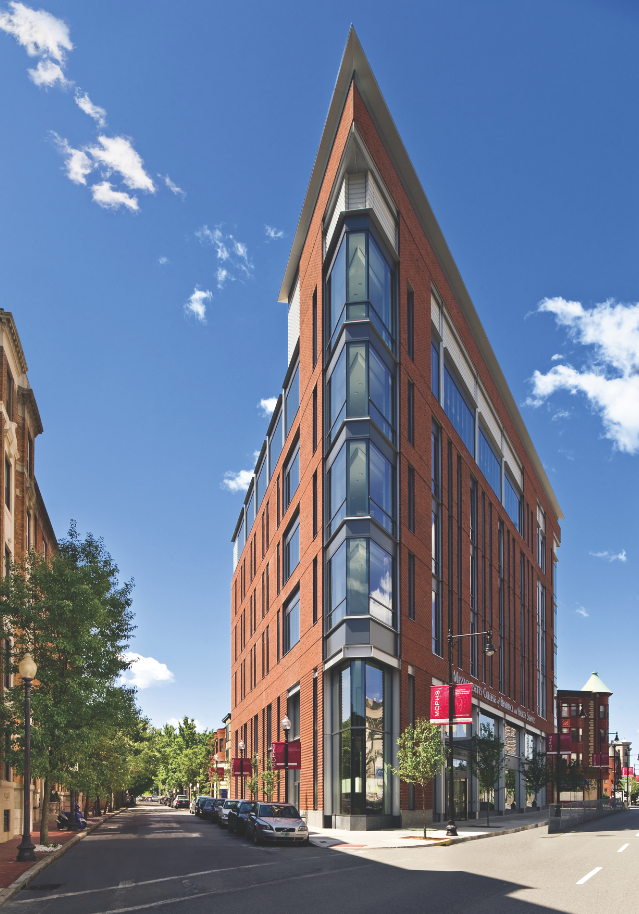
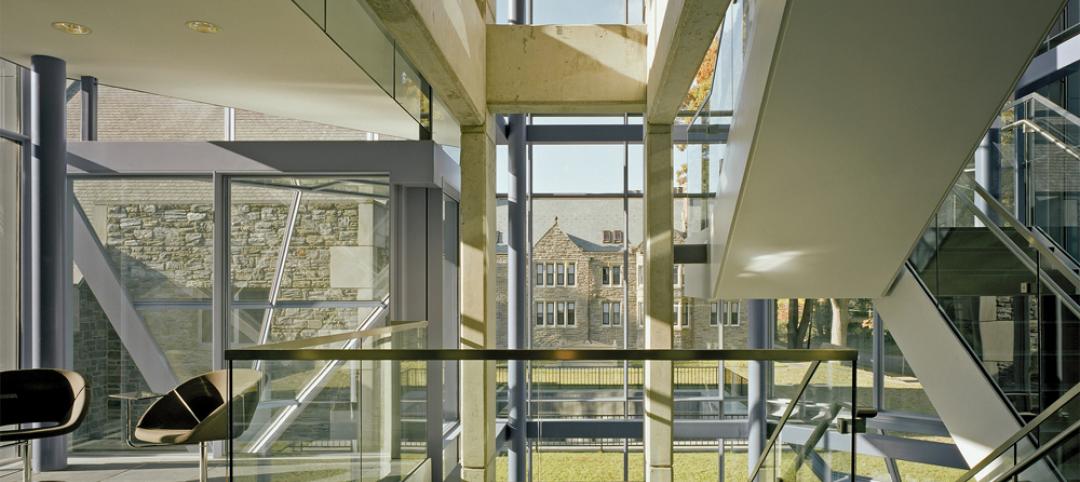
The small, triangular speck of land — a brownfield site once occupied by a gas station — barely measured 7,500 sf and hardly seemed suitable for building much of anything, let alone a 49,700-sf academic and administrative center. However, its location in Boston's prestigious Longwood Medical Area, with an address on Huntington Avenue—known as the city's Avenue of the Arts —made it impossible for the Massachusetts College of Pharmacy and Health Sciences to pass up the unwieldy property. By early 2007, it was clear that the MCPHS's Boston campus was quickly outgrowing its current digs in the heart of the densely populated and land-scarce medical district. Hoping to build a modern new facility within walking distance of its main campus, MCPHS administrators jumped at the chance to develop the compact parcel.
Teaming with Perkins+Will for their fourth project together, MCPHS worked with the architects to create an infill plan that addressed the school's need for additional space. At the same time, the plan had to meet the concerns of the adjacent residential community — the Mission Hill Triangle Historic District, an old neighborhood full of Victorian brownstones and single-family homes and active, vocal residents. Huntington Avenue serves as the boundary between the two, with the Richard E. Griffin Academic Center at ground zero and forced to meet the needs of two very different communities.
The Mission Hill community had long been wary of new development encroaching on their neighborhood, and they'd been burned by urban renewal efforts in the past, including construction of public housing apartment towers — some 20 stories tall — in the middle of their neighborhood. Taking their concerns to heart, MCPHS made the neighbors part of the Building Team and invited them (and other stakeholders) to regular design meetings.
Gerald Autler, senior project manager and planner with the Boston Redevelopment Authority, credits the school's decision to include its neighbors early in the planning process with diffusing what could have been a contentious situation. Autler points to the Building Team's request for additional height as something that "could have been an explosive issue." Instead, with the community a part of the decision-making process, the bid for extra height won their support. "The process went as smoothly as any I have ever been involved in," says Autler.
Even with the extra height, the building still rises only six stories above ground (with two additional below-ground levels) and matches the scale of its residential neighbors. A brick facade adds a traditional Bostonian touch, while abundant glazing and a glass street-level lobby inject contemporary elements expected of an urban, modern educational facility focused on the health sciences. The Perkins+Will designers also made sure to mask the service and equipment acess on the side of the building facing the neighborhood, to minimize any perception of that facade as being the"service area."
A Revit BIM model aided the project's fast-track design and construction schedule and allowed the Building Team, including general contractor Bond Brothers, Inc., to simultaneously produce renderings and construction documents for concurrent city and client approval and to issue early bid packages for earthwork, concrete foundations, steel, and mechanical systems in timely fashion. To remediate the brownfield site (which also abuts a transit line), most of the soil had to be abated on site and trucked away because there was no place to store excavated materials. With minimal staging and laydown space, delivery and storage of materials was another nightmare. The Building Team utilized sidewalks and just-in-time delivery and worked closely with the Boston Transportation Department to coordinate deliveries.
Despite the tight squeeze, a nearly fifty-thousand-square-foot facility was successfully shoehorned into the remnant property, housing the college's School of Nursing, School of Physician Assistant Studies, Office of Institutional Advancement, and Office of College Relations. The six-story center contains a technology center, student commons, classrooms, patient assessment and clinical simulation teaching labs, and faculty offices.
A 230-seat auditorium — which required a 30-foot-deep excavation — sits below-grade, while a multifunction conference space (which is available for use by the community) occupies the top floor and offers unobstructed views of the Boston skyline.
In honoring the Richard E. Griffin Academic Center with a Silver Award, the jury members were impressed with the Building Team's community outreach and its ability to overcome unusually difficult site constraints.
PROJECT SUMMARY
Silver Award
The Richard E. Griffin Academic Center,
Massachusetts College of Pharmacy and Health Sciences
Boston, Mass.
Building Team
Submitting firm: Perkins+Will (architect)
Owner: Massachusetts College of Pharmacy and Health Sciences
Interior designer: Kristine Stoller Interior Design
Structural engineer: Souza True Partners
MEP engineer: RDK Engineers
General contractor: Bond Brothers, Inc.
General Information
Project size: 49,700 sf
Construction cost: Confidential, at client’s request
Construction time: August 2007 to January 2009
Delivery method: CM at risk
Related Stories
| May 13, 2014
19 industry groups team to promote resilient planning and building materials
The industry associations, with more than 700,000 members generating almost $1 trillion in GDP, have issued a joint statement on resilience, pushing design and building solutions for disaster mitigation.
| May 11, 2014
Final call for entries: 2014 Giants 300 survey
BD+C's 2014 Giants 300 survey forms are due Wednesday, May 21. Survey results will be published in our July 2014 issue. The annual Giants 300 Report ranks the top AEC firms in commercial construction, by revenue.
| May 10, 2014
How your firm can gain an edge on university projects
Top administrators from five major universities describe how they are optimizing value on capital expenditures, financing, and design trends—and how their AEC partners can better serve them and other academic clients.
| May 9, 2014
5 trends transforming higher education
Performance-based funding models and the adoption of advanced technologies like augmented reality for teaching are just a few of the predictions offered by CannonDesign's higher education sector leader, Brad Lukanic.
| May 5, 2014
8 modern trends in student dining
Creating a dining experience for the modern millennial requires not only a deep knowledge of good design, but also an understanding of what makes today’s students tick. Culinary designers and consultants provide insights into what trends are transforming the campus table.
| May 1, 2014
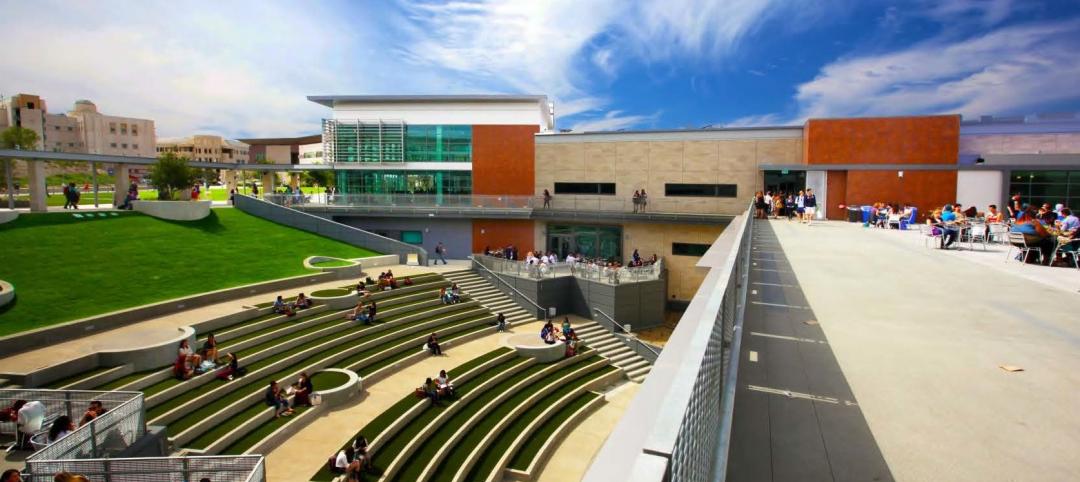
First look: Cal State San Marcos's posh student union complex
The new 89,000-sf University Student Union at CSUSM features a massive, open-air amphitheater, student activity center with a game lounge, rooftop garden and patio, and ballroom space.
| Apr 29, 2014
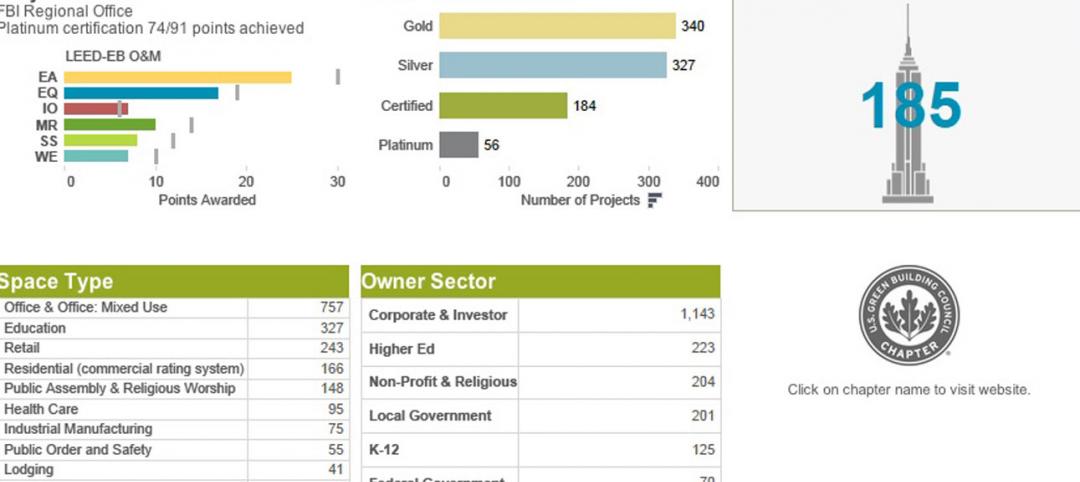
USGBC launches real-time green building data dashboard
The online data visualization resource highlights green building data for each state and Washington, D.C.
Smart Buildings | Apr 28, 2014
Cities Alive: Arup report examines latest trends in urban green spaces
From vertical farming to glowing trees (yes, glowing trees), Arup engineers imagine the future of green infrastructure in cities across the world.
| Apr 23, 2014
Mean and Green: Top 10 green building projects for 2014 [slideshow]
The American Institute of Architects' Committee on the Environment has selected the top ten examples of sustainable architecture and ecological design projects that protect and enhance the environment. Projects range from a project for Portland's homeless to public parks to a LEED Platinum campus center.
| Apr 16, 2014
Upgrading windows: repair, refurbish, or retrofit [AIA course]
Building Teams must focus on a number of key decisions in order to arrive at the optimal solution: repair the windows in place, remove and refurbish them, or opt for full replacement.