Forty-five percent of the country's elementary, middle, and high schools were built between 1950 and 1969 and will soon reach the end of their usefulness, according to the 2005–2008 K-12 School Market for Design & Construction Firms, published by ZweigWhite, a Massachusetts-based market-research firm.
Almost 30% of U.S. schools were built before 1950 and need major modernization because enrollments continue to increase. Between 1988 and 2004, the number of students in public and private K-12 schools increased almost 20%, from 44 million to 54 million, according to the National Center for Education Statistics. That trend is expected to continue as new immigrants and the children of baby boomers enter secondary schools.
According to ZweigWhite, increasing numbers of school districts are demanding new facilities in response to enrollment growth. American School & University magazine estimates $89.8 billion in K-12 construction will be completed by 2006. Of that, $56.9 billion will be new work.
"It's definitely one of the stronger markets we've seen for firms," with Florida and California leading the way, said Christopher Klein, managing editor of the report and a ZweigWhite principal. "Of the 25 different market sectors we rank in our annual AEC industry outlook, [schools] ranked just behind healthcare and higher education in the top three."
Market trends providing unique opportunities in K-12 construction include:
-
New financing mechanisms, such as public-private partnerships
-
More technologically advanced and collaborative learning schools
-
Greater use of sustainable building designs
-
Designing schools that also serve as community centers
-
Improvements in school security
New finance mechanisms. To finance new construction and major renovations, some school districts are bringing in private investors through lend-lease agreements. These deals create public/private partnerships that are not subject to state requirements for multiple contractors and open bidding. School districts can also circumvent bonding limits and exempt building projects from federal tax using these financing instruments.
Niagara Falls High School became the first privately financed, privately managed school construction project in New York State last year. The school district currently leases the school for $4.8 million a year from private partner Honeywell International. Ownership transfers to the school district in 27 years.
"It's something that's occurring as a novelty in the marketplace right now," said Klein. "The driver, of course, is getting funding to build these new facilities that otherwise wouldn't be there."
Klein says new funding is also coming from foundations, such as the Bill and Melinda Gates and Carnegie foundations. These institutions donate large sums to create high-tech environments in even the lowest grades.
Technology improvements. The ZweigWhite report predicts technology will dominate new school construction, with cost-control measures such as distance education over the Internet, and basic education programs delivered through computers, networks, and software. Smaller class sizes and changes in teaching methods (such as providing alcoves or flexible spaces with fewer hard walls) will continue the trend of smaller groups, collaborative instruction, and more sustainable designs.
Sustainable design or green building elements that firms can use in K-12 schools include designs that reduce the reliance on automobiles, use alternate energy sources, and orient school buildings to take advantage of sunlight. The number of school projects registered under the U.S. Green Building Council's LEED rating program grew from 52 in 2003 to 124 in April 2005.
The most important of the environmental elements addressed by sustainable design for schools, according to ZweigWhite, is indoor air quality. Recent lawsuits claimed that mold had sickened children in two Florida school districts.
"There's now a pretty decent awareness among architects, builders, and facilities managers of sustainable design in K-12 construction," Klein said. "I suspect you will see that awareness broaden out as new projects continue to be built and the idea of sustainable design reaches the school boards and the people running schools."
Community use of schools. More community members—such as theater groups and senior citizens—are using K-12 schools for everything from libraries to athletic, computer, and art facilities. Opening up K-12 schools for use by community groups is helping to broaden support for school bond measures, particularly among voters who do not have children in schools. Firms will need to design and create structures for more intense use and flexibility, the report claims.
Security demands. At the same time schools are opening their doors to greater community use, there is equally strong emphasis to build more secure schools in the face of Columbine-like school violence and terrorism. Firms will have to balance the openness of a community center with design concepts like territorial reinforcement (giving users a sense of control), natural access control (denying access to crime targets and creating a perception of risk in offenders), and target hardening (dead bolts and other visible security features).
"There is steam left in (the growing school market)," says Klein. "All the drivers point to major construction, especially in the 9–12 market."
Related Stories
| Nov 18, 2013
ASSA ABLOY, CertainTeed team up to tackle classroom acoustics
The new alliance has uncovered easily accessible solutions to address these acoustical challenges and reduce the sound reverberation that further complicates noise issues.
| Nov 15, 2013
Greenbuild 2013 Report - BD+C Exclusive
The BD+C editorial team brings you this special report on the latest green building trends across nine key market sectors.
| Nov 13, 2013
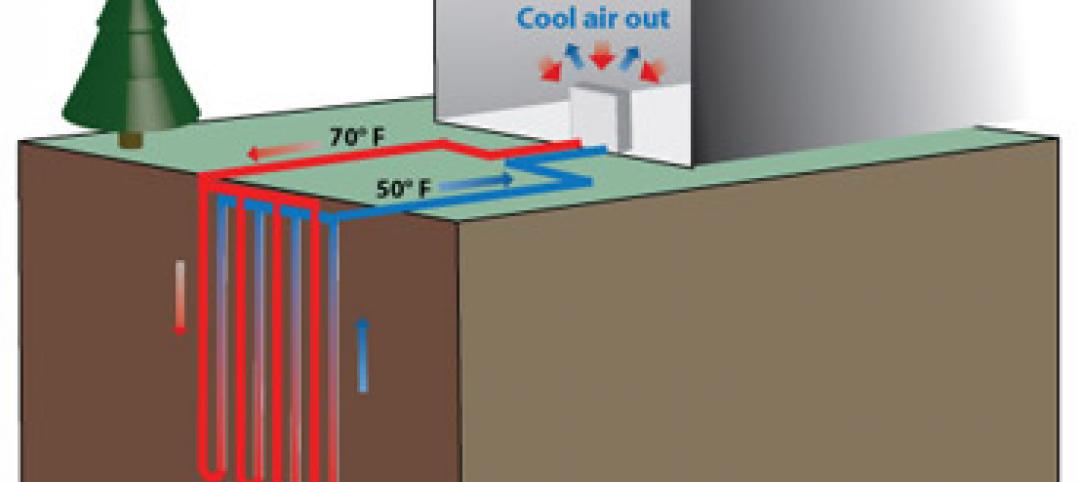
Installed capacity of geothermal heat pumps to grow by 150% by 2020, says study
The worldwide installed capacity of GHP systems will reach 127.4 gigawatts-thermal over the next seven years, growth of nearly 150%, according to a recent report from Navigant Research.
| Nov 5, 2013
Net-zero movement gaining traction in U.S. schools market
As more net-zero energy schools come online, school officials are asking: Is NZE a more logical approach for school districts than holistic green buildings?
| Oct 30, 2013
11 hot BIM/VDC topics for 2013
If you like to geek out on building information modeling and virtual design and construction, you should enjoy this overview of the top BIM/VDC topics.
| Oct 28, 2013
Urban growth doesn’t have to destroy nature—it can work with it
Our collective desire to live in cities has never been stronger. According to the World Health Organization, 60% of the world’s population will live in a city by 2030. As urban populations swell, what people demand from their cities is evolving.
| Oct 18, 2013
Researchers discover tension-fusing properties of metal
When a group of MIT researchers recently discovered that stress can cause metal alloy to fuse rather than break apart, they assumed it must be a mistake. It wasn't. The surprising finding could lead to self-healing materials that repair early damage before it has a chance to spread.
| Oct 15, 2013
15 great ideas from the Under 40 Leadership Summit – Vote for your favorite!
Sixty-five up-and-coming AEC stars presented their big ideas for solving pressing social, economic, technical, and cultural problems related to the built environment. Which one is your favorite?
| Oct 7, 2013
10 award-winning metal building projects
The FDNY Fireboat Firehouse in New York and the Cirrus Logic Building in Austin, Texas, are among nine projects named winners of the 2013 Chairman’s Award by the Metal Construction Association for outstanding design and construction.
| Oct 7, 2013
Geothermal system, energy-efficient elevator are key elements in first net-zero public high school in Rhode Island
The school will employ a geothermal system to heat and cool a portion of the building. Other energy-saving measures will include LED lighting, room occupancy sensors, and an energy-efficient elevator.