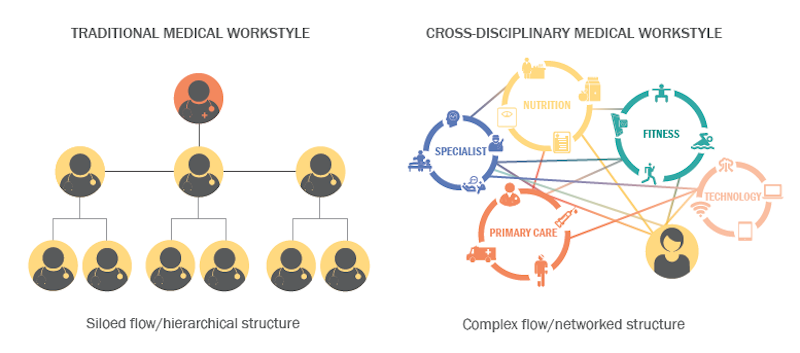
“Collaboration” has become an abiding design goal for many nonresidential building types, such as offices and educational institutions. But the medical field, with its hierarchical divisions and silo mentality among professionals, continues to resist a more collaborative workplace culture.
Perkins Eastman set out to find out why, and used one of its own projects—the 95,000-sf NYU Winthrop Hospital Research and Academic Center in Mineola, N.Y.—as a test case a year after it opened in 2015.
The firm's post-occupancy evaluation—whose findings it published in a recently released white paper “The Effectiveness of Collaborative Spaces in Healthcare and Research Environments”—focuses on the activities within a third-floor multi-use space in the facility that the firm designed specifically with employee interaction in mind.
The white paper touches on the evolution of collaborative design, and singles out two examples—Bell Labs’ headquarters in Murray Hill, N.J., in the 1960s, and Google’s national headquarters in Mountain View, Calif.—where cross-disciplinary collaboration took root and where “activity based” working is now on full display.
The paper notes that offices and education facilities are creating these kinds of environments by planning for collaboration early in the design process, “to include a variety of different kinds of areas to support one-on-one, individual, small group and large groupings.”
However, even the most thoughtfully designed space won’t lead to meaningful change in a workspace if it isn’t supported by policies and attitudes that foster collaboration. And that support is what Perkins Eastman found was missing at NYU Winthrop Research and Academic Center.
Its third-floor space was seen as a microcosm of Perkins Eastman’s design intent. Its programmatic elements include a pantry with small cook and prep area and two vending machines, a café dining space with tables and chairs, a break area with soft seating, a low four-person conference table and sit-up bar; a work room with a TV, tablet chairs and writable magnetic wall; a research area with a large writable wall, movable ottomans, and high-top tables and writing table tops; and a conference room with a large executive meeting table, digital projection capabilities, wet bar and seating banquette.
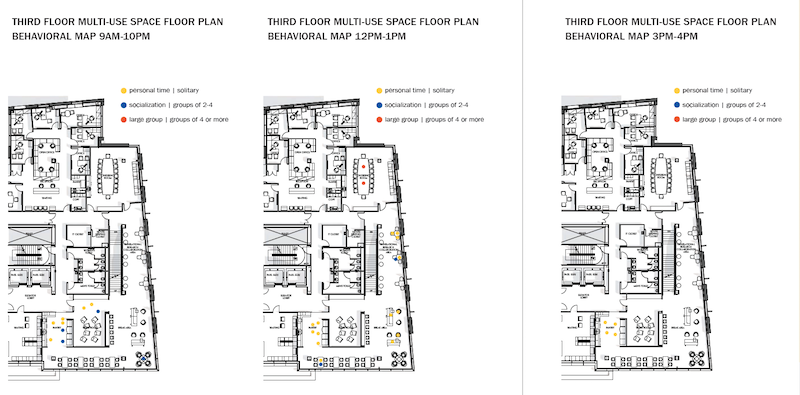
To assess employee engagement in a multi-use space within NYU Winthrop's Research and Academic Center, Perkins Eastman observed and place-mapped activities over a nine-hour period in several time intervals. It found scant indepartmental connectivity, and virtually no use of this space for work. Image: Perkins Eastman
Perkins Eastman observed and place-mapped employee interactions in that space over a nine-hour period in four intervals during the day. The firm tracked how long people spent in any one place, and what they were doing. It also noted whether people were alone or in groups.
“Very little interaction among users from different departments was observed,” Perkins Eastman found. Most people used to space to eat their lunches or talk on their phones. And they usually hung out with people from their own departments. “No spontaneous meetings of small or large groups were observed, and the amenities provided to support impromptu collaboration…went unused.”
Subsequent interviews with 17 user groups from various departments found that while employees generally like the space, they didn’t know how to use it other than to eat lunch or buy food from the vending machines.
None of the people interviewed used the space for work, primarily because their jobs require computers and other tools located at their designated workstations. More surprising, though, was the finding that many of the interviewees weren’t sure if they were even allowed to use the third-floor space for meetings or presentations. In fact, they were “simply uninformed about the potential uses of the third-floor space,” the white paper reports.
Perkins Eastman found that most doctors, researchers, nurses, and administrators within the user groups interviewed would like to collaborate. But a suggestive design wasn’t enough to instigate that interaction. “The faculty and staff needed to be shown how to use the third-floor in order to promote its use as a collaborative space.”
The white paper concedes that research often requires quiet, focused study supported by specialized workstations or lab equipment. And the need for privacy can be a barrier to collaborating in a healthcare environment.
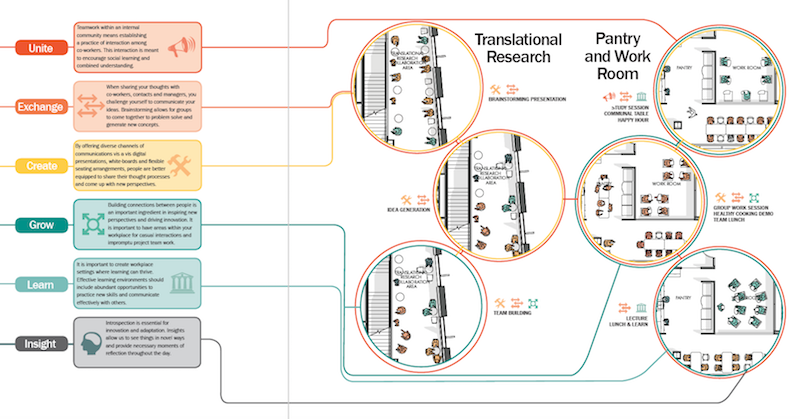
The white paper provides ways that medical centers could encourage collaborative use of their common spaces. The suggestions revolve around providing workers with more imformation about the potential uses of those areas. Image: Perkins Eastman
But there are “simple measures” that the Center could do to foment collaboration and communication, at least in the multi-use space with an open floor plan. These include:
•Create a schedule of programs and presentations for that space
•Assign an IT specialist to educate and assist users with technologies provided in the workroom and conference room
•Post information and signage that suggests how the space can be used
•Orient new employees about how to use the space, and
•Provide greater spatial variety, and the ability to close certain spaces for private meetings. (A number of interviewees said they didn’t conduct meetings on the third floor because none of the rooms could be closed off.)
In the final analysis, Perkins Eastman remains convinced that design, reinforced by programming, can support collaboration and employee engagement within a medical building. But the medical profession also needs to shift toward a more positive attitude about collaboration. “If users are uninformed about the potential uses of a space, it is difficult for a culture of collaboration to thrive.”
Related Stories
| May 5, 2011
Hospitals launch quiet campaigns to drown out noise of modern medicine
Worldwide, sound levels inside hospitals average 72 decibels during the day and 60 decibels at night, which far exceeds the standard of 40 decibels or less, set by the World Health Organization. The culprit: modern medicine. In response, hospitals throughout Illinois and the U.S. are launching "quiet campaigns" that include eliminating intercom paging, replacing metal trash cans, installing sound-absorbing flooring and paneling, and dimming lights at night to remind staff to keep their voices down.
| Apr 14, 2011
USGBC debuts LEED for Healthcare
The U.S. Green Building Council (USGBC) introduces its latest green building rating system, LEED for Healthcare. The rating system guides the design and construction of both new buildings and major renovations of existing buildings, and can be applied to inpatient, outpatient and licensed long-term care facilities, medical offices, assisted living facilities and medical education and research centers.
| Apr 13, 2011
Virginia hospital’s prescription for green construction: LEED Gold
Rockingham Memorial Hospital in Harrisonburg, Va., is the commonwealth’s first inpatient healthcare facility to earn LEED Gold. The 630,000-sf facility was designed by Earl Swensson Associates, with commissioning consultant SSRCx, both of Nashville.
| Apr 12, 2011
Mental hospital in Boston redeveloped as healthcare complex
An abandoned state mental health facility in Boston’s prestigious Longwood Medical Area is being transformed into the Mass Mental Health Center, a four-building mixed-use complex that includes a mental health day hospital, a clinical and office building, a medical research facility for Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and a residential facility.
| Mar 17, 2011
Perkins Eastman launches The Green House prototype design package
Design and architecture firm Perkins Eastman is pleased to join The Green House project and NCB Capital Impact in announcing the launch of The Green House Prototype Design Package. The Prototype will help providers develop small home senior living communities with greater efficiency and cost savings—all to the standards of care developed by The Green House project.
| Mar 14, 2011
Renowned sustainable architect Charles D. Knight to lead Cannon Design’s Phoenix office
Cannon Design is pleased to announce that Charles D. Knight, AIA, CID, LEED AP, has joined the firm as principal. Knight will serve as the leader of the Phoenix office with a focus on advancing the firm’s healthcare practice. Knight brings over 25 years of experience and is an internationally recognized architect who has won numerous awards for his unique contributions to the sustainable and humanistic design of healthcare facilities.
| Mar 11, 2011
Renovation energizes retirement community in Massachusetts
The 12-year-old Edgewood Retirement Community in Andover, Mass., underwent a major 40,000-sf expansion and renovation that added 60 patient care beds in the long-term care unit, a new 17,000-sf, 40-bed cognitive impairment unit, and an 80-seat informal dining bistro.
| Mar 11, 2011
Research facility added to Texas Medical Center
Situated on the Texas Medical Center’s North Campus in Houston, the new Methodist Hospital Research Institute is a 12-story, 440,000-sf facility dedicated to translational research. Designed by New York City-based Kohn Pedersen Fox, with healthcare, science, and technology firm WHR Architects, Houston, the building has open, flexible labs, offices, and amenities for use by 90 principal investigators and 800 post-doc trainees and staff.
| Mar 11, 2011
Mixed-income retirement community in Maryland based on holistic care
The Green House Residences at Stadium Place in Waverly, Md., is a five-story, 40,600-sf, mixed-income retirement community based on a holistic continuum of care concept developed by Dr. Bill Thomas. Each of the four residential floors houses a self-contained home for 12 residents that includes 12 bedrooms/baths organized around a common living/social area called the “hearth,” which includes a kitchen, living room with fireplace, and dining area.