California regulators voted unanimously recently on a series of measures that include a ban on the sale of natural gas-powered heating and hot water systems beginning in 2030.
If the decision goes forward, it would be the first time a state has banned fossil fuel heaters for existing buildings as well as for new construction. The California Air Resources Board (CARB), the agency that oversees the state’s climate targets and regulates pollution, passed the measure as part of a larger plan to cut greenhouse gas emissions and comply with federal air quality targets.
The ban is not a done deal, however, according to a CARB spokesperson. “The commitment the Board made in approving the State SIP (State Implementation Plan) Strategy was for California Air Resources Board staff to pursue each measure in the document and take it to the Board for consideration,” says Melanie J. Turner, CARB information officer. “CARB will need to hold workshops and look at the issues related to the space and water heater measure. If the concept is not feasible, CARB staff will present the information to the Board who could determine they will not pursue it.”
If the ban on fossil fuel heating does go into effect, homeowners in California would only be able to buy zero-emission furnaces or hot-water heaters. Regulators expect this would prompt a switch to heat pumps and heat pump water heaters.
The use of fossil fuels in homes accounts for about 10% of U.S. carbon emissions. Since 2019, several cities and states have either enacted fossil fuel hookup bans for new buildings or have considered such bans. California is the first jurisdiction to extend such bans to existing buildings.
A switch to heat pumps, a more efficient cooling appliance than commonly used air conditioning units, could cut peak energy demand during heat waves, reducing the risk of brownouts and blackouts. To help residents make the transition to heat pumps, California’s most recent budget includes $1.4 billion to decarbonize buildings. Most of that funding is targeted for low-income families.
Related Stories
| Jul 30, 2014
German students design rooftop solar panels that double as housing
Students at the Frankfurt University of Applied Sciences designed a solar panel that can double as living space for the Solar Decathlon Europe.
| Jul 28, 2014
Post Tower Wins CTBUH 10-Year Award
The 10 Year Award recognizes proven value and performance in a tall building, across one or more of a wide range of criteria, over a period of 10 years since its completion.
| Jul 24, 2014
MIT researchers explore how to make wood composite-like blocks of bamboo
The concept behind the research is to slice the stalk of bamboo grass into smaller pieces to bond together and form sturdy blocks, much like conventional wood composites.
| Jul 17, 2014
A harmful trade-off many U.S. green buildings make
The Urban Green Council addresses a concern that many "green" buildings in the U.S. have: poor insulation.
| Jul 17, 2014
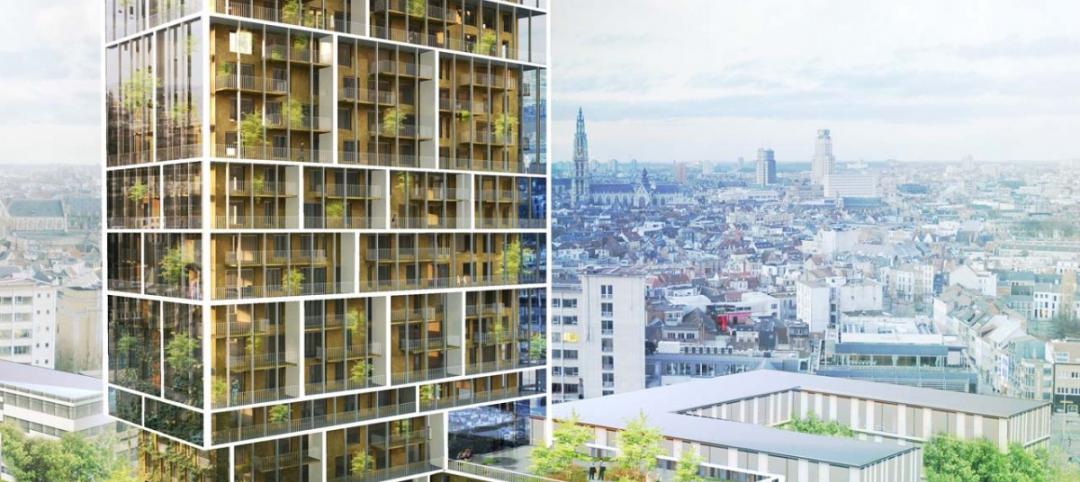
A high-rise with outdoor, vertical community space? It's possible! [slideshow]
Danish design firm C.F. Møller has developed a novel way to increase community space without compromising privacy or indoor space.
| Jul 16, 2014
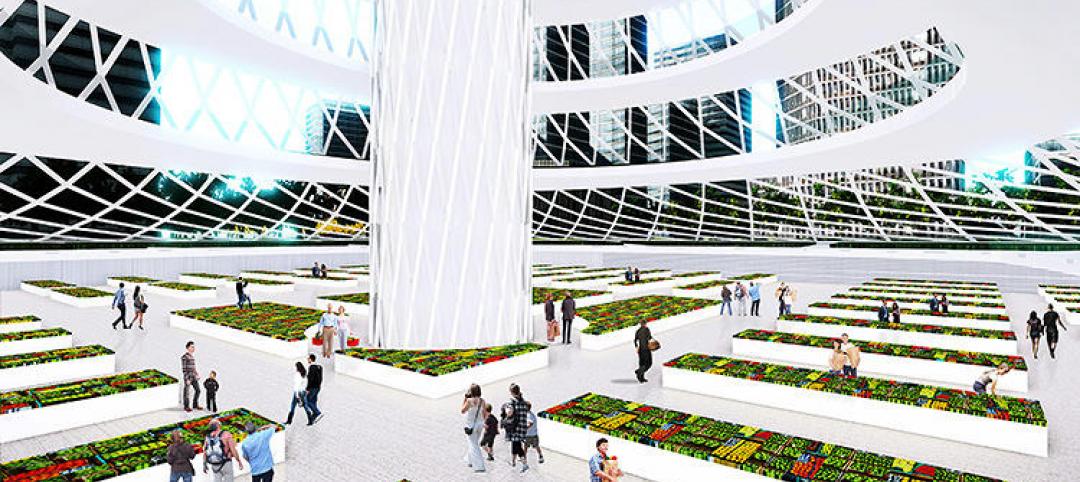
Check out this tree-like skyscraper concept for vertical farming
Aprilli Design Studio has stepped forward with a new idea for a vertical farm, which is intended to resemble a giant tree. It uses lightweight decks as outdoor growing space, adding up to about 25 acres of space.
| Jul 15, 2014
A look into the history of modular construction
Modular construction is more than a century old, and throughout its lifespan, the methods have been readapted to meet specific needs of different eras.
| Jul 14, 2014
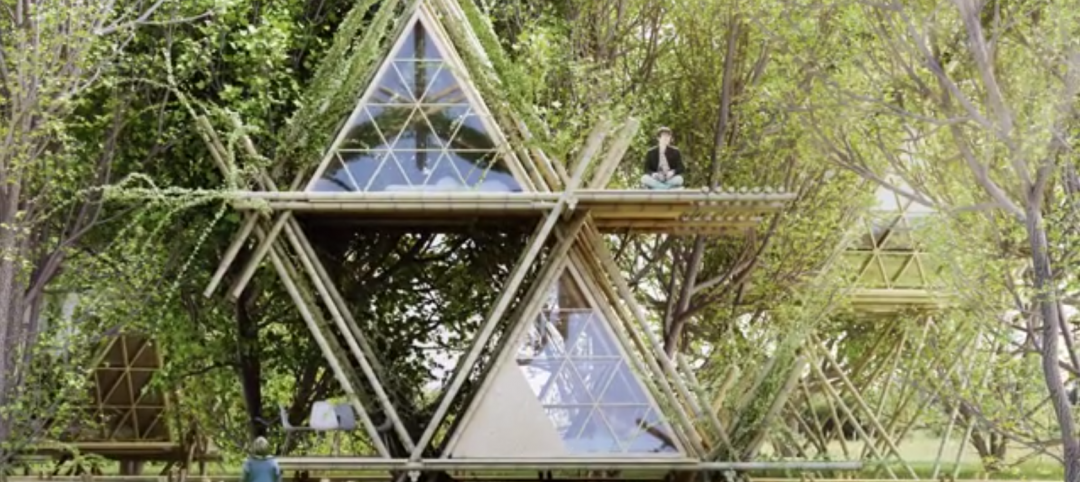
Meet the bamboo-tent hotel that can grow
Beijing-based design cooperative Penda designed a bamboo hotel that can easily expand vertically or horizontally.
| Jul 11, 2014
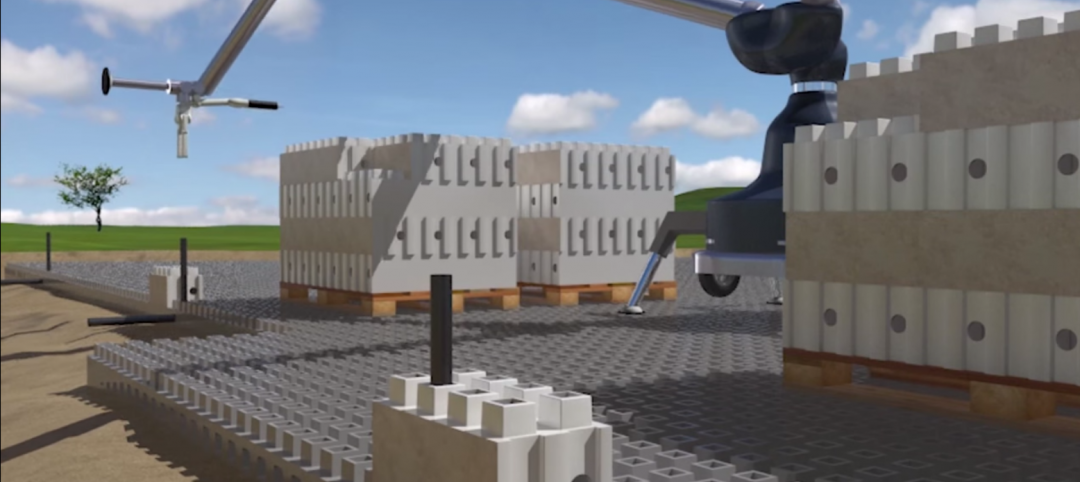
Are these LEGO-like blocks the future of construction?
Kite Bricks proposes a more efficient way of building with its newly developed Smart Bricks system.
| Jul 10, 2014
BioSkin 'vertical sprinkler' named top technical innovation in high-rise design
BioSkin, a system of water-filled ceramic pipes that cools the exterior surface of buildings and their surrounding micro-climates, has won the 2014 Tall Building Innovation Award from the Council on Tall Buildings and Urban Habitat.