial
From lightweight wooden pallets to the largest lengths of CLT-slabs that can be shipped across North America
University Buildings | Oct 16, 2015
5 ways architecture defines the university brand
People gravitate to brands for many reasons. Campus architecture and landscape are fundamental influences on the college brand, writes Perkins+Will's David Damon.
Architects | Oct 13, 2015
Architects Foundation expands National Resilience Initiative
The group is launching a search for three more NRI members.
Architects | Oct 13, 2015
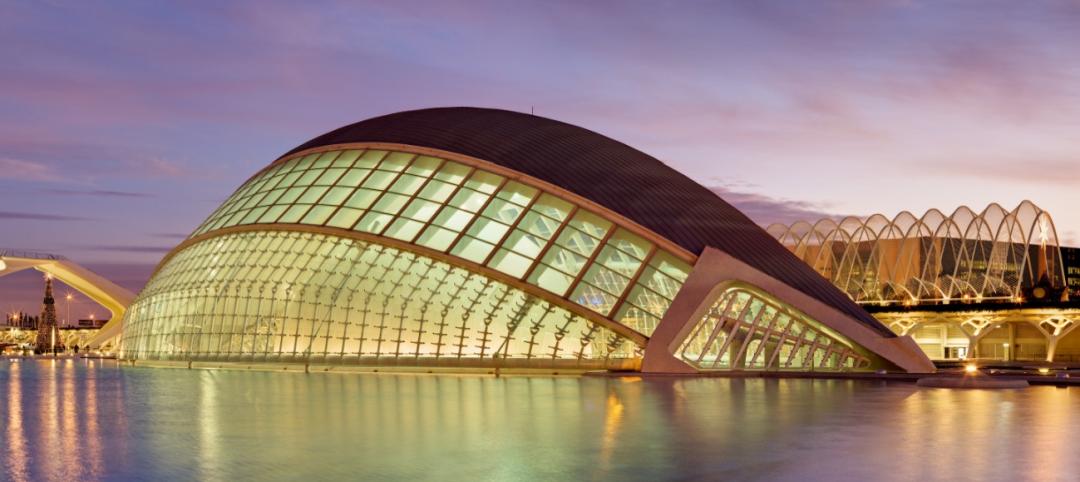
Santiago Calatrava wins the European Prize for Architecture
The award honors those who "forward the principles of European humanism."
Office Buildings | Oct 5, 2015
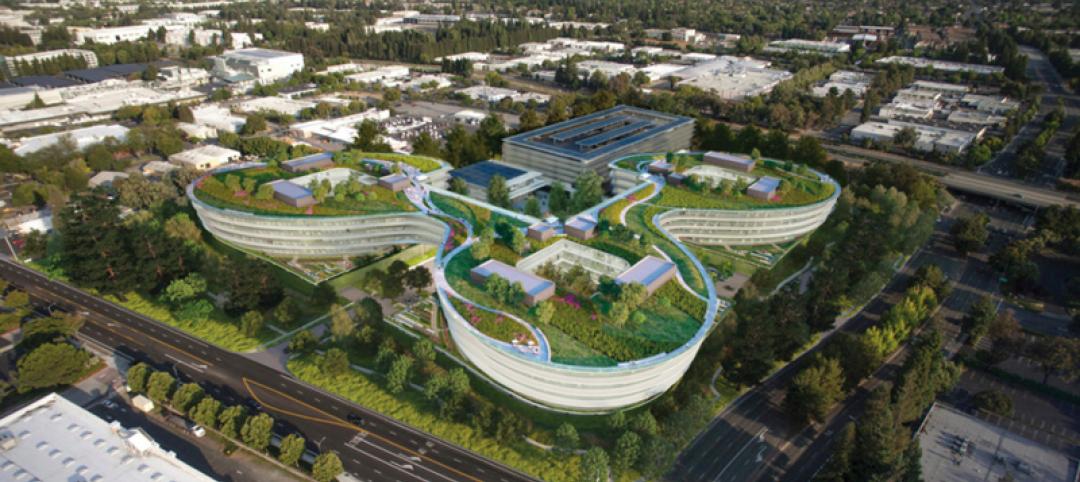
Renderings revealed for Apple's second 'spaceship': a curvy, lush office complex in Sunnyvale
The project has been dubbed as another “spaceship,” referencing the nickname for the loop-shaped Apple Campus under construction in Cupertino.
Airports | Oct 5, 2015
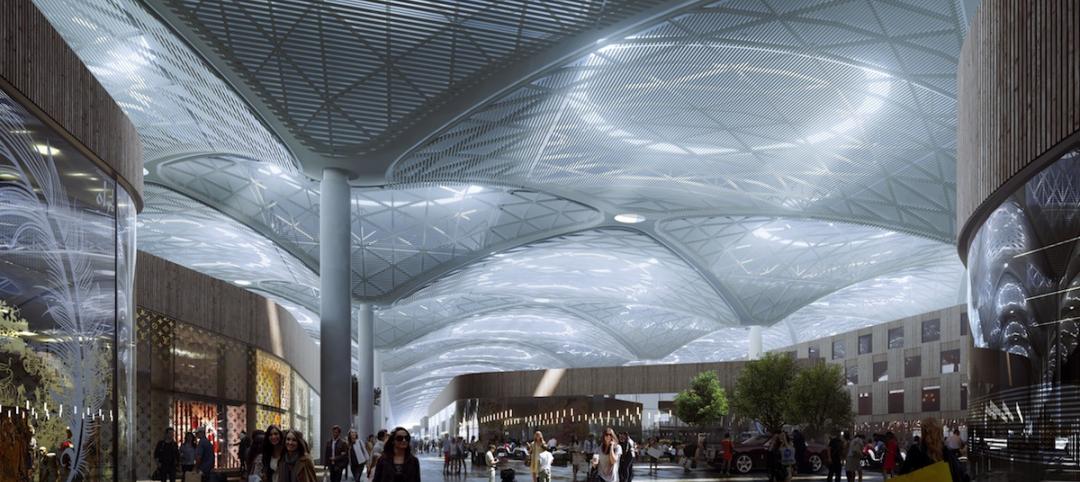
Perkins+Will selected to design Istanbul’s 'Airport City'
The mixed-use development will be adjacent to the Istanbul New Airport, which is currently under construction.
High-rise Construction | Oct 5, 2015
Zaha Hadid designs cylindrical office building with world’s tallest atrium
The 200-meter-high open space will cut the building in two.
Architects | Oct 2, 2015
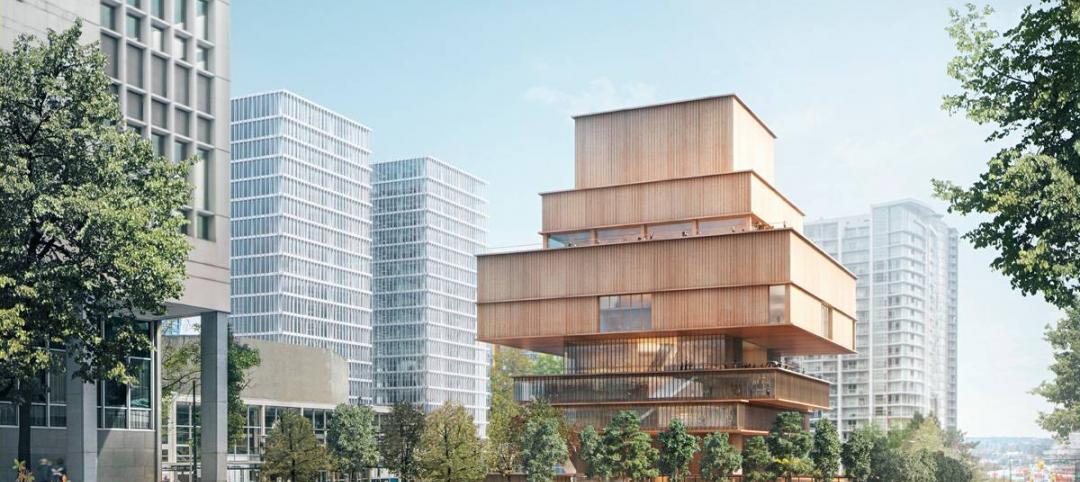
Herzog & de Meuron unveils design for Vancouver Art Gallery expansion
The blocky, seven-story wood and concrete structure is wider in the middle and uppermost floors.
Airports | Sep 30, 2015
Takeoff! 5 ways high-flyin' airports are designing for rapid growth
Nimble designs, and technology that humanizes the passenger experience, are letting airports concentrate on providing service and generating revenue.