An expanding engineering and construction industry faces a digital future that is not only reshaping cities but also how the industry’s businesses operate.
This is one of the key observations that Deloitte Consulting presents in its recent paper “2019 Engineering and Construction Industry Outlook.” The paper’s author—Michelle Meisels, Principal and Engineering and Construction Leader—emphasizes the centrality of data analysis in the ability of the industry to deliver urban projects for cities whose buildings and infrastructures are becoming “smarter” and more connected.
Deloitte anticipates that the industry’s growth in the U.S.—estimated at around 5% in 2018—will continue next year. Merger-and-acquisition activity, which this year has accounted for at least 344 deals valued at more than $20 billion, is allowing EC firms to compete for megaprojects “infused with advanced technologies.”
Meisels sees cities as growth engines for the U.S. economy and its society. However, America’s crumbling infrastructure right now isn’t up to the task of keeping pace with urbanization. She’s optimistic, though, about the willingness of cities around the world to invest in “connected infrastructure” that enables better management of urban assets such as public transit, wastewater systems, and roads. Meisels cites one estimate, from IDC, which projects that smart cities’ spending will reach $158 billion globally by 2022, with Singapore, Tokyo and New York being among the top spenders.
These investments should help to create digital touchpoints of connectivity between people and their vehicles, homes, and workplaces. What would advance this movement, says Meisels, is “a clearly articulated strategy for leveraging advanced technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT), analytics, and artificial intelligence.” She points specifically to the recently announced alliance between AECOM and Arrow Electronics as an example of how scale and digital are intersecting.
Digital, in fact, is transforming how engineering and construction companies run their companies. Such things as robotic process automation and BIM are evolving and improving in ways that are making project development and management far more efficient and less costly. Meisels also speaks of “connected construction” tools, such as drones, wearables, and augmented reality, that are “revolutionizing” job sites, improving worker productivity and safety, and capturing valuable data.
Meisels believes that data and analytics will become the industry’s future core. But data are coming from outside traditional ERP systems, so companies need to devise a strategy to analyze this torrent of information “to deliver smart buildings and smart cities projects, identify and address diminishing margins, and manage increasing project size and complexity.”
Companies can use a data-driven approach to unlock smart decision making, identify the optimal location for their project, and source the best materials to use, all through an interface that enables decision makers to ask questions and work through scenarios.
This analytical approach might also provide some answers to a problem that continues to vex EC firms across the country: finding and retaining talent.
The U.S. construction industry has been consistently adding workforce, and currently employs around 7.2 million professionals, the highest levels since the Great Recession of 2008. But that’s still an 18-year low. “Labor shortages are reaching crisis proportions and are expected to continue through 2019,“ predicts Meisels.
Today, winning the talent war includes projecting a positive brand for your company out to the market—one that reflects the advanced technologies that are part of the connected construction site. To appeal to new generations entering the workforce, that brand should also showcase the sustainability initiatives that many firms have adopted.
On a fundamental level, Meisels tells EC firm that their talent search should be buttressed by their support of apprenticeships and technical schools. “And considering the rise of digital, it is also important to understand how skills are changing and then design a talent management strategy that reflects this,” she recommends.
Related Stories
| Apr 23, 2014
Experimental bot transfers CAD plans onto construction sites
The Archibot is intended to take technical data and translate it into full-scale physical markings on construction sites.
Sponsored | | Apr 23, 2014
Ridgewood High satisfies privacy, daylight and code requirements with fire rated glass
For a recent renovation of a stairwell and exit corridors at Ridgewood High School in Norridge, Ill., the design team specified SuperLite II-XL 60 in GPX Framing for its optical clarity, storefront-like appearance, and high STC ratings.
| Apr 9, 2014
Steel decks: 11 tips for their proper use | BD+C
Building Teams have been using steel decks with proven success for 75 years. Building Design+Construction consulted with technical experts from the Steel Deck Institute and the deck manufacturing industry for their advice on how best to use steel decking.
| Apr 2, 2014
8 tips for avoiding thermal bridges in window applications
Aligning thermal breaks and applying air barriers are among the top design and installation tricks recommended by building enclosure experts.
| Apr 2, 2014
Check out the stunning research facility just named 2014 Lab of the Year [slideshow]
NREL's Energy Systems Integration Facility takes top honors in R&D Magazine's 48th annual lab design awards.
| Mar 26, 2014
Callison launches sustainable design tool with 84 proven strategies
Hybrid ventilation, nighttime cooling, and fuel cell technology are among the dozens of sustainable design techniques profiled by Callison on its new website, Matrix.Callison.com.
| Mar 26, 2014
First look: Lockheed Martin opens Advanced Materials and Thermal Sciences Center in Palo Alto
The facility will host advanced R&D in emerging technology areas like 3D printing, energetics, thermal sciences, and nanotechnology.
| Mar 21, 2014
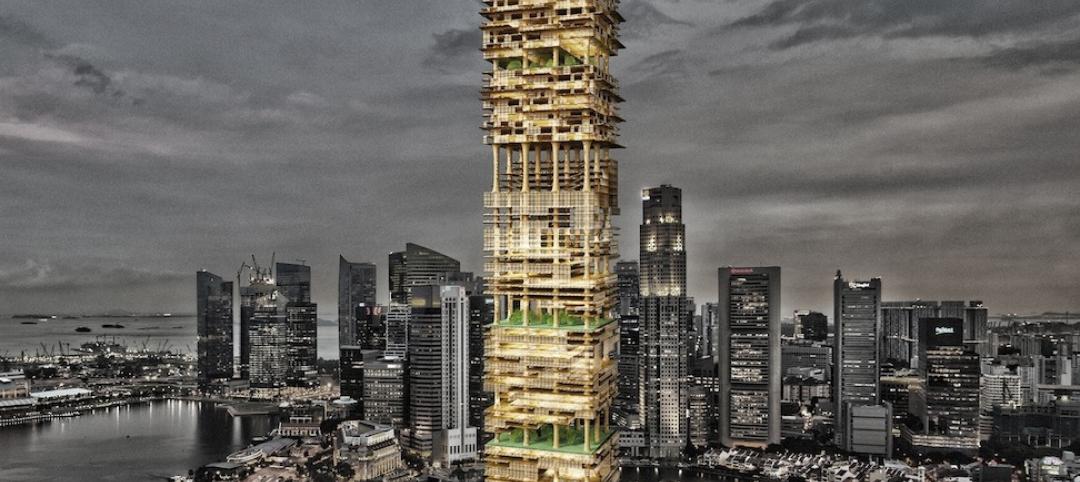
Forget wood skyscrapers - Check out these stunning bamboo high-rise concepts [slideshow]
The Singapore Bamboo Skyscraper competition invited design teams to explore the possibilities of using bamboo as the dominant material in a high-rise project for the Singapore skyline.
| Mar 20, 2014
Common EIFS failures, and how to prevent them
Poor workmanship, impact damage, building movement, and incompatible or unsound substrate are among the major culprits of EIFS problems.
| Mar 13, 2014
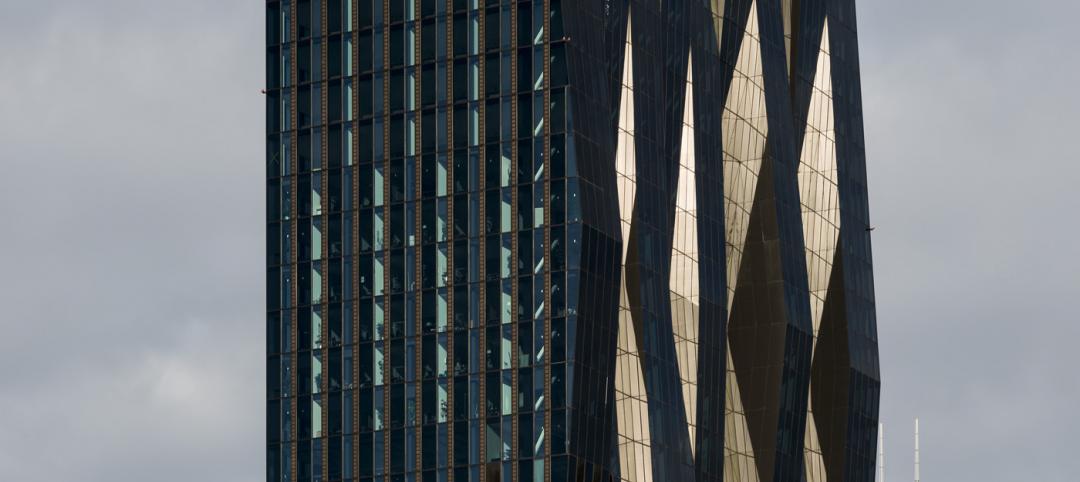
Austria's tallest tower shimmers with striking 'folded façade' [slideshow]
The 58-story DC Tower 1 is the first of two high-rises designed by Dominique Perrault Architecture for Vienna's skyline.