Last summer, the New York Times ran a story with the headline “The Capital of Car Culture, Los Angeles Warms to Mass Transit.” That article focused on the recent opening of extensions of L.A.’s Expo and Gold transit lines, and a tax-funded initiative that would finance 40 major transit projects over the next 40 years, including 100 miles of new rail lines and a train tunnel through the Sepulveda Pass to connect the L.A. Basin with the San Fernando Valley.
Cities around the country, from Denver to Tyler, Texas, have embraced transit investment as an economic stimulus. The Federal Transit Administration (FTA) estimates that every dollar spent on transit translates to $4 in economic returns. Property located near transit is up to 150% more valuable. And every $1 billion invested in transit supports at least 20,000 jobs.
Amtrak recorded a record $3.4 billion in revenue in fiscal 2018 from 31.7 million passenger trips, and its lowest operating loss ($168 million) since 1973. And transit-oriented development is now an abiding model for such new construction projects as office buildings, stadiums, and entertainment districts.
So it’s not surprising that public transit ridership across the U.S. was up by 11% between 2010 and 2017, compared to a 6% increase in car ridership during that period, according to a new report on urban public transportation trends that the website STORAGECafé released late last month. STORAGECafé is part of Yardi, the property management software provider.
“Better public transit can make and shape a neighborhood and improve the character of a city,” the report states. “It can provide for the whole range of workers that are needed from refuse collectors to college professors, not to mention addressing environmental concerns. The U.S.’s largest and most rider-friendly cities are showing how this can be done.”
However, more recent FTA data paints a less sanguine portrait of public transit ridership per capita, which with the exception of three metros—Seattle, Las Vegas, and Salt Lake City—declined between 2010 and 2018 (see chart below), despite major investments in such cities as Los Angeles, Houston, and Atlanta. Last month, the Los Angeles Times reported on San Diego’s proposal to use billions in taxpayer money to fund a high-speed rail system.
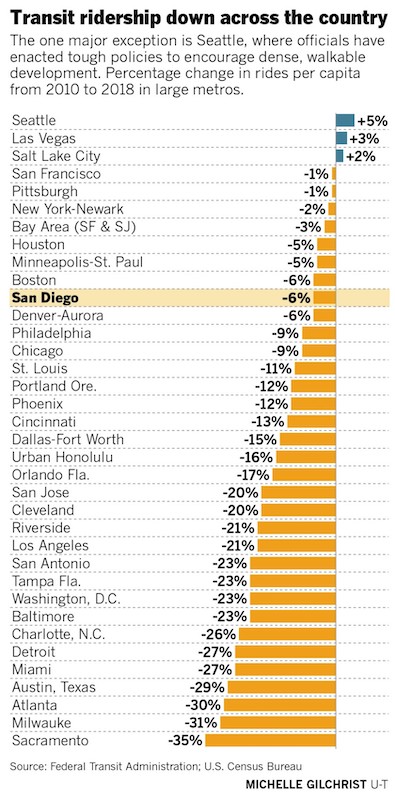
Last year, despite major investments by some big cities, public transit ridership declined in most cities, according to Federal Transit Administration estimates. Chart: Los Angeles Times/San Diego Union-Tribune
Objectively, Americans still prefer the comfort and convenience of their personal cars and trucks: 127 million drove to work in 2017. But STORAGECafé still sees public transit as an emerging transportation mode, with 7.5 million people commuting by bus or train in 2017. In New York City, which operates the country’s largest mass-transit system, its public transit ridership increased by nearly 239,000 in 2017.
Among the 30 largest cities in the U.S., San Jose saw a 46.7% increase in public transit ridership in 2017, vis a vis 2010, followed by Jacksonville, Fla. (35.8%, Nashville (26%), Columbus, Ohio (17.3%), and Dallas (14.1%).
Washington D.C. ranks as STORAGECafé’s No. 1 city for public transportation, based on a combination of factors: share of people who use it, time it takes to get to work, travel time compared to car travel, and cost as a portion of median income. In D.C., 35.4% of its residents use public transit. It takes them, on average, 38 minutes to get to work (9.6 minutes quicker than had they drove), and costs $104 per month, or 2.2% of the market’s median earnings.
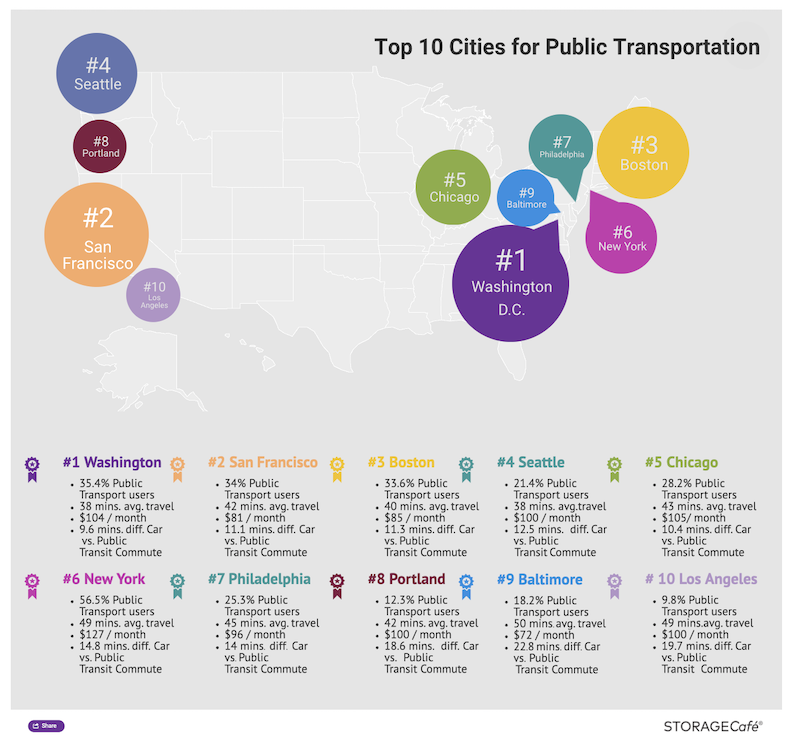
STORAGECafé ranks Washington DC as the No. 1 public transit city in the country, based on such factors as users per population, travel time, and commuter costs. Image: STORAGECafé
Washington’s public transit ranking is followed by San Francisco, Boston (which on Nov. 4 decided to convert its commuter rail network into a regional rail network), Seattle, Chicago, New York, Philadelphia, Portland, Ore., Baltimore, and Los Angeles.
STORAGECafé acknowledges the challenges associated with providing public transit service in large cities that, in many cases, are experiencing population growth. It notes that improving public transit “requires planning and legislation, which can take time.” But many of America’s metros, already clogged by vehicular congestion, have little choice but to move toward public transit as a means of moving people to and from where they live, and to present their cities as attractive options for businesses.
The benefits of public transit are manifold, says the report, especially in light of the 4.5 million serious injuries and 40,000 fatalities caused by car crashes last year, according to the National Safety Council. STORAGECafe’s report contends that public transit is 10 times safer than driving a car, and uses less fuel per passenger, which means cleaner air for cities. (The U.S. Department of Transportation states that public transit produces 95% less carbon monoxide than private vehicles.)
The report also suggests that public transit is less stressful than individual driving. It cites a study of Millennial mobility by the American Public Transportation Association and the Transit Cooperative Research Program, which found that public transit is conducive to Millennials’ preferences for working and socializing online while they travel.
The notion that public transit is the preferred mode for mostly lower-income commuters is starting to change, too. STORAGECafé found that 23.3% of public transit users earn more than $75,000 annually, compared to 17.6% in that earnings bracket in 2010.
Related Stories
Urban Planning | Mar 14, 2017
Denmark-based architecture firm gives China the world’s longest elevated bike path
The Xiamen Bicycle Skyway stretches for 7.6 kilometers throughout the central part of the city.
Urban Planning | Feb 9, 2017
Abandoned WWII-era military village to become 'commune for the 21st century'
The village in Heidelberg, Germany, which 16,000 Americans called home at one time, is being redesigned as a commune for up to 4,000 people.
Green | Feb 6, 2017
A to Z: Seoul’s elevated park features 24,000 alphabetized plants
The plants will represent 250 species found in South Korea.
Urban Planning | Jan 17, 2017
Using 'hidden data' to probe urban problems
The Center for Neighborhood Technology has been tackling poverty, housing, transportation, and environmental issues for four decades.
Architects | Nov 11, 2016
Six finalists selected for London’s Illuminated River competition
The competition is searching for the best design for lighting the bridges of central London.
Building Tech | Nov 9, 2016
Dubai to Abu Dhabi in 12 minutes: A hyperloop from Hyperloop One and BIG could make it possible
The pods can reach speeds of up to 1,100 kilometers per hour.
Urban Planning | Nov 4, 2016
Rail Park breaks ground in Philadelphia
The project is finally moving forward after nine years in the making.
Urban Planning | Oct 27, 2016
Paris plans to transform the right bank of the river Seine into car-free pedestrian zone
Drivers are worried the move will cause an increase in traffic congestion.
Urban Planning | Oct 27, 2016
The lawsuit blocking the construction of Pier 55 has been thrown out
Construction on the $130 million project can now proceed as planned.
Urban Planning | Oct 20, 2016
Despite troubled development, Masdar City forges ahead
The detailed master plan for Phase 2 of Masdar City has been unveiled by CBT.