Designed by Chicago architect Jarvis Hunt and constructed in 1903, Building 13 is one of 39 structures within the Great Lakes Historic District at Naval Station Great Lakes, Ill. The original boathouse, considered a “contributing structure with major significance,” reflects the Beaux Arts vocabulary and classical forms that Hunt applied to his work (1902-1911) at the Naval Station campus.
After more than a century of use, however, the building envelope, brick, terra cotta, windows, and roof were in sore need of repair, even as the Navy was seeking to expand the function of the nearly 27,000-sf boathouse to support year-round marine activity of the Great Lakes harbor with the addition of shops, classrooms, offices, toilets, and showers. However, any renovation had to be done within the strict guidelines of the Secretary of the Interior Standards for Rehabilitation, the National Historic Preservation Act, and the Base Exterior Architecture Plan (BEAP).
The design-build team, led by Chicago firm Johnson Lasky Architects, took on the structural problems more or less from top to bottom. Visual and physical inspections, materials testing (including brick and mortar analyses), and soundings on each individual terra cotta unit were conducted.
The roof was replaced with shingles over three-inch polyiso ventilated nail base insulation panels. Forty-year asphalt shingles rated for 110 mph wind loads were used to meet the BEAP’s historic requirements. New copper gutters, flashings, and terminations were installed.
At the turn of the 20th century, terra cotta was used as a mass-produced alternative to carved stone, and Hunt made extensive use of it in Building 13. Damaged terra cotta was replaced with new matching material from California manufacturer Gladding McBean. Brick was salvaged from Navy supplies of matching historic brick. Mortar was replicated based on an analysis of existing original material. New exterior doors replicated the original wood panel design. The glass transom above the main entrance door was fitted with laminated glass.
Windows were completely restored off site; missing glass was replaced with glazing that matched the original in texture, thickness, and type (“wavy”) to meet state historical preservation standards.
With the building now providing year-round use, it was necessary to upgrade the mechanical system to forced air, with an air handler, ductwork, controls, and other equipment. The Building Team solved this problem by housing a new mechanical room between two existing mezzanines on opposite sides of the building within the warehouse.
In granting the project a Gold Award, the jury praised the Building Team’s attention to detail. “They had to tackle a lot of different components: brick, terra cotta, the windows, etc.,” said K. Nam Shiu, PE, SE, VP at Walker Restoration Consultants, Elgin, Ill. “This was a labor of love. It doesn’t look like any corners were cut,” said Tom Brooks, VP, Restoration Division, Berglund Construction, Chicago. “Instead of remove and throw away, they chose to remove and restore,” said George Tuhowski III, LEED AP, Director of Sustainability and General Superintendent, Leopardo Construction, Hoffman Estates, Ill.
Judge Darlene Ebel, Director, Facility Information Management, University of Illinois at Chicago, called it “a good restoration, with good sustainability. The building still fits in with the whole area.” BD+C
* Note: Walker Johnson, FAIA, recused himself from the proceedings during the judging of this entry.
PROJECT SUMMARY
Building Team
Submitting firm: Johnson Lasky Architects (architect)
Owner: Naval Station Great Lakes
Environmental design: EDI, Inc.
Structural engineer: AHG Structural Engineering
MEP/fire protection engineer: KJWW Engineering
GC: Boaz Friedler Joint Venture
General Information
Area: 26,900 gsf
Construction cost: $5 million
Construction time: May 2007 to August 2009
Delivery method: Design-build
Related Stories
K-12 Schools | Mar 1, 2015
Are energy management systems too complex for school facility staffs?
When school districts demand the latest and greatest, they need to think about how those choices will impact the district’s facilities employees.
Office Buildings | Mar 1, 2015
Google unveils dramatic tent-like, modular-focused plan for corporate HQ
The master plan by Bjarke Ingels and Thomas Heatherwick will wrap highly flexible office blocks in soaring translucent canopies.
Industrial Facilities | Feb 27, 2015
Massive windmill will double as mixed-use entertainment tower in Rotterdam
The 571-foot structure will house apartments, a hotel, restaurants, even a roller coaster.
Architects | Feb 27, 2015
5 finalists announced for 2015 Mies van der Rohe Award
Bjarke Ingels' Danish Maritime Museum and the Ravensburg Art Museum by Lederer Ragnarsdóttir Oei are among the five projects vying for the award.
Office Buildings | Feb 26, 2015
Using active design techniques to strengthen the corporate workplace and enhance employee wellness
The new Lentz Public Health Center in Nashville, Tenn., serves as a model of how those progressive and healthy changes can be made.
K-12 Schools | Feb 26, 2015
Should your next school project include a safe room?
Many school districts continue to resist mandating the inclusion of safe rooms or storm shelters in new and existing buildings. But that may be changing.
K-12 Schools | Feb 26, 2015
Construction funding still scarce for many school districts
Many districts are struggling to have new construction and renovation keep pace with student population growth.
K-12 Schools | Feb 26, 2015
D.C.'s Dunbar High School is world's highest-scoring LEED school, earns 91% of base credits
The 280,000-sf school achieved 91 points, out of 100 base points possible for LEED, making it the highest-scoring school in the world certified under USGBC’s LEED for Schools-New Construction system.
K-12 Schools | Feb 25, 2015
Polish architect designs modular ‘kids city’ kindergarten using shipping container frames
Forget the retrofit of a shipping container into a building for one moment. Designboom showcases the plans of Polish architect Adam Wiercinski to use just the recycled frames of containers to construct a “kids city.”
Cultural Facilities | Feb 25, 2015
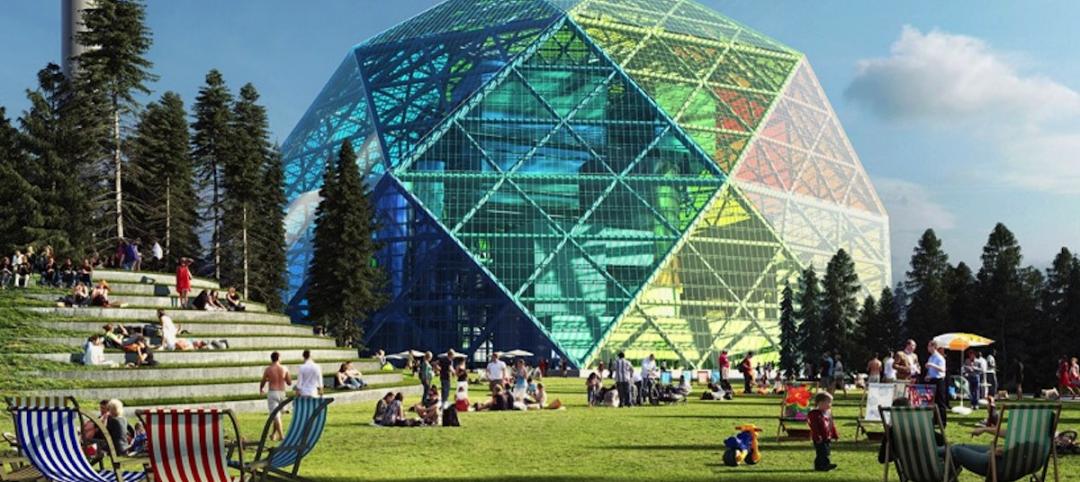
Bjarke Ingels designs geodesic dome for energy production, community use
A new building in Uppsala, Sweden, will serve as a power plant during the winter and a venue for shows, festivals, and music events during the warm months.