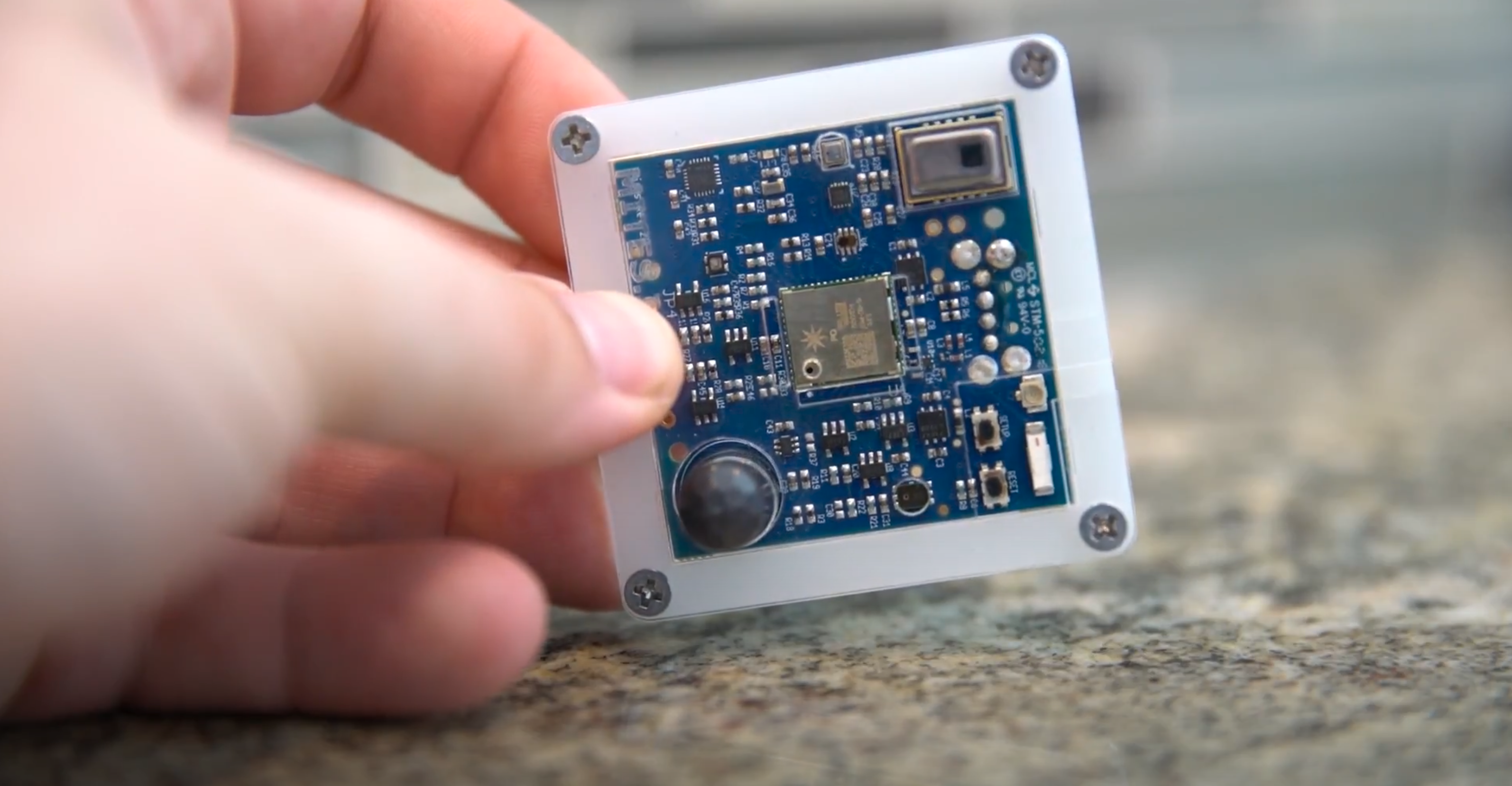
A research project to test next-generation building sensors at Carnegie Mellon University provoked intense debate over the privacy implications of widespread deployment of the devices in a new 90,000-sf building.
The light-switch-size devices, called Mites, are capable of measuring 12 types of data, including motion and sound. The sensors were mounted in more than 300 locations throughout the building—on walls and ceilings of hallways, in conference rooms, and in private offices—as part of a research project on smart buildings.
Students and faculty who research the social impacts of technology felt that the device’s microphone, infrared sensor, thermometer, and other sensors, would subject them to experimental surveillance. They objected to the fact that the devices were installed without their explicit consent.
Researchers behind the project had taken steps to anonymize data collected by the building sensors, but that didn’t staunch concerns by building occupants. The project highlights latent mistrust over technologies that can be used as surveillance devices.
“Current IoT systems offer little transparency about exactly what data is being collected, how it is being transmitted, and what security protocols are in place—while erring on the side of over-collection,” according to a report in Technology Review.
Widely reported incidents of smart-home devices such as baby monitors, Google Home and Amazon Alexa speakers, and robot vacuums being hacked or having their data shared without users’ knowledge or consent, complicate the climate for public acceptance of building sensors.
As work continues on the project, how Carnegie Mellon researchers build in privacy safeguards, and how well they communicate those measures to the university community, may be instructive about whether this technology is accepted by the public.
Related Stories
| May 18, 2011
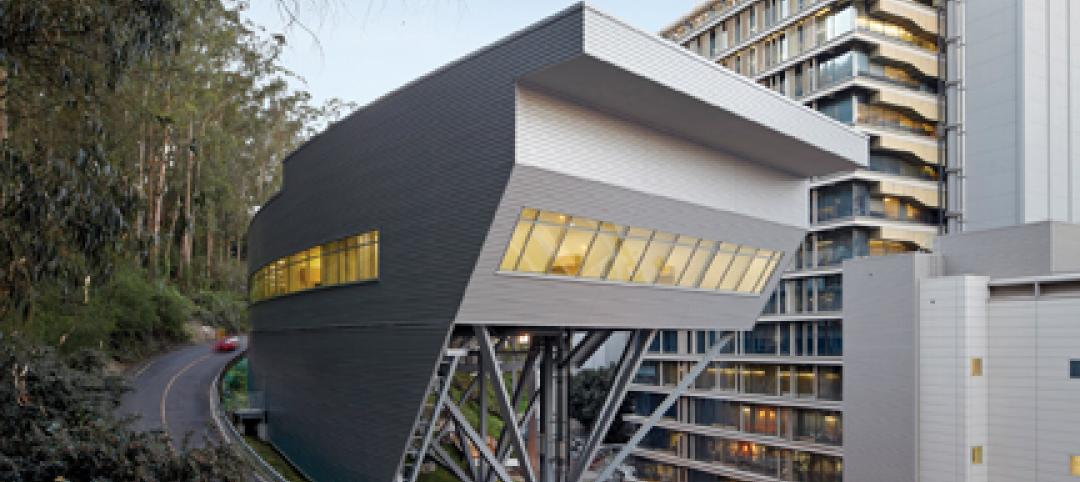
Raphael Viñoly’s serpentine-shaped building snakes up San Francisco hillside
The hillside location for the Ray and Dagmar Dolby Regeneration Medicine building at the University of California, San Francisco, presented a challenge to the Building Team of Raphael Viñoly, SmithGroup, DPR Construction, and Forell/Elsesser Engineers. The 660-foot-long serpentine-shaped building sits on a structural framework 40 to 70 feet off the ground to accommodate the hillside’s steep 60-degree slope.
| May 18, 2011
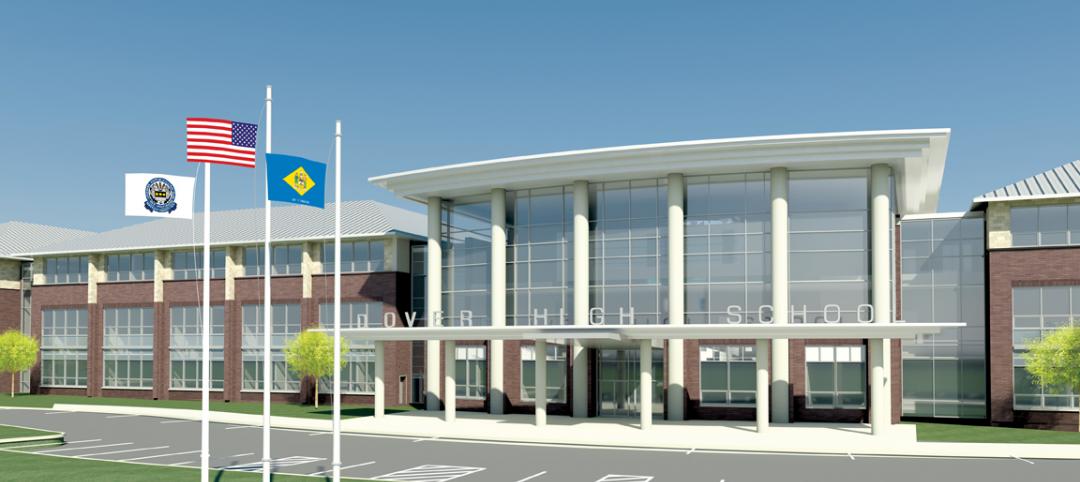
One of Delaware’s largest high schools seeks LEED for Schools designation
The $82 million, 280,000-sf Dover (Del.) High School will have capacity for 1,800 students and feature a 900-seat theater, a 2,500-seat gymnasium, and a 5,000-seat football stadium.
| May 17, 2011
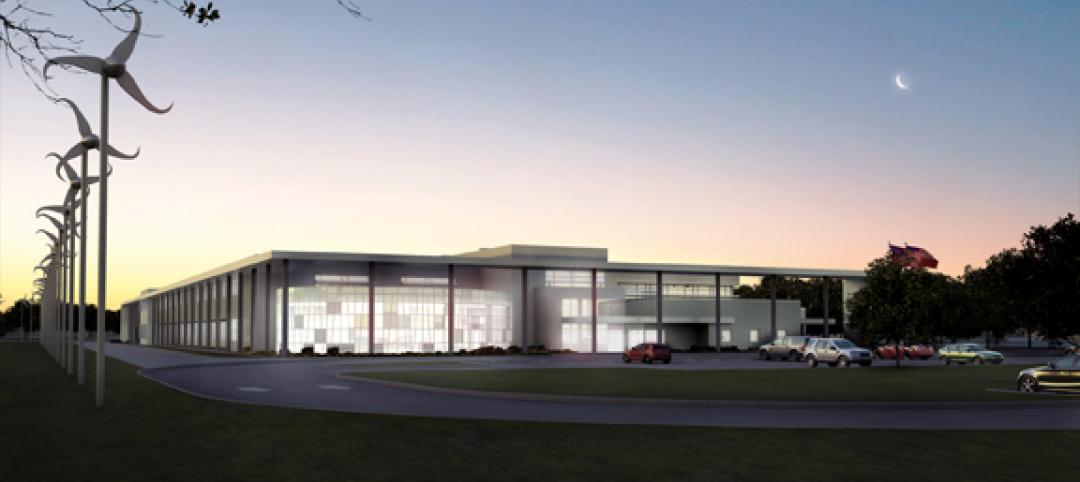
Sustainability tops the syllabus at net-zero energy school in Texas
Texas-based firm Corgan designed the 152,200-sf Lady Bird Johnson Middle School in Irving, Texas, with the goal of creating the largest net-zero educational facility in the nation, and the first in the state. The facility is expected to use 50% less energy than a standard school.
| May 16, 2011
USGBC and AIA unveil report for greening K-12 schools
The U.S. Green Building Council and the American Institute of Architects unveiled "Local Leaders in Sustainability: A Special Report from Sundance," which outlines a five-point national action plan that mayors and local leaders can use as a framework to develop and implement green schools initiatives.
| May 10, 2011
Greenest buildings: K-12 and commercial markets
Can you name the nation’s greenest K-12 school? How about the greenest commercial building? If you drew a blank, don’t worry because our friends at EarthTechling have all the information on those two projects. Check out the Hawai’i Preparatory Academy’s Energy Lab on the Big Island and Cascadia Green Building Council’s new Seattle headquarters.
| Apr 12, 2011
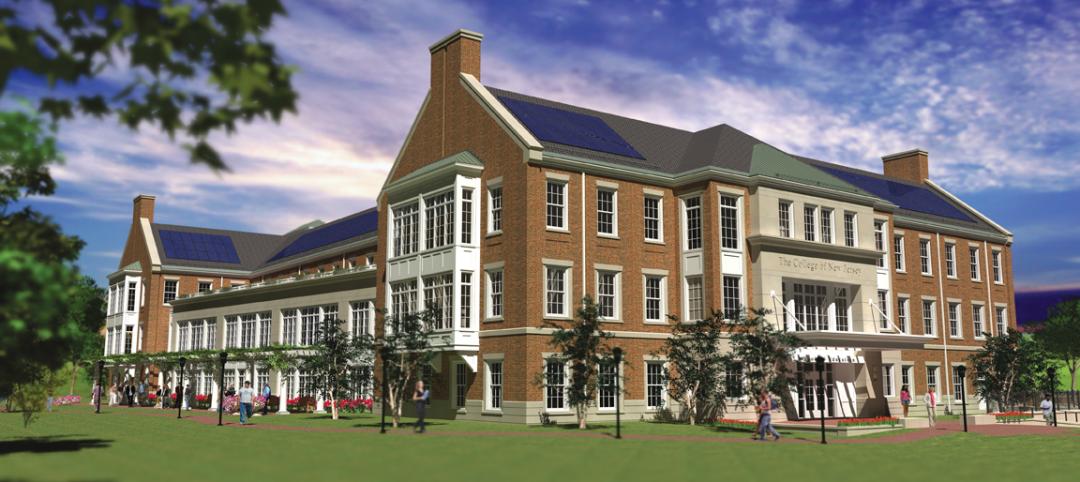
College of New Jersey facility will teach teachers how to teach
The College of New Jersey broke ground on its 79,000-sf School of Education building in Ewing, N.J.
| Mar 15, 2011
What Starbucks taught us about redesigning college campuses
Equating education with a cup of coffee might seem like a stretch, but your choice of college, much like your choice of coffee, says something about the ability of a brand to transform your day. When Perkins + Will was offered the chance to help re-think the learning spaces of Miami Dade College, we started by thinking about how our choice of morning coffee has changed over the years, and how we could apply those lessons to education.
| Mar 15, 2011
Passive Strategies for Building Healthy Schools, An AIA/CES Discovery Course
With the downturn in the economy and the crash in residential property values, school districts across the country that depend primarily on property tax revenue are struggling to make ends meet, while fulfilling the demand for classrooms and other facilities.
| Mar 11, 2011
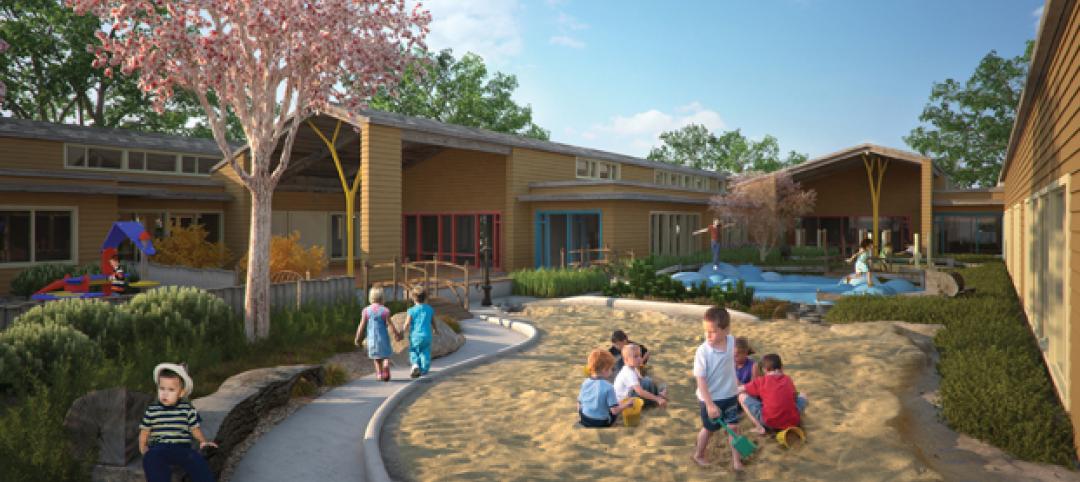
Oregon childhood center designed at child-friendly scale
Design of the Early Childhood Center at Mt. Hood Community College in Gresham, Ore., focused on a achieving a child-friendly scale and providing outdoor learning environments.