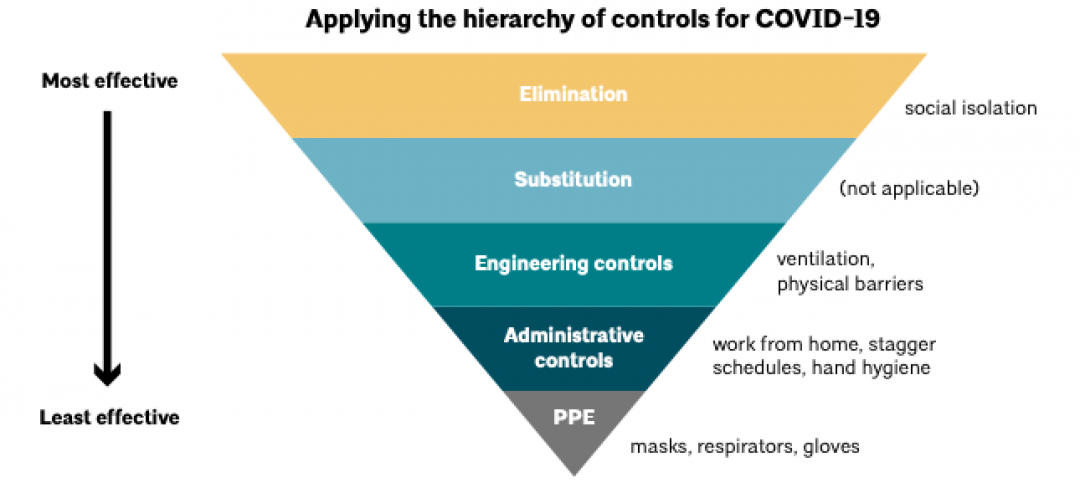
Eppstein Uhen Architects (EUA) has released a 16-page guide that provides pandemic considerations for health facility design. The document focuses on four objectives:
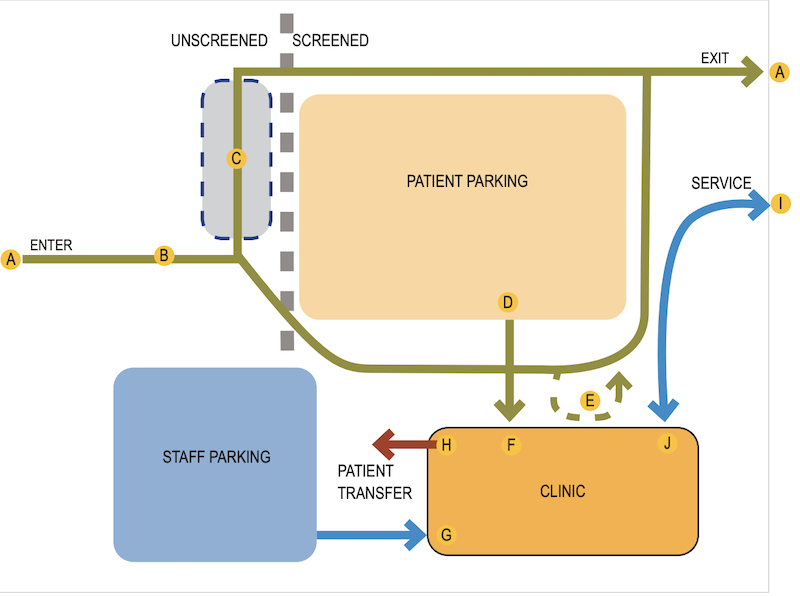
1. Reducing patient presentations at facilities, with specific focuses on telehealth, site design and planning, and drive-through testing. For example, the guide’s considerations for reducing patient presentations include using the facility’s parking lot to manage who enters the building. It recommends a single point of entry and exit, a staffed gatehouse to direct and track patients (via smartphone technology), and drive-through services for pharmacies and labs.
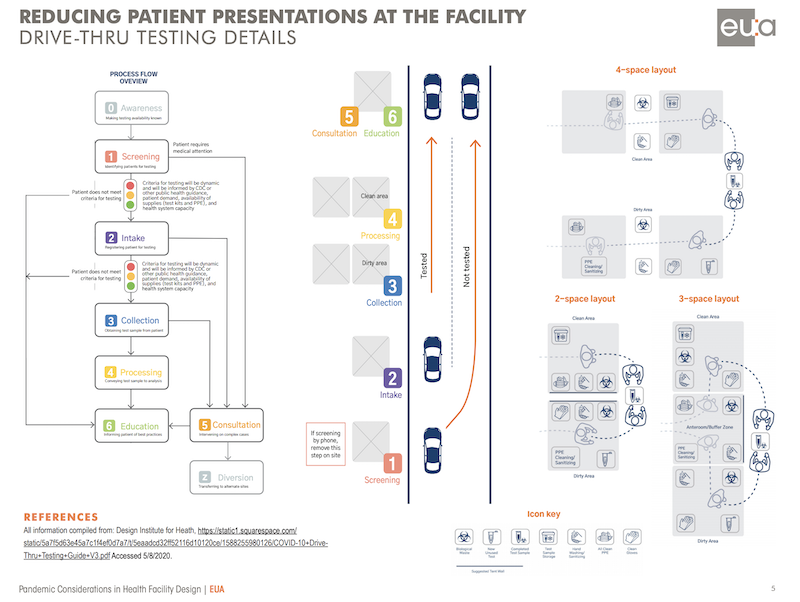 The guide emphasizes the importance of drive-through options for controlling who enters a healthcare building.
The guide emphasizes the importance of drive-through options for controlling who enters a healthcare building.
2. Isolating infectious patients, and how to prepare vestibules, entries, waiting rooms, and reception areas. The guide recommends larger vestibules to accommodate more functions and equipment, as well as temperature screening, physical distancing, and touchless entry supplemented by hand sanitizer stations and mask dispensers. Planning, the guide states, will also consider “placing a negative pressure multipurpose room adjacent to registration to isolate patients with symptoms of infectious diseases.
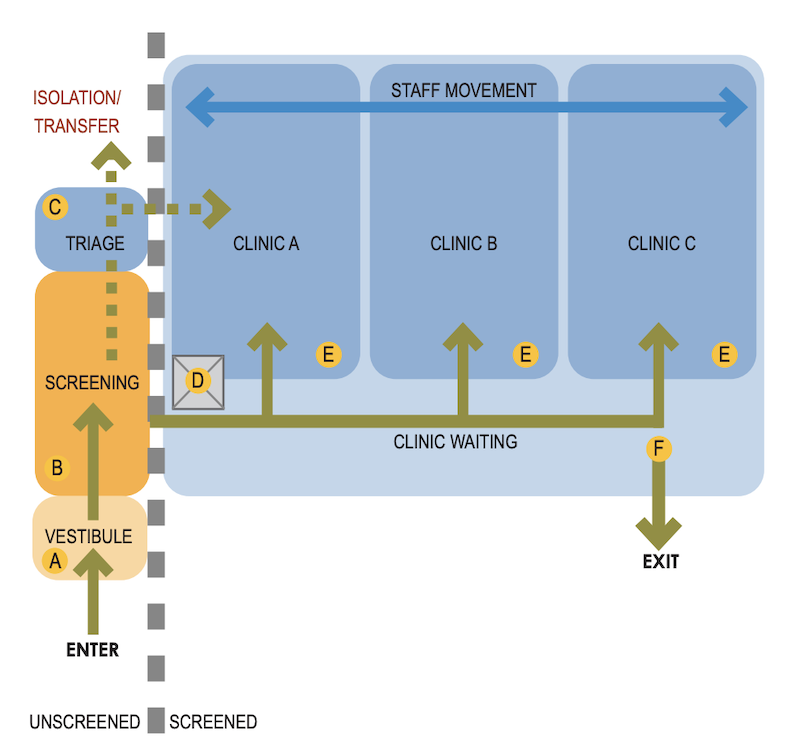 Screening patients as they enter a building is imperative.
Screening patients as they enter a building is imperative.
3. Improving facilities’ ability to reduce the spread of infection. The guide makes specific planning recommendations for clinics, hospital lobbies, emergency departments, elevators, materials management, and restrooms. Triage areas at the front door will help sort well and unwell patients. One-way patient flow will ensure patients don’t cross paths with potentially unwell patients who are entering the building.
For clinics, EUA favors a “library” model that includes community spaces (e.g., rooms for meetings and group therapies, physical therapy, or for staff break rooms) with access to the building’s main entrance. During a pandemic, a community space would be converted to serve as a buffer between screened and unscreened patients.
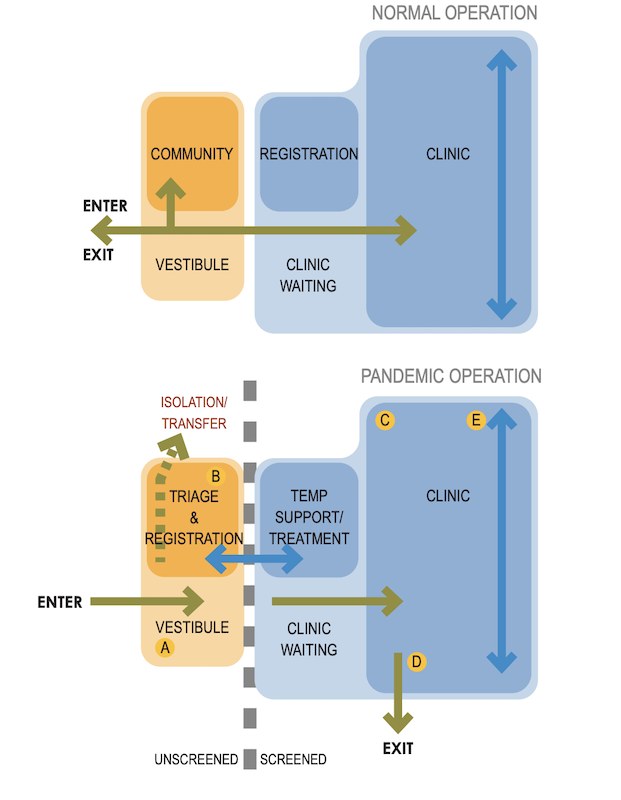 The guide recommends one-way traffic so that well and unwell patients don't intersect.
The guide recommends one-way traffic so that well and unwell patients don't intersect.
4. Providing surge capacity for high-volume episodes. The guide offers considerations for separating infected patients, providing separate entrances, ventilation (including providing a negative pressure relationship in the infectious side of the unit), and repurposing lower-acuity patient care spaces for increased patient beds.
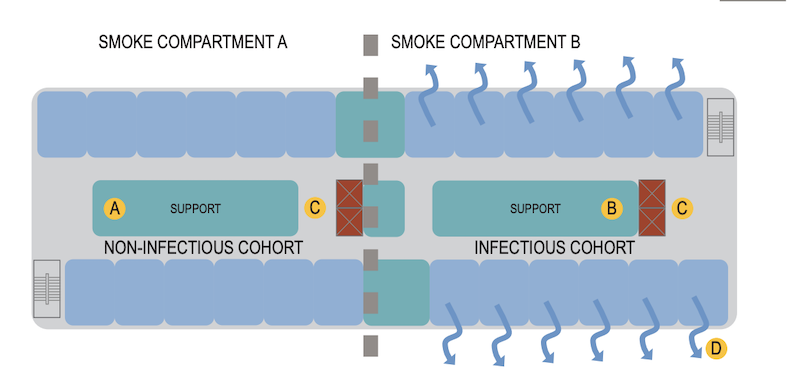 This diagram of an inpatient nursing unit shows how strategies can be employed to separate non-infectious and infectious patients in the same bed unit.
This diagram of an inpatient nursing unit shows how strategies can be employed to separate non-infectious and infectious patients in the same bed unit.
“Planning a building that seeks to fully address all aspects of operations during a pandemic is a major undertaking,” the guide concedes. Therefore, “it is important to be intentional about the decisions each organization makes around pandemic planning for each project.”
Related Stories
Coronavirus | May 7, 2020
White paper clarifies steps, roles for use of metal composite material
Responsibilities of manufacturers, distributors, and fabricators outlined.
Coronavirus | May 7, 2020
Architects release new resource for safer re-occupancy of buildings
The American Institute of Architects (AIA) is releasing a new Re-occupancy Assessment Tool today that provides strategies for limiting exposure to COVID-19 in buildings.
Coronavirus | May 6, 2020
Reopening Main Street post-COVID-19 quarantine
Cities and communities will need to adjust public space to allow customers back in with distancing in mind.
Coronavirus | May 6, 2020
Making jobsites safer in the COVID-19 world
A leading construction manager and installer certification alliance share their insights.
Coronavirus | May 6, 2020
National Construction Association and Procore to release new data showing the impacts of the coronavirus on the constructionindustry
Data will be released on Friday, may 8 at 12 pm EDT.
Healthcare Facilities | May 5, 2020
Holt Construction, U.S. Army Corps of Engineers complete temporary hospital in two weeks
The project is located in Paramus, N.J.
Coronavirus | May 5, 2020
How will COVID-19 change the procurement of professional design services?
We can use this moment as a test-case to build greater flexibility into how we pursue, win and deliver capital projects, better preparing the industry to meet the next disruption.
Coronavirus | May 4, 2020
Design steps for reopening embattled hotels
TPG Architecture recommends post-coronavirus changes in three stages.
Coronavirus | Apr 30, 2020
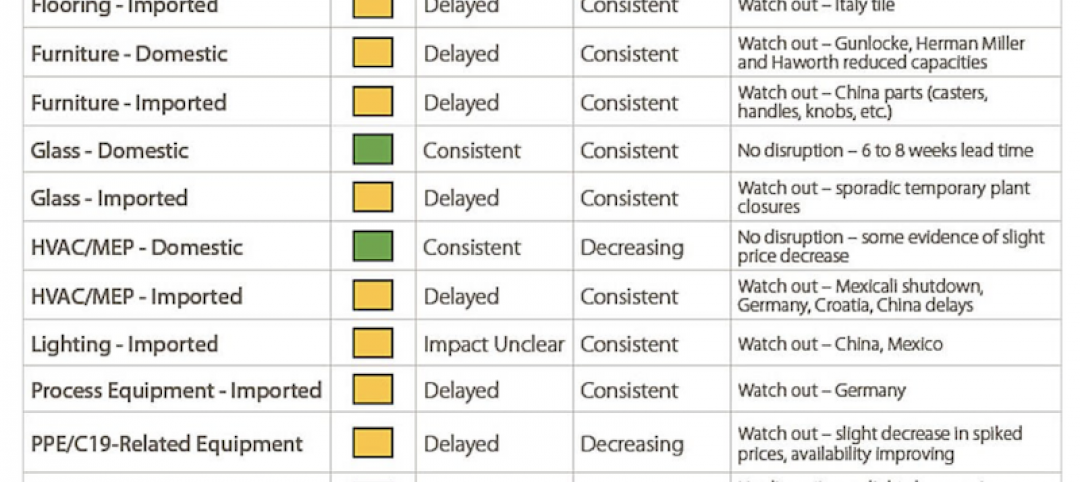
Gilbane shares supply-chain status of products affected by coronavirus
Imported products seem more susceptible to delays
Coronavirus | Apr 26, 2020
PCL Construction rolls out portable coronavirus testing centers
The prefabricated boxes offer walk-up and drive-thru options.