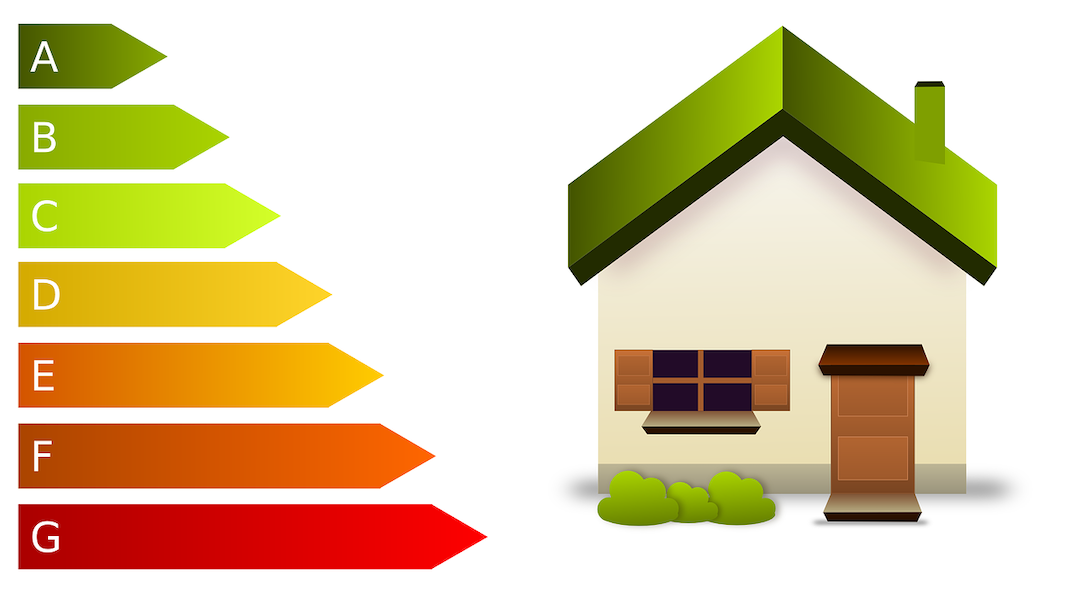
Recent findings from the Better Buildings Partnership raise serious questions about the efficacy of energy efficiency ratings used in the United Kingdom.
The study found that buildings that have received the highest rating—an A Energy Performance Certificate—use more energy than some of their peers rated C, D, E, or F. The analysis of self-reported energy data in 2020 for more than 1,100 commercial properties found that the median energy intensity for all B-rated buildings is higher than for C-rated buildings.
The disparity between how buildings are designed and their actual greenhouse gas emissions is widespread in the U.K. The findings are in line with past evidence that green building certifications based on predicted energy use don’t necessarily translate to energy savings in the field.
Some studies have found that LEED certification yields better energy efficiency, but others have found that certified buildings use more energy than non-certified buildings. The U.S. Green Building Council maintains that its own research shows certified buildings are overall more efficient.
Part of the explanation for the disparity between ratings systems and real-world results could be due to the limitation of assessments that only predict potential energy efficiency. In practice, building management systems may not be set up or used properly. In addition, people sometimes undo the efficiency design by bringing fans into buildings or installing additional air conditioners.
Related Stories
HVAC | Feb 6, 2015
ASHRAE, REHVA publish guide to chilled beam systems
The guide provides tools and advice for designing, commissioning, and operating chilled-beam systems.
Codes and Standards | Feb 2, 2015
AGC working with EPA on website to help with environmental rule compliance
The goal is for the site to be improved to make it easier for construction contractors to learn how to comply with federal and state environmental guidelines.
| Feb 2, 2015
New York law requires informing firefighters of wood truss construction
New York enacted a law that could make firefighting a bit safer by mandating property owners inform government and first-responders when they build or rehabilitate a building using "truss-type" pre-engineered wood or timber.
| Jan 14, 2015
Ontario code changes boost accessibility for people with disabilities
The new amended Ontario building code includes several provisions that improve accessibility for those with disabilities.
| Jan 14, 2015
American Concrete Institute releases Spanish edition of structural concrete code
New York City last year adopted the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) recommendation to require additional exit stairways in high-rise buildings.
| Jan 14, 2015
Terrorism Risk Insurance Act renewed
President Barack Obama signed the Terrorism Risk Insurance Act law on Jan. 12.
| Jan 9, 2015
Academy of Art in San Francisco under fire for code violations
The fast-growing Academy of Art is under intense scrutiny by the City of San Francisco for code violations.
| Jan 9, 2015
New law mandates storm shelters in Illinois schools
An Illinois law took effect on Jan. 1 that requires all new and remodeled schools to have storm shelters.
| Jan 9, 2015
New OSHA regulations on reporting workplace deaths, hospitalizations take effect
As of Jan. 1, all employers under the jurisdiction of OSHA are required to report all work-related fatalities within eight hours and all in-patient hospitalizations, amputations, and losses of an eye within 24 hours.
| Jan 9, 2015
Zoning policy makes Bethesda, Md., a model walkable suburb
In sharp contrast to most suburban communities in the Washington, D.C. area, Bethesda, Md., stands out as a fine exemplar of the new urbanism ethos.