Get ready for a surge in prefabrication activity by contractors.
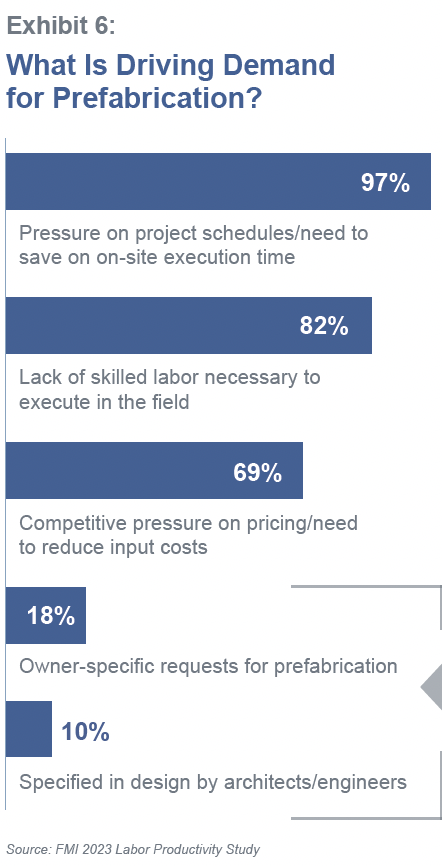
FMI, the consulting and investment banking firm, recently polled contractors about how much time they were spending, in craft labor hours, on prefabrication for construction projects. More than 250 contractors participated in the survey, and the average response to that question was 18%. More revealing, however, was the participants’ anticipation that craft hours dedicated to prefab would essentially double, to 34%, within the next five years.
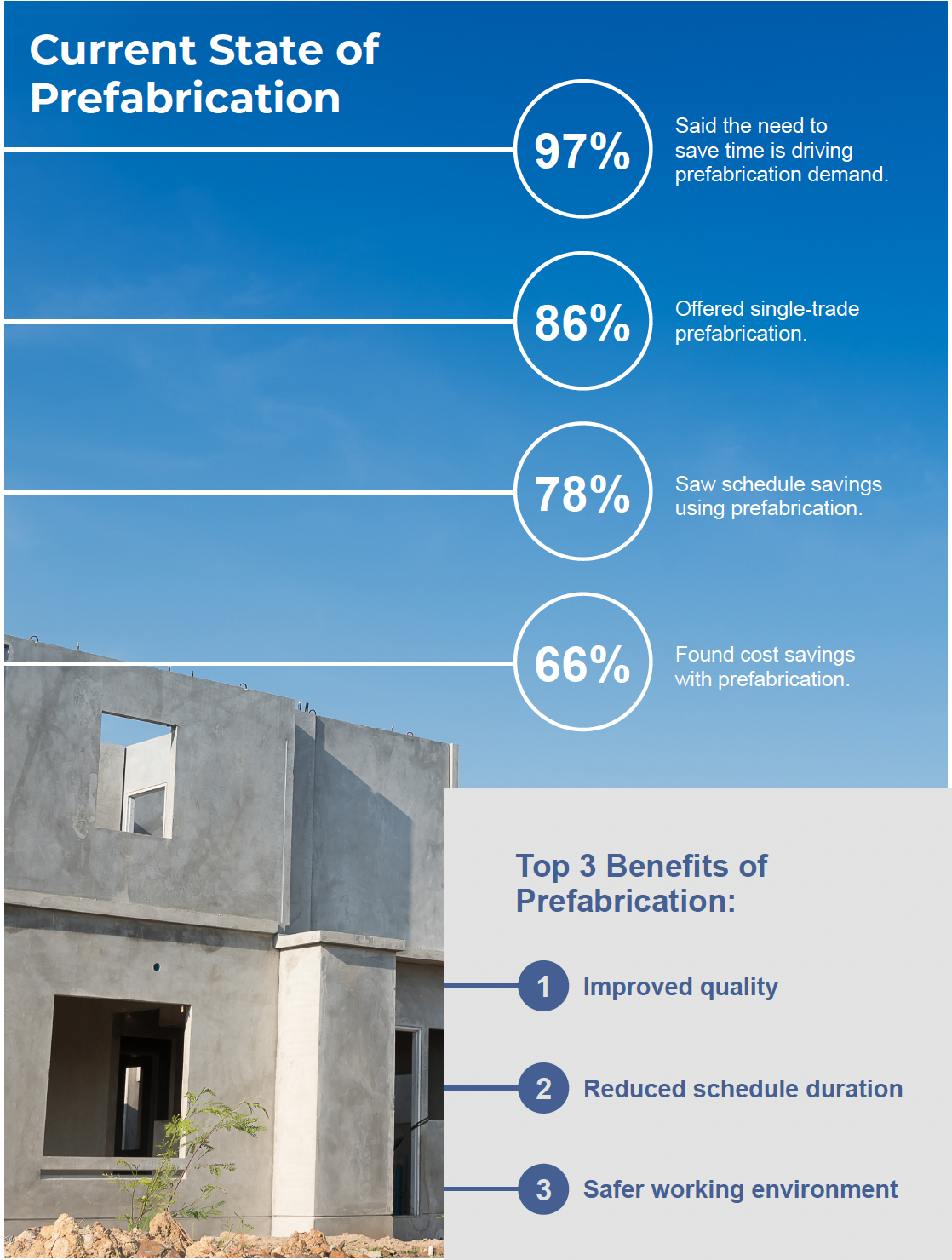
The study—a sequel to FMI’s 2023 Labor Productivity Study—reiterates how the industry’s receptivity to prefab solutions corresponds with its ongoing labor shortages and compressed project schedules. (Contractors experienced approximately $30 billion to $40 billion in lost profits due to labor inefficiencies in 2022.) In its latest study, contractors told FMI that “improved quality” was prefab’s greatest perceived benefit. “Reducing the risk and variability” is how one contractor put it. Other benefits cited include reductions in construction schedules and improved worker safety.
(Nearly three fifths of the respondents to FMI’s study are MEP contractors, with another 15% being framing and drywall contractors.)
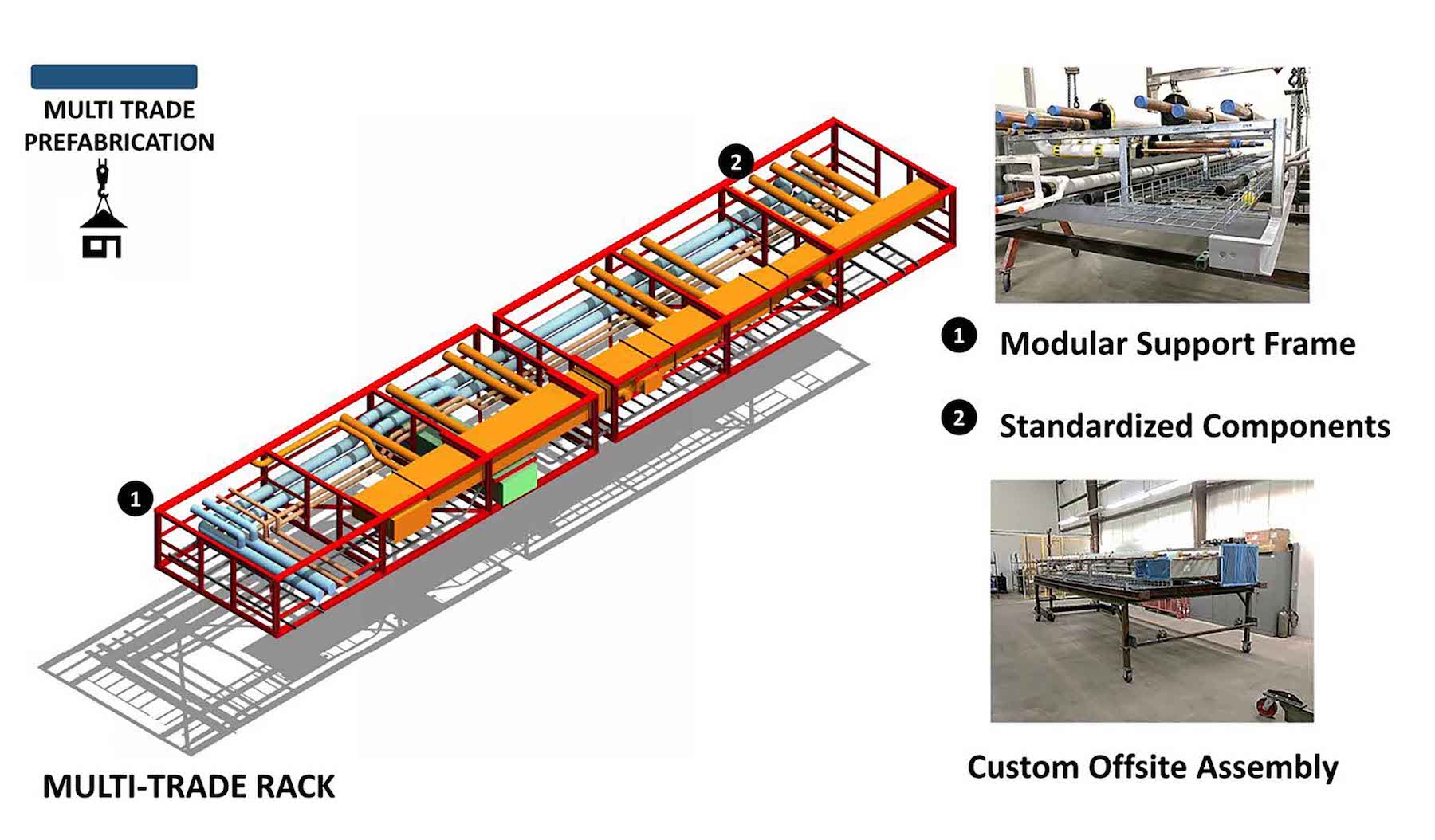
Contractors that consider prefabrication must determine how to do it at scale, profitably, and in a way that increases company earnings. Successful prefab practices, says FMI, require long-term strategic thinking and planning across an organization, along with the development of a comprehensive operational blueprint.
Which prefab model is right for pros?
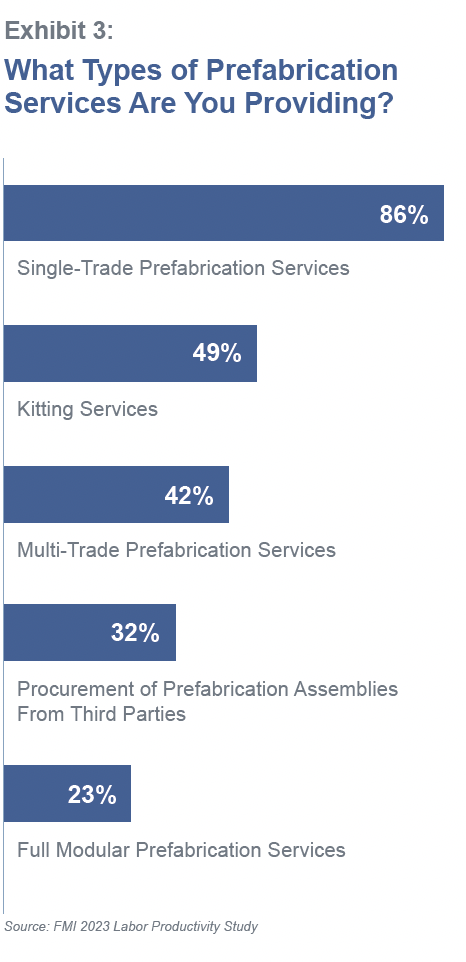
It’s not like prefabrication is an alien concept for contractors. FMI’s study found that 86% of respondents currently offer single-trade prefab services. Three quarters of the concrete contractors surveyed said they are prefabricating on their jobsites; 57% of self-performing general contractors polled are prefabbing on-site, too.
What’s often lacking, however, is a clear vision of what they want their prefab capabilities to become. To make prefab work, says FMI, contractors need to shift their operating models, processes and systems. Contractors also need to decide which prefab models and combinations would work best for their companies; these include kitting services, multi-trade services, procurement, and modular services.
In making these determinations, contractors should be asking themselves:
•Why do we want to do more prefabrication?
•What is the total addressable portion of our work mix (today) that could be prefabricated?
•What investments would need to be made to scale our prefabrication capabilities to capture that opportunity?
•When fully optimized, what does the earnings stream from prefabrication look like?
•What does the return on investment look like for the enterprise?
•Do we have alternative investment options for other initiatives in the business? How do those options stack up against our prefabrication ambitions?
•Will prefab make the company better, more profitable, and resilient?
Prefabrication a different kind of business
Prefabrication is a manufacturing endeavor that’s different from building construction. Contractors diving into prefab in a bigger way need to think about whether prefab will be a unique business or separate entity, and how autonomously construction and prefabrication operate? Will prefab services be proprietary or available to other contractors? Will prefab be a profit or cost center? How will manufacturing cost overruns, if there are any, be accounted for?
FMI says that contractors need to establish clear project management lines that encompass how prefabricated products are tracked, stored, and billed for. Tracking labor productivity across prefabrication and field installation is key.
Owners and designers need to buy in more
One of the contractors whom FMI polled mentioned a recent casino and hotel project that required 25% less labor in the field, and cut nearly two months off of its installation time, by using prefabrication methods.
Scheduling is driving prefab demand, says FMI. But expanding that demand depends on acceptance by owners and AEC firms, and right now, that acceptance is middling: only 18% of the contractors polled by FMI said that owner-specific requests drove prefab, and only 10% said that prefab was specified by architects or engineers.
“For the industry to realize substantial gains in prefabrication and productivity, owners and designers need to be a bigger part of the demand equation,” says FMI.
FMI’s study found that the industry still struggles with broad adoption. The biggest challenges to adopting prefab are a project’s design and coordination, stakeholder awareness and education, the mindset and culture of a project’s active players, and the investment in facilities and equipment.
But given current and projected labor force limitations, “it’s clear that prefabrication will need to become part of the solution.” For that to happen, building teams need to demonstrate a bolder vision, strategic planning, commitment to investing, consistent communication, and a proactive engagement by external stakeholders.
Related Stories
| Aug 11, 2010
PCA partners with MIT on concrete research center
MIT today announced the creation of the Concrete Sustainability Hub, a research center established at MIT in collaboration with the Portland Cement Association (PCA) and Ready Mixed Concrete (RMC) Research & Education Foundation.
| Aug 11, 2010
Study explains the financial value of green commercial buildings
Green building may be booming, especially in the Northwest, but the claims made for high-performance buildings have been slow to gain traction in the financial community. Appraisers, lenders, investors and brokers have found it difficult to confirm the value of high-performance green features and related savings. A new study of office buildings identifies how high-performance green features and systems can increase the value of commercial buildings.
| Aug 11, 2010
Architecture Billings Index drops to lowest level since June
Another stall in the recovery for the construction industry as the Architecture Billings Index (ABI) dropped to its lowest level since June. The American Institute of Architects (AIA) reported the August ABI rating was 41.7, down slightly from 43.1 in July. This score indicates a decline in demand for design services (any score above 50 indicates an increase in billings).
| Aug 11, 2010
Construction employment declined in 333 of 352 metro areas in June
Construction employment declined in all but 19 communities nationwide this June as compared to June-2008, according to a new analysis of metropolitan-area employment data released today by the Associated General Contractors of America. The analysis shows that few places in America have been spared the widespread downturn in construction employment over the past year.
| Aug 11, 2010
Jacobs, Hensel Phelps among the nation's 50 largest design-build contractors
A ranking of the Top 50 Design-Build Contractors based on Building Design+Construction's 2009 Giants 300 survey. For more Giants 300 rankings, visit http://www.BDCnetwork.com/Giants
| Aug 11, 2010
Balfour Beatty agrees to acquire Parsons Brinckerhoff for $626 million
Balfour Beatty, the international engineering, construction, investment and services group, has agreed to acquire Parsons Brinckerhoff for $626 million. Balfour Beatty executives believe the merger will be a major step forward in accomplishing a number of Balfour Beatty’s objectives, including establishing a global professional services business of scale, creating a leading position in U.S. civil infrastructure, particularly in the transportation sector, and enhancing its global reach.
| Aug 11, 2010
Construction unemployment rises to 17.1% as another 64,000 construction workers are laid off in September
The national unemployment rate for the construction industry rose to 17.1 percent as another 64,000 construction workers lost their jobs in September, according to an analysis of new employment data released today. With 80 percent of layoffs occurring in nonresidential construction, Ken Simonson, chief economist for the Associated General Contractors of America, said the decline in nonresidential construction has eclipsed housing’s problems.