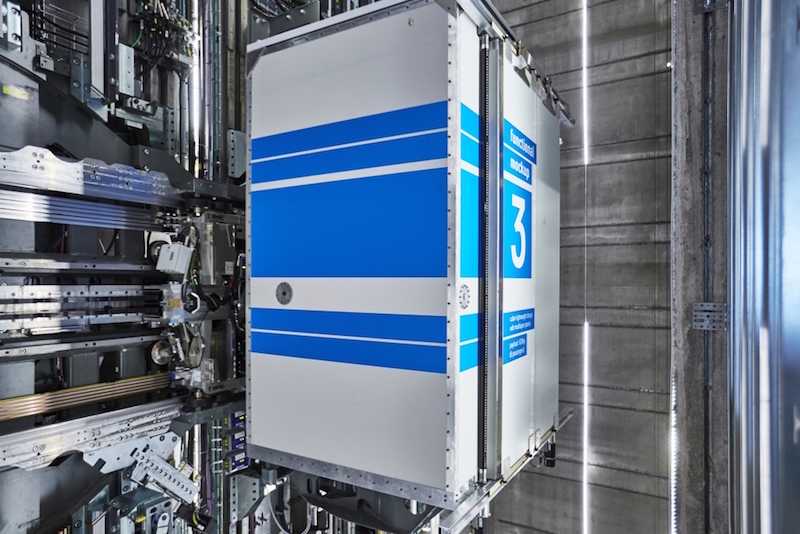
 Later this year, the new 459-ft-tall East Side Tower in Berlin, Germany, will be the first building in the world to install an elevator system that travels both vertically and horizontally.
Later this year, the new 459-ft-tall East Side Tower in Berlin, Germany, will be the first building in the world to install an elevator system that travels both vertically and horizontally.
OVG Real Estate and FREO Group, the building’s developers, are working in partnership with thyssenkrupp, one of the world’s largest industrial groups, whose thyssenkrupp Elevator division has devised MULTI, the first cable-free elevator that moves sideways as well as up and down.
Thyssenkrupp unveiled this concept in 2014, and after two-and-a-half years of construction demonstrated MULTI last month at its 807-ft-tall, 12-shaft innovation test tower in Rottweil, Germany. This tower can test elevator speeds up to 22.45 miles per hour. Three of its shafts were designed specifically for certifying the new cable-free elevator system.
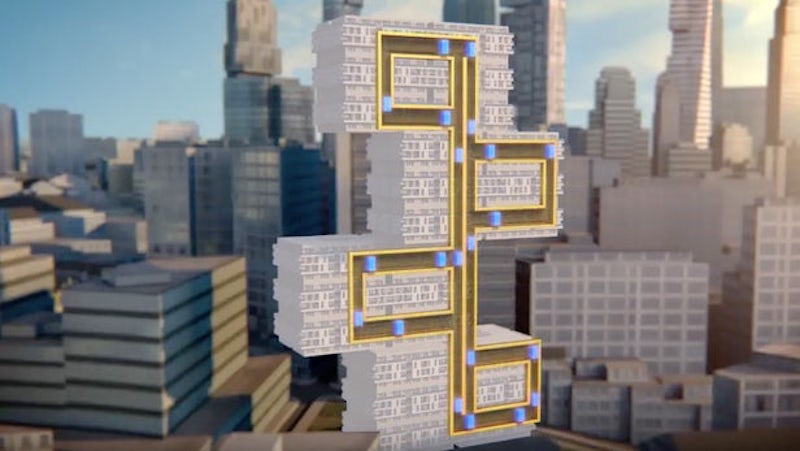
 MULTI operates along the same principals as a metro system. Image: Thyssenkrupp
MULTI operates along the same principals as a metro system. Image: Thyssenkrupp
Instead of one cabin per shaft moving up and down, MULTI offers multiple cabins operating in loops, similar to a metro system but inside a building. Its exchange system allows the linear drive and guiding equipment to make 90-degree turns by leveraging the linear motor technology developed for the magnetic levitation Transrapid train. MULTI runs on a multi-level brake system and redundant wireless data and energy management system on the cars.
A short animated video of how this system works can be seen here.
Nearly 200 building industry representatives attended the demonstration, including Antony Wood, Executive Director of the Council on Tall Buildings and Urban Habitat. Wood calls MULTI “perhaps the biggest development in the elevator industry since the invention of the safety elevator some 165 years ago.”
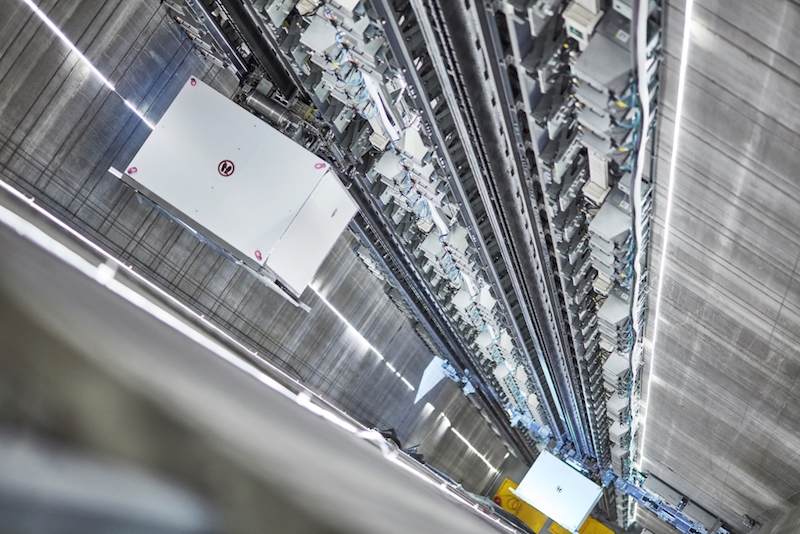

At a time when developers are challenging AEC firms to come up with new and faster ways to transport people in taller buildings. MULTI is promising 50% higher transport capacities. Image: thyssenkrupp
As cities expand and buildings get larger and taller to accommodate more people, planners and architects face significant challenges around moving people comfortably and quickly to their destinations. McKinsey Global Institute estimates that cities will need to construct floor space equivalent to 85 percent of all of today’s residential and commercial building stock by 2025.
To that end, thyssenkrupp claims that MULTI can achieve up to 50% higher transport capacity and reduce peak power demand by as much as 60% when compared to conventional elevator systems.
MULTI requires fewer and smaller shafts than conventional elevators and can increase the building’s usable area by up to 25%. (Thyssenkrupp notes that current elevator-escalator footprints can occupy up to 40% of a high rise building’s floor space, depending on the building height.) The system will also reduce the wait time for a ride to between 15 and 30 seconds.
In April, MULTI took top honors at the 2017 Edison Awards in New York, an annual competition honoring new product and service excellence. The first MULTI system will be installed in the East Side Tower, which is scheduled for completion by 2019. In an interview with Wired magazine, thyssenkrupp's CEO Andreas Schierenbeck said that while MULTI could cost between three and five times more than a standard lift system, the space savings in a large building are “definitely overcompensating the price of the product.”
Related Stories
Mechanical Systems | Jun 16, 2023
Cogeneration: An efficient, reliable, sustainable alternative to traditional power generation
Cogeneration is more efficient than traditional power generation, reduces carbon emissions, has high returns on the initial investment, improves reliability, and offers a platform for additional renewable resources and energy storage for a facility. But what is cogeneration? And is it suitable for all facilities?
AEC Innovators | Jun 15, 2023
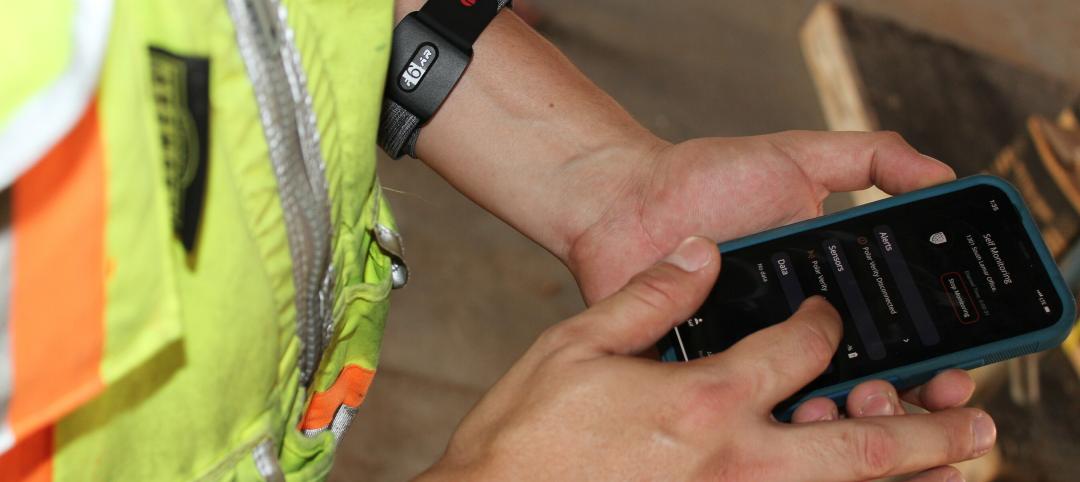
Rogers-O'Brien Construction pilots wearables to reduce heat-related injuries on jobsites
Rogers-O'Brien Construction (RO) has launched a pilot program utilizing SafeGuard, a safety-as-a-service platform for real-time health and safety risk assessment. Non-invasive wearables connected to SafeGuard continuously monitor personnel to prevent heat exhaustion on jobsites, reducing the risk of related injuries. RO is the first general contractor to pilot this program.
Mass Timber | Jun 13, 2023
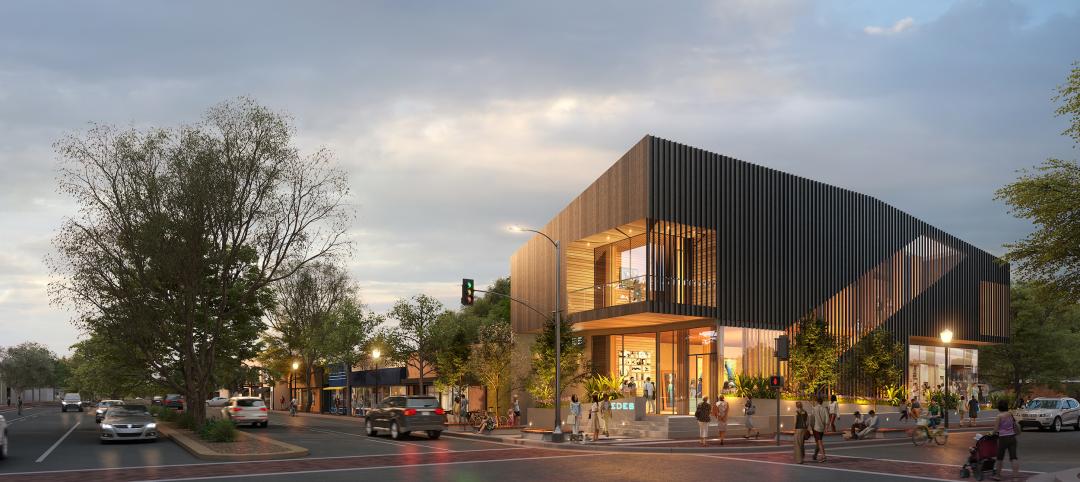
Mass timber construction featured in two-story mixed-use art gallery and wine bar in Silicon Valley
The Edes Building, a two-story art gallery and wine bar in the Silicon Valley community of Morgan Hill, will prominently feature mass timber. Cross-laminated timber (CLT) and glulam posts and beams were specified for aesthetics, biophilic properties, and a reduced carbon footprint compared to concrete and steel alternatives.
Engineers | Jun 5, 2023
How to properly assess structural wind damage
Properly assessing wind damage can identify vulnerabilities in a building's design or construction, which could lead to future damage or loss, writes Matt Wagner, SE, Principal and Managing Director with Walter P Moore.
Cladding and Facade Systems | Jun 5, 2023
27 important questions about façade leakage
Walter P Moore’s Darek Brandt discusses the key questions building owners and property managers should be asking to determine the health of their building's façade.
Office Buildings | May 15, 2023
Sixteen-story office tower will use 40% less energy than an average NYC office building
This month marks the completion of a new 16-story office tower that is being promoted as New York City’s most sustainable office structure. That boast is backed by an innovative HVAC system that features geothermal wells, dedicated outdoor air system (DOAS) units, radiant heating and cooling, and a sophisticated control system to ensure that the elements work optimally together.
AEC Tech Innovation | May 12, 2023
Meet Diverge, Hensel Phelps' new ConTech investment company
Thai Nguyen, Director of Innovation with Hensel Phelps, discusses the construction giant's new startup investment platform, Diverge.
3D Printing | May 12, 2023
World’s first 3D-printed medical center completed
3D construction printing reached new heights this week as the world’s first 3D-printed medical center was completed in Thailand.
AEC Tech | May 9, 2023
4 insights on building product manufacturers getting ‘smart’
Overall, half of building product manufacturers plan to invest in one or more areas of technology in the next three years.
University Buildings | May 5, 2023
New health sciences center at St. John’s University will feature geothermal heating, cooling
The recently topped off St. Vincent Health Sciences Center at St. John’s University in New York City will feature impressive green features including geothermal heating and cooling along with an array of rooftop solar panels. The geothermal field consists of 66 wells drilled 499 feet below ground which will help to heat and cool the 70,000 sf structure.