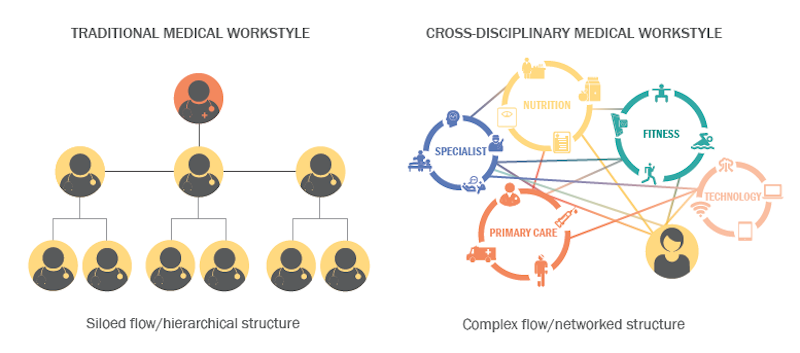
“Collaboration” has become an abiding design goal for many nonresidential building types, such as offices and educational institutions. But the medical field, with its hierarchical divisions and silo mentality among professionals, continues to resist a more collaborative workplace culture.
Perkins Eastman set out to find out why, and used one of its own projects—the 95,000-sf NYU Winthrop Hospital Research and Academic Center in Mineola, N.Y.—as a test case a year after it opened in 2015.
The firm's post-occupancy evaluation—whose findings it published in a recently released white paper “The Effectiveness of Collaborative Spaces in Healthcare and Research Environments”—focuses on the activities within a third-floor multi-use space in the facility that the firm designed specifically with employee interaction in mind.
The white paper touches on the evolution of collaborative design, and singles out two examples—Bell Labs’ headquarters in Murray Hill, N.J., in the 1960s, and Google’s national headquarters in Mountain View, Calif.—where cross-disciplinary collaboration took root and where “activity based” working is now on full display.
The paper notes that offices and education facilities are creating these kinds of environments by planning for collaboration early in the design process, “to include a variety of different kinds of areas to support one-on-one, individual, small group and large groupings.”
However, even the most thoughtfully designed space won’t lead to meaningful change in a workspace if it isn’t supported by policies and attitudes that foster collaboration. And that support is what Perkins Eastman found was missing at NYU Winthrop Research and Academic Center.
Its third-floor space was seen as a microcosm of Perkins Eastman’s design intent. Its programmatic elements include a pantry with small cook and prep area and two vending machines, a café dining space with tables and chairs, a break area with soft seating, a low four-person conference table and sit-up bar; a work room with a TV, tablet chairs and writable magnetic wall; a research area with a large writable wall, movable ottomans, and high-top tables and writing table tops; and a conference room with a large executive meeting table, digital projection capabilities, wet bar and seating banquette.
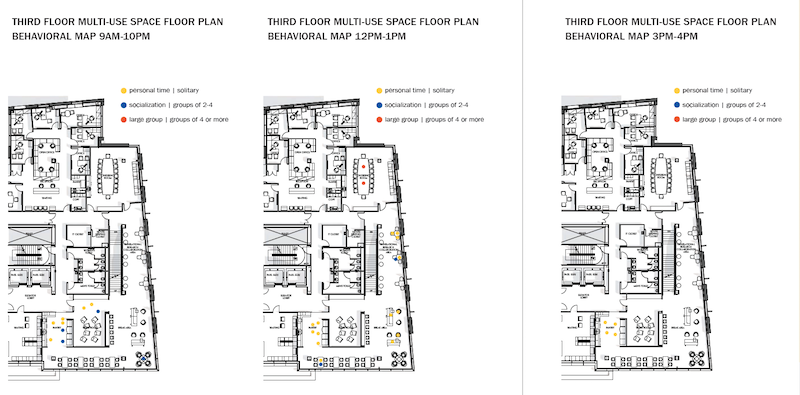
To assess employee engagement in a multi-use space within NYU Winthrop's Research and Academic Center, Perkins Eastman observed and place-mapped activities over a nine-hour period in several time intervals. It found scant indepartmental connectivity, and virtually no use of this space for work. Image: Perkins Eastman
Perkins Eastman observed and place-mapped employee interactions in that space over a nine-hour period in four intervals during the day. The firm tracked how long people spent in any one place, and what they were doing. It also noted whether people were alone or in groups.
“Very little interaction among users from different departments was observed,” Perkins Eastman found. Most people used to space to eat their lunches or talk on their phones. And they usually hung out with people from their own departments. “No spontaneous meetings of small or large groups were observed, and the amenities provided to support impromptu collaboration…went unused.”
Subsequent interviews with 17 user groups from various departments found that while employees generally like the space, they didn’t know how to use it other than to eat lunch or buy food from the vending machines.
None of the people interviewed used the space for work, primarily because their jobs require computers and other tools located at their designated workstations. More surprising, though, was the finding that many of the interviewees weren’t sure if they were even allowed to use the third-floor space for meetings or presentations. In fact, they were “simply uninformed about the potential uses of the third-floor space,” the white paper reports.
Perkins Eastman found that most doctors, researchers, nurses, and administrators within the user groups interviewed would like to collaborate. But a suggestive design wasn’t enough to instigate that interaction. “The faculty and staff needed to be shown how to use the third-floor in order to promote its use as a collaborative space.”
The white paper concedes that research often requires quiet, focused study supported by specialized workstations or lab equipment. And the need for privacy can be a barrier to collaborating in a healthcare environment.
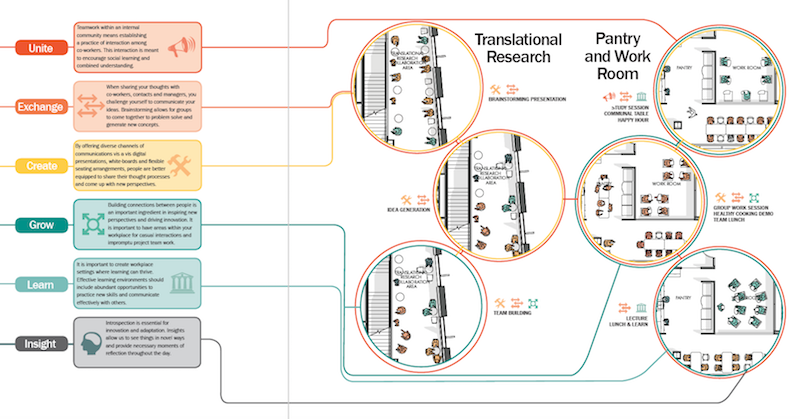
The white paper provides ways that medical centers could encourage collaborative use of their common spaces. The suggestions revolve around providing workers with more imformation about the potential uses of those areas. Image: Perkins Eastman
But there are “simple measures” that the Center could do to foment collaboration and communication, at least in the multi-use space with an open floor plan. These include:
•Create a schedule of programs and presentations for that space
•Assign an IT specialist to educate and assist users with technologies provided in the workroom and conference room
•Post information and signage that suggests how the space can be used
•Orient new employees about how to use the space, and
•Provide greater spatial variety, and the ability to close certain spaces for private meetings. (A number of interviewees said they didn’t conduct meetings on the third floor because none of the rooms could be closed off.)
In the final analysis, Perkins Eastman remains convinced that design, reinforced by programming, can support collaboration and employee engagement within a medical building. But the medical profession also needs to shift toward a more positive attitude about collaboration. “If users are uninformed about the potential uses of a space, it is difficult for a culture of collaboration to thrive.”
Related Stories
| Aug 11, 2010
MOB added to new hospital project
A late-2009 ground breaking is planned for a $20 million medical office building on the grounds of the $211 million, 106-bed Loma Linda University Medical Center in Murrieta, Calif., which itself is under construction. Minneapolis-based Frauenshuh HealthCare Real Estate Solutions is developing the five-story, 160,000-sf MOB, which will accommodate 60 physician offices.
| Aug 11, 2010
Rehabilitation center helps patients transition
Construction is under way on the Polytrauma Transitional Rehabilitation Center on the VA Medical Center campus in Richmond, Va. The $8 million, 22,000-sf facility will provide physical therapy, housing, and education to veterans as part of their transition back into their communities. The center was designed by HDR, Alexandria, Va.
| Aug 11, 2010
Medical office building planned in Fort Worth, Texas
Dallas-based TGS Architects has unveiled its design for the five-story, 130,000-sf Plaza Medical Office Building, planned for Fort Worth, Texas. The Class A development will include space for orthopedic care, surgery, breast center, diagnostic imaging, cardiovascular, and rehabilitation therapy services.
| Aug 11, 2010
Philadelphia cancer center seeks LEED certification
The New York office of Thornton Tomasetti provided structural engineering services for the Ruth and Raymond Perelman Center for Advanced Medicine in Philadelphia, a $232 million medical research center and advanced treatment center for cancer and cardiovascular disease. Designed by a joint venture of Perkins Eastman Architects and Rafael Vinõly Architects, the 340,000-sf facility will hous...
| Aug 11, 2010
High-level NICU opens in Washington, D.C.
Design to the highest distinction available by the American Academy of Pediatrics, the new Level IIIC neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) at Children's National Medical Center in Washington D.C., is equipped to care for the sickest premature babies, including those that require open-heart surgery. The 54-bed facility, designed by Karlsberger with KLMK Group as space planner, is four times large...
| Aug 11, 2010
San Bernardino health center doubles in size
Temecula, Calif.-based EDGE was awarded the contract for California State University San Bernardino's health center renovation and expansion. The two-phase, $4 million project was designed by RSK Associates, San Francisco, and includes an 11,000-sf, tilt-up concrete expansion—which doubles the size of the facility—and site and infrastructure work.
| Aug 11, 2010
New hospital expands Idaho healthcare options
Ascension Group Architects, Arlington, Texas, is designing a $150 million replacement hospital for Portneuf Medical Center in Pocatello, Idaho. An existing facility will be renovated as part of the project. The new six-story, 320-000-sf complex will house 187 beds, along with an intensive care unit, a cardiovascular care unit, pediatrics, psychiatry, surgical suites, rehabilitation clinic, and ...
| Aug 11, 2010
Manhattan's Gouverneur Healthcare Services tops out renovation, expansion
One year after breaking ground, the Building Team for the renovation and expansion of the Gouverneur Healthcare Services facility on Manhattan's Lower East Side topped out the $180 million project. Designed by New York-based RMJM, the development involves a 316,000-sf renovation and 108,000-sf addition that will house a 295-bed nursing facility and five-story ambulatory care center.
| Aug 11, 2010
Decline expected as healthcare slows, but hospital work will remain steady
The once steady 10% growth rate in healthcare construction spending has slowed, but hasn't entirely stopped. Spending is currently 1.7% higher than the same time last year when construction materials costs were 8% higher. The 2.5% monthly jobsite spending decline since last fall is consistent with the decline in materials costs.
| Aug 11, 2010
Construction under way on LEED Platinum DOE energy lab
Centennial, Colo.-based Haselden Construction has topped out the $64 million Research Support Facilities, located on the U.S. Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) campus in Golden, Colo. Designed by RNL and Stantec to achieve LEED Platinum certification and net zero energy performance, the 218,000-sf facility will feature natural ventilation through operable ...