A team of AEC firms, assembled by Generate, an AEC technology company that advocates for the greater use of mass timber in construction, has developed a digital catalog of integrated design systems that focus on the structural application of mass timber as a carbon-conscious response to high-density urban building needs, especially for housing.
Meeting those needs within the status quo—where buildings currently account to two-fifths of greenhouse gas emissions—is at odds with many cities’ environmental aspirations. For example, Boston’s goal of reducing its carbon footprint 80% by 2050 would be unachievable if that metro also hits its parallel goal of building 300,000 more housing units and 40 million sf of commercial buildings over the next 30 years.
To bring down those CO2 emissions and streamline the construction process, an AEC coalition has developed Tallhouse, a digital catalog of customizable systems comprised of four mass timber structural solutions. That catalog illustrates a range of mass timber design options that are engineered for speedier delivery, sustainability, and cost savings.
Also see: San Jose affordable housing project will feature mass timber frame
The coalition includes Generate, Niles Bolton Associates (architect), Buro Happold (SE, MEP, sustainability consultant, embodied carbon analyst), Consigli Construction (GC), Arup (fire engineering, structural review), Code Red (code consultant), Urbanica (developer), and Olifant Market Development (carbon and forests).
The coalition’s work has been supported by the National Science Foundation, the U.S. Department of Agriculture, the Softwood Lumber Board, the Binational Softwood Lumber Council, and the Commonwealth of Massachusetts.
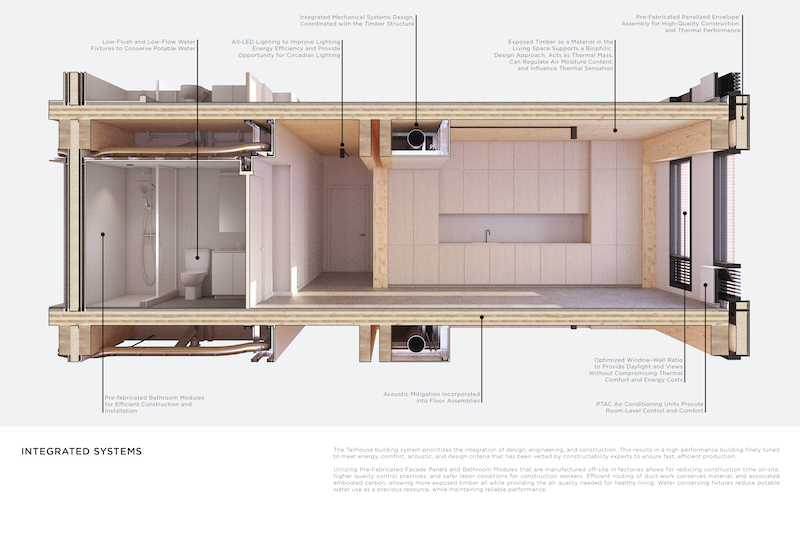
Tallhouse's systems are designed as kits of parts to accommodate most countries' products and transportation.
THE DESIGNS ANTICIPATE TALLER WOOD BUILDING CODES
Tallhouse’s four options are a hybrid steel/cross-laminated timber (CLT) structure, a mass-timber post, beam and plate structure; a hybrid light-gauge metal/CLT structure, and a full CLT plate honeycomb structure.
By “hybridizing” conventional construction materials with timber, the Tallhouse designs can offset near-term emissions by greatly reducing emissions from the manufacture of materials, while storing carbon in the timber structure over the lifetime of buildings. The team sees synergies between the steel and timber industries, as both materials lend themselves to digitization and carbon efficiency.
To evaluate each design, the coalition developed a Carbon Data Analysis tool that validated savings in embodied emissions ranging from 14% to 52%.
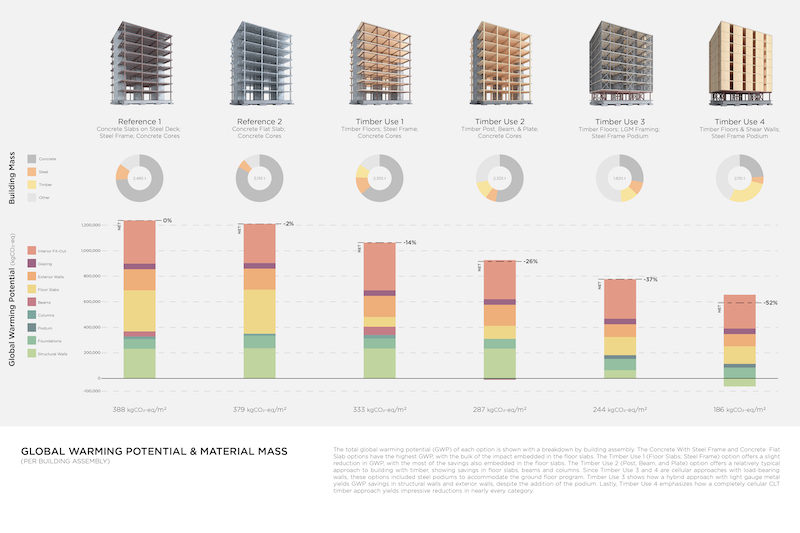
The coalition used a Carbon Data Analysis tool to gauge the impact of its designs on carbon emissions and global warming.
The Tallhouse system is adaptable for buildings eight to 18 stories, in line with the upcoming 2021 U.S. Tallwood Codes that would allow the use of mass timber for structures at those heights under the 2021 International Building Code. According to Generate, the systems are designed as kits of parts to accommodate most American, Canadian, and European manufacturers’ products and shipping logistics.
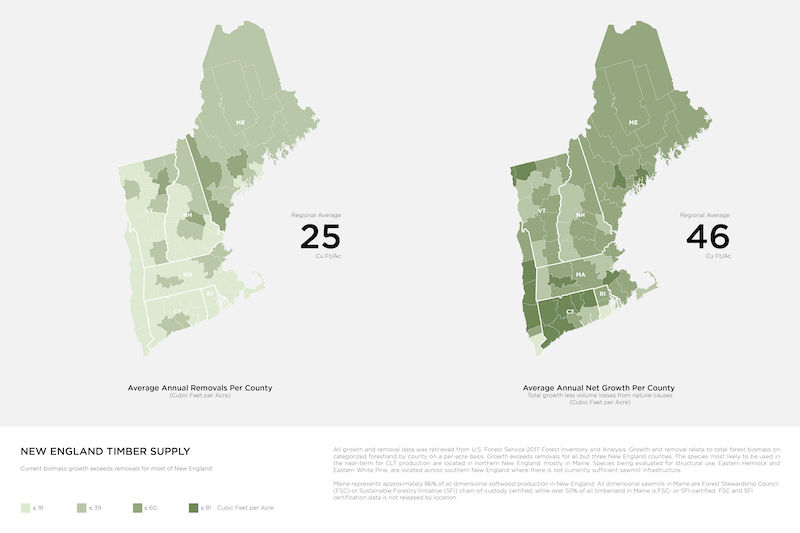
The U.S. Northeast is home to the highest percentage of sustainably managed timber in the U.S. Long-lived forest products such as mass timber building materials have longer timelines than paper or pulp products for keeping CO2 stored in wood post-harvesting.
The Tallhouse team is implementing these systems in over 1 million sf of construction in the U.S., and is looking for additional developers. The Tallhouse catalog, says John Klein, Generate’s CEO and project leader, “was developed with the specific intent of at once enabling our cities to achieve their ambitious CO2 footprint reduction goals, and to meet growing demand for affordable, biophilic housing.” As these systems become widely accessible to architectural communities globally, they will “serve as a vehicle to deploy sustainable materials at scale,” says Klein.
Related Stories
| Aug 11, 2010
Report: Building codes and regulations impede progress toward uber-green buildings
The enthusiasm for super green Living Buildings continues unabated, but a key stumbling block to the growth of this highest level of green building performance is an existing set of codes and regulations. A new report by the Cascadia Region Green Building Council entitled "Code, Regulatory and Systemic Barriers Affecting Living Building Projects" presents a case for fundamental reassessment of building codes.
| Aug 11, 2010
Call for entries: Building enclosure design awards
The Boston Society of Architects and the Boston chapter of the Building Enclosure Council (BEC-Boston) have announced a High Performance Building award that will assess building enclosure innovation through the demonstrated design, construction, and operation of the building enclosure.
| Aug 11, 2010
Portland Cement Association offers blast resistant design guide for reinforced concrete structures
Developed for designers and engineers, "Blast Resistant Design Guide for Reinforced Concrete Structures" provides a practical treatment of the design of cast-in-place reinforced concrete structures to resist the effects of blast loads. It explains the principles of blast-resistant design, and how to determine the kind and degree of resistance a structure needs as well as how to specify the required materials and details.
| Aug 11, 2010
Rice concrete can cut greenhouse emissions
Rajan Vempati of ChK Group, Inc. in Plano, Texas, and a team of researchers found a way to make nearly carbon-free rice husk ash for concrete, which can lead to a boom in green construction.
| Aug 11, 2010
Sika Sarnafil launches sustainable roofing resource website SustainabilityThatPays.com
Sika Sarnafil, the worldwide market leader in thermoplastic roofing and waterproofing membranes, today launched a new web site dedicated to supporting sustainability principals and environmentally responsible building. The streamlined site, SustainabilityThatPays.com &http://www.SustainabilityThatPays.com> provides the building owner with critical information on selecting roofing and waterproofing systems...
| Aug 11, 2010
Jacobs, CH2M Hill, AECOM top BD+C's ranking of the 75 largest federal government design firms
A ranking of the Top 75 Federal Government Design Firms based on Building Design+Construction's 2009 Giants 300 survey. For more Giants 300 rankings, visit http://www.BDCnetwork.com/Giants
| Aug 11, 2010
Manhattan's Pier 57 to be transformed into cultural center, small business incubator, and public park as part of $210 million redevelopment plan
LOT-EK, Beyer Blinder Belle, and West 8 have been selected as the design team for Hudson River Park’s Pier 57 at 15th Street and the Hudson River as part of the development group led by New York-based real estate developer YoungWoo & Associates. The 375,000 square foot vacant, former passenger ship terminal will be transformed into a cultural center, small business incubator, and public park, including a rooftop venue for the Tribeca Film Festival.







