Last year, in a tech report on artificial intelligence (AI), BD+C reported that Arup had applied a “neural network” to a light rail design and reduced the number of utility clashes by over 90%, saving nearly 800 hours of engineering.
The same report described an algorithm developed by workspace-sharing giant WeWork that is 40% more accurate than humans at predicting meeting room usage. The article proposed that machine learning is “still a theoretical proposition” for most of the AEC industry, even though the practical results of these examples suggest that AI has bridged the gap from theory to practice.
In fact, the consensus in our industry seems to be that AI’s limitations will always hold it back. In 2015, WeWork’s then Director of Research, Daniel Davis, declared that “it is—for now—impossible to get computers to think creatively, manage multidisciplinary teams, and do many of the other day-to-day tasks.” Citing University of Oxford research estimating that there’s a less than 2% chance that architects’ jobs will be automated, Davis concludes that architecture cannot be automated at all. (The statistics stickler in me wants to point out that 2% is not zero.)
As long ago as 2012, Wired’s Kevin Kelly insisted otherwise, predicting that automation in every industry was “just a matter of time.” “It doesn’t matter if you are a doctor, lawyer, architect, reporter, or even programmer. The robot takeover will be epic,” wrote Kelly.
ALSO SEE: 4 fundamental relationships between buildings and machines
And despite Davis’ claim that computers cannot “think creatively,” others forecast the opposite—that computers in fact will be responsible for the “coming creativity explosion.”
The underlying question here is simply this: Are machines capable of design? To answer that, we’d have to clarify the meaning of design, a surprisingly elusive term. One dictionary defines it as “an arrangement of lines or shapes created to form a pattern or decoration.”
Computer programs have been capable of automating this process since the early ’60s. Later that decade, in The Sciences of the Artificial (1969), Nobel economist Herbert Simon famously defined design as “devising courses of action aimed at changing existing situations into preferred ones.”
The examples from Arup and WeWork certainly demonstrate how to create “preferred situations.” Today, whole businesses are being founded around AI-driven design. Using a proprietary algorithm, California-based Cover can develop custom house plans within a few hours.
Nevertheless, many are skeptical. “I am convinced,” says innovation expert Nick Seneca Jankel, “that no computer, no matter how powerful, will ever be able to purposefully innovate an artistic breakthrough like hip hop, or a commercial one like Instagram. Breakthrough creativity is fundamentally organic, not algorithmic.”
Yet, this point of view suggests that computer processes will always be defined as they are now and will remain incapable of becoming “organic, not algorithmic.” Google’s Ray Kurzweil is certain that machines will achieve human-level intelligence in a decade and significantly outpace us thereafter. How can we possibly envision the capability of computers once they have exponentially exceeded our awareness?
So, instead of debating about whether machines can design, why don’t we ask, What if they could? How might architecture change if computers take over the process entirely?
Already, machine-driven procedures can dramatically improve the efficiency of design, construction, and operations—for example, by increasing energy performance and decreasing fabrication time and costs. Yet, often architects get in the way of these improvements because we insert our personal aesthetic preferences.
How much smarter could buildings get if we let them design themselves for optimal performance? A growing wealth of research is revealing how people respond to light, space, form, pattern, texture, and color, and much of this information could be automated during design. “Beauty is merely a function of mathematical distances or ratios,” explains computer scientist Daniel Cohen-Or, who invented a “beauty engine” that subtly improves photos—with an 80% success rate, according to polling.
So, if architects were to step out of the way and allow architecture to evolve beyond our imaginings, what kind of world might emerge? Louis Kahn famously asked, “What does the building want to be?” If Kurzweil is correct, and buildings achieve self-awareness soon, they could become what they want to be without asking us. Self-actualized architecture.
For now, the likelihood of architects letting go of their traditional services seems low. A BD+C reader survey in January revealed that 81% of designers believe that computers will never match human intelligence, and only half said that job losses would be justified if AI could create better buildings. This begs a big question: What do we value more—architects or architecture?
Lance Hosey, FAIA, LEED Fellow, is a Design Director with Gensler. His book, The Shape of Green: Aesthetics, Ecology, and Design, has been an Amazon #1 bestseller in the Sustainability & Green Design category.
Related Stories
Urban Planning | Dec 15, 2021
EV is the bridge to transit’s AV revolution—and now is the time to start building it
Thinking holistically about a technology-enabled customer experience will make transit a mode of choice for more people.
Designers / Specifiers / Landscape Architects | Nov 16, 2021
‘Desire paths’ and college campus design
If a campus is not as efficient as it could be, end users will use their feet to let designers know about it.
AEC Tech | Oct 25, 2021
Token Future: Will NFTs revolutionize the design industry?
How could non-fungible tokens (NFTs) change the way we value design? Woods Bagot architect Jet Geaghan weighs risk vs. reward in six compelling outcomes.
Sponsored | BD+C University Course | Oct 15, 2021
7 game-changing trends in structural engineering
Here are seven key areas where innovation in structural engineering is driving evolution.
AEC Tech Innovation | Oct 7, 2021
How tech informs design: A conversation with Mancini's Christian Giordano
Mancini's growth strategy includes developing tech tools that help clients appreciate its work.
AEC Tech | Oct 5, 2021
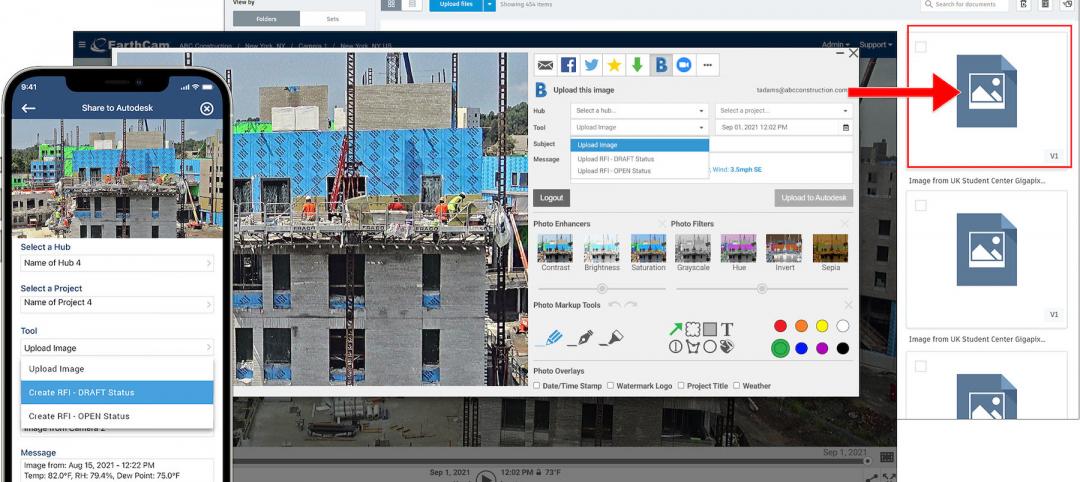
EarthCam Builds On its Connectivity with Autodesk Construction Cloud
Premiering new visual verification features for Autodesk Build and BIM 360
AEC Tech | Sep 21, 2021
A new webtool follows ConTech from incubation to application and beyond
MIT and JLL have created Tech Tracker to help real estate professionals see what’s hot now and what might be.
Architects | Aug 5, 2021
Lord Aeck Sargent's post-Katerra future, with LAS President Joe Greco
After three years under the ownership of Katerra, which closed its North American operations last May, the architecture firm Lord Aeck Sargent is re-establishing itself as an independent company, with an eye toward strengthening its eight practices and regional presence in the U.S.
Architects | Aug 5, 2021
Lord Aeck Sargent's post-Katerra future, with LAS President Joe Greco
After three years under the ownership of Katerra, which closed its North American operations last May, the architecture firm Lord Aeck Sargent is re-establishing itself as an independent company, with an eye toward strengthening its eight practices and regional presence in the U.S.
AEC Tech | Jul 14, 2021
Bjarke Ingels Group and UNStudio invest in SpaceForm, a virtual workspace for architects
Squint/Opera developed the platform in 2018.