LEED, though controversial, still dominates the world of sustainability rating systems. Photovoltaics and geothermal are gaining traction in high-performance projects. And many firms don’t push clients very hard toward sustainability certification.
These are among the findings of an exclusive survey of BD+C readers in the architecture sector, conducted in October. More than 150 architects, mostly from the U.S., responded with data about their sustainable design practices. Since respondents were self-selected, it’s likely that they have more than a casual interest in the topic—as evidenced by the intensity of some of their comments. Though based on a sizable number of responses, results should be viewed as a snapshot rather than a statistically valid random sample.
In particular, the survey indicates that architects are seeking affirmation that the complex array of programs, systems, and tools at their disposal actually do result in more sustainable buildings. They want real value rather than—in the words of one respondent—“a lot of green bologna.”
Through all the changes, LEED still leads
Fifteen years after its birth, LEED remains powerful, with 64% of respondents saying they have used the program to register or certify projects in the past 12 to 18 months. Energy Star for buildings is also fairly popular (28%). Usage of every other green-rating program we asked about was in the single digits, including Green Globes (8%), the National Green Building Standard (8%), the Living Building Challenge (6%), BREEAM (4%), and the Collaborative for High Performance Schools (2%).
Respondents have widely varied practices when it comes to client discussions about green rating systems. Only 3% said they routinely seek the highest possible certification level for all projects. A majority (62%) either don’t push their clients or let clients lead.
The familiar “we’re green but not certified” refrain was shared by a high percentage of respondents. Nearly 25% said more than half of their projects achieve a fairly high level of sustainability (at least LEED Silver or equivalent) but do not complete green certification of any kind. Another 27% of respondents said that 25 to 49% of their work falls into the “green but uncertified” category. The remaining respondents said that less than 25% of their work is “highly sustainable but uncertified.” (This answer may include responses from those who are doing some “green but uncertified” work, as well as responses from those whose work is not highly sustainable, period.)
The cost and complexity of LEED prompted a fair amount of spontaneous commentary. “The ever-evolving LEED standards threaten to make them irrelevant in the face of more practical and readily understood design and construction programs,” said one reader. Another characterized the cost of long-term recertification requirements as “unsustainable.” (Nevertheless, about two-thirds of our respondents have continued to use the program.)
Green-rating systems, whatever their pros and cons, still represent a useful sustainability framework for many Building Teams and owners. To better understand architect-client interactions involving this issue, we asked respondents to select one of five statements reflecting their firms’ typical engagement levels with rating systems—from habitual to minimal (Figure 1).
Ready for v4? Not so much
We asked architects about their individual and firm-level involvement with LEED v4, still in its infancy. Though fewer than 10% of respondents’ firms had participated in a v4 beta project or currently have a v4 project under way, 27% of respondents had taken the initiative to view a v4 webinar. Other individual activities include downloading the user guide (19%) and attending a related lunch-and-learn (12%) or USGBC chapter program (10%). However, 35% of respondents said they have taken no individual action to gear up for v4, and 45% said their firms have not taken action.
LEED v4 represents a major revision, not just a tweak, and pushback emerged in numerous comments. “I am concerned that a great many of the LEED credits are becoming so labor-intensive that the cost to the client for certification services will be prohibitive,” said one respondent. “The amount of detail on materials content and so on will require the design firm to hire an outside specialist or create an in-house position specifically for that task, pricing actual certification above the reach of more common projects.”
The long-term measurement and recertification aspects of the program are also a concern for some architects. “Adding this burden to the design profession via certification programs or building codes is asking architects to be responsible for actions outside their skill set,” said one respondent.
Another reader, who termed v4 “a big challenge,” continues to support efforts to refine the standard. “I hope that the changes don’t cause owners to give up on LEED. Passing LEED v4 was important; LEED must continue to be a leader in the world of green building.”
“We don’t push certification unless the client specifically brings it up” was the most popular response (36%), followed by “We encourage clients to pursue certification but let them take the lead” (26%) and “We pursue all projects to at least a minimum level, whether or not the client requests it” (21%). Only 14% of respondents said they “actively encourage clients to pursue certification, and challenge them to consider the highest possible certification levels.”
One respondent said, “I see the trend as expecting professionals to design to a specific sustainability goal, but not to spend precious money certifying.”
Even as LEED continues to evolve, it remains voluntary. Not so with several new green standards (or major revisions) that are likely to be incorporated in building codes. We asked readers how the International Green Construction Code, the 2012 International Energy Conservation Code, and ASHRAE Standard 90.1-2013 would affect their practice. Sixty-three percent of respondents predicted “some changes,” while 29% said there will be little immediate impact—in other words, business as usual. However, 8% expected the new standards to cause significant changes in their practice.
One respondent who derided certification as “useless P.R.” was more enthusiastic about these consensus standards, saying “code requirements and common sense will make the profession work toward better, more efficient buildings.”
Venerable labels trusted for sustainable products
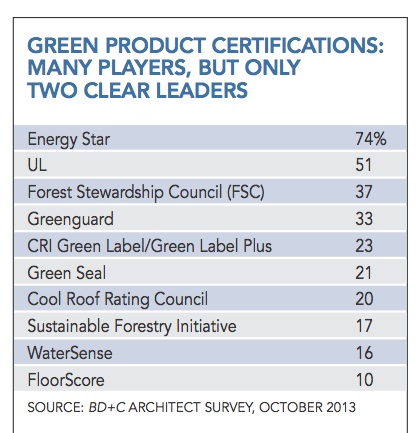
Product selection is an important aspect of sustainable design. We asked respondents which of 15 green-product certification systems they use most often in their daily work. The time-honored Energy Star (74%) and UL (51%) ratings were by far the most frequently chosen. Forest Stewardship Council (37%) and Greenguard (33%) certification are also fairly popular (Figure 2).
Greenbuild coverage of Architecture Firms is brought to you by:
Many architects are increasingly concerned about the potential environmental and health impacts of the products they specify. Environmental product declarations and health product declarations are at least “somewhat important” to more than 50% of respondents, with 11% terming them “extremely important.” However, 23% said they’re unfamiliar with EPDs and HPDs.
“I feel that healthy building materials will be the biggest transformation in the industry for the near future,” said one respondent. “This will be driven in the industry by LEED v4, but also, a general awareness of harmful substances has taken hold. Look at the new ingredient transparency policies being put into place by Walmart and Target. As designers, what liability do we incur with the knowledge that comes with material transparency?”
Net-zero and beyond
Some Building Teams and owners no longer see “sustainable” as a big enough goal. Instead, they’re striving for high-performance buildings that have minimal detrimental effects on the environment and maximum benefits for occupants. A dizzying array of targets exists, including net-zero energy, net-zero water, net-zero waste, net-plus, net-zero-ready, and zero-net-energy.
Of 15 green-product certification systems, Energy Star was the most popular, used frequently in daily work by nearly three-fourths of respondents. Five of the systems (BIFMA and ANSI/BIFMA, Cradle to Cradle, NSF Environmental Claims Initiative, Pharos Project, and Scientific Certification Systems) were used by fewer than 10% of respondents.
About 80% of respondents said they have not yet done any projects in such a high performance category. The remainder said they’ve done one or two, with only a couple saying they’ve tackled more than five. “The buzz is net-zero, but I think it’s a long way off from becoming universal or easy to obtain,” said one respondent.
In most cases, a combination of advanced strategies is required to get to net-zero, or anywhere close. Technologies once considered cutting-edge have now become commonplace—especially high-efficiency HVAC, water-conserving plumbing, and daylighting—and architects are exploring new tactics.
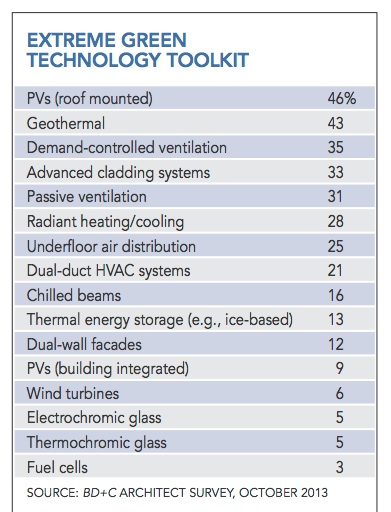
Figure 3 summarizes the relative popularity of emerging technologies. Roof-mounted photovoltaics were the clear winner, with 46% of respondents saying they’d used them on a project in the past 12 to 18 months. Also popular are geothermal (43%), demand-controlled ventilation (35%), and advanced cladding systems (33%). The relative lack of consensus around most emerging technologies may reflect climate and project-type differences, as well as respondents’ lack of familiarity with some technologies.
According to one respondent, techniques for making the building envelope more efficient are “coming to the forefront” in green design, abetted by code changes. “We are already seeing maximum air infiltration values in the IECC 2012 energy code, and the concept is now ingrained in the IgCC as well. Whole-building air-infiltration testing and extra scrutiny on construction techniques and tightness to the envelope will become the norm.”
Several respondents see renovation and O&M as priorities for a more sustainable built environment. “The systems and products that apply to new buildings usually are not applicable to existing structures, especially those with historic value,” said one reader. “This is a challenge for owners, designers, engineers, and manufacturers.”
Another said, “We need to embrace the notion of controlling the implementation of energy strategies, rather than pushing that task off to the MEP engineers or ESCOs. Mastery of energy-modeling tools can put the architect in the lead as the strategist for energy retrofits, and hopefully result in holistic improvements.”
Of 16 “advanced” green strategies used by respondents in the past 12 to 18 months, roof-mounted PV systems and geothermal were the most popular. Passive ventilation, an old principle, is making a comeback.
Related Stories
Multifamily Housing | Feb 21, 2023
Multifamily housing investors favoring properties in the Sun Belt
Multifamily housing investors are gravitating toward Sun Belt markets with strong job and population growth, according to new research from Yardi Matrix. Despite a sharp second-half slowdown, last year’s nationwide $187 billion transaction volume was the second-highest annual total ever.
Multifamily Housing | Feb 21, 2023
New multifamily housing and mixed-use buildings in Portland, Ore., must be ready for electric vehicle charging
The Portland, Ore., City Council recently voted unanimously to require all new residential and mixed-use buildings to be ready for electric vehicle charging. The move amends Portland’s zoning laws to require all new multi-dwelling and mixed-use development of five or more units with onsite parking to provide electric vehicle charging infrastructure.
Steel Buildings | Feb 21, 2023
AISC releases SpeedCore design guide for building concrete-filled composite steel plate shear wall core systems
The American Institute of Steel Construction has released Design Guide 38, SpeedCore Systems for Steel Structures. The document pertains to the nonproprietary concrete-filled composite steel plate shear wall core system that “shaved a whopping 10 months off the erection schedule of Seattle’s 58-story Rainier Square,” according to AISC.
Codes and Standards | Feb 21, 2023
Standards vs Guidelines: The benefits of establishing process
The unsung hero of standards may be the impact they can have on speed to market and price of product and project, according to IA Interior Architects.
K-12 Schools | Feb 18, 2023
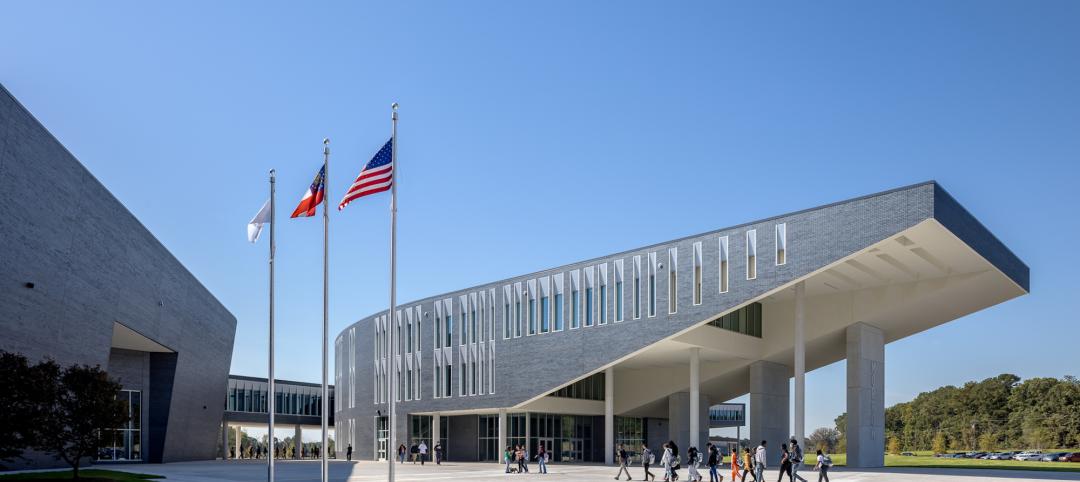
Atlanta suburb opens $85 million serpentine-shaped high school designed by Perkins&Will
In Ellenwood, Ga., a southeast suburb of Atlanta, Perkins and Will has partnered with Clayton County Public Schools and MEJA Construction to create a $85 million secondary school. Morrow High School, which opened in fall 2022, serves more than 2,200 students in Clayton County, a community with students from over 30 countries.
Museums | Feb 17, 2023
First Americans Museum uses design metaphors of natural elements to honor native worldview
First Americans Museum (FAM) in Oklahoma City honors the 39 tribes in Oklahoma today, reflecting their history through design metaphors of nature’s elements of earth, wind, water, and fire. The design concept includes multiple circles suggested by arcs, reflecting the native tradition of a circular worldview that encompasses the cycle of life, the seasons, and the rotation of the earth.
Senior Living Design | Feb 15, 2023
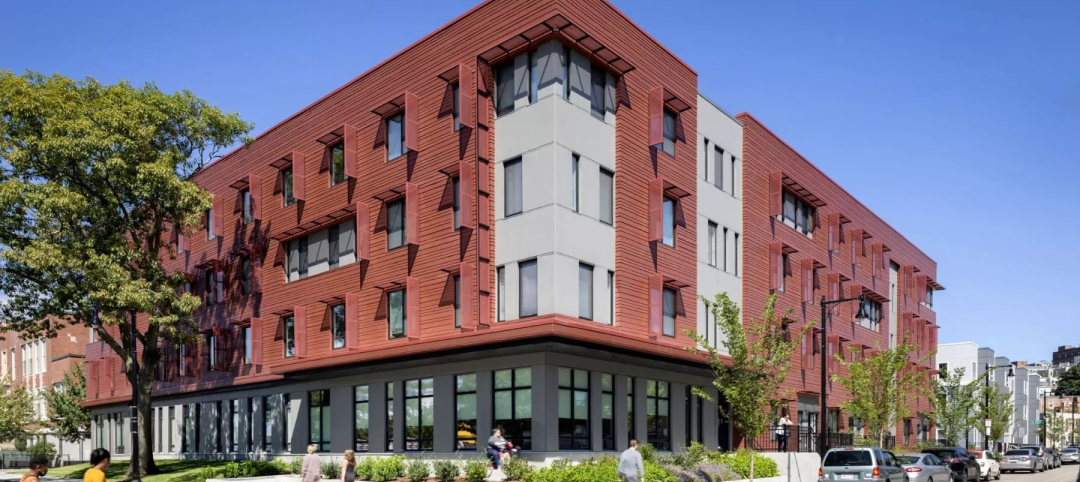
Passive House affordable senior housing project opens in Boston
Work on Phase Three C of The Anne M. Lynch Homes at Old Colony, a 55-apartment midrise building in Boston that stands out for its use of Passive House design principles, was recently completed. Designed by The Architectural Team (TAT), the four-story structure was informed throughout by Passive House principles and standards.
Designers | Feb 13, 2023
Hoffmann Architects + Engineers Establishes Diversity Advancement Scholarship Fund
Hoffmann Architects + Engineers, a design firm specializing in the rehabilitation of building exteriors, contributed $25,000 to fund the Hoffmann Diversity Advancement Scholarship, administered through the Connecticut Architecture Foundation. The fund provides scholarships for students from underrepresented racial or ethnic groups who are seeking degrees in architecture or engineering.
Office Buildings | Feb 12, 2023
Smyrna Ready Mix’s new office HQ mimics the patterns in the company’s onsite stone quarry
Designed by EOA Architects to showcase various concrete processes and applications, Smyrna Ready Mix's new office headquarters features vertical layering that mimics the patterns in the company’s stone quarry, located on the opposite end of the campus site. The building’s glass and concrete bands are meant to mirror the quarry’s natural contours and striations.
Multifamily Housing | Feb 10, 2023
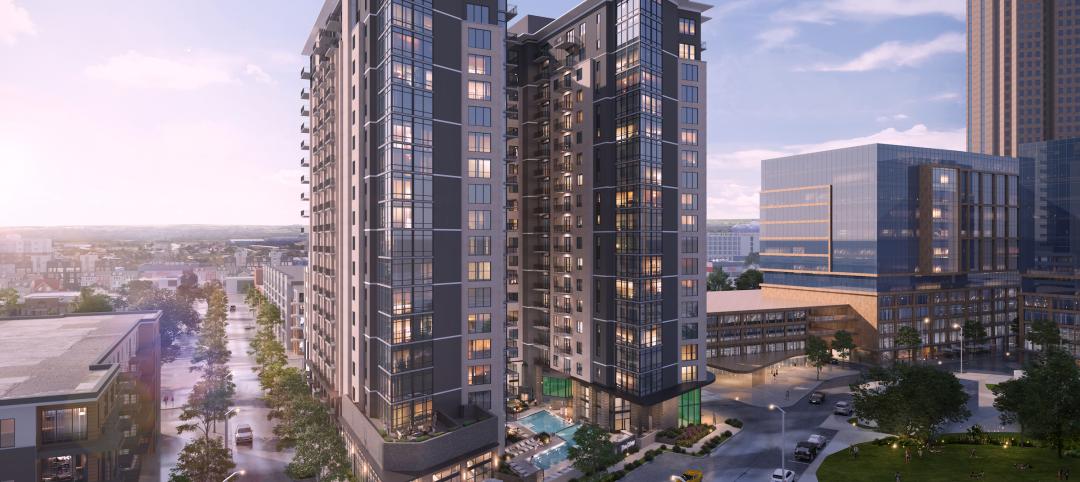
Dallas to get a 19-story, 351-unit residential high-rise
In Dallas, work has begun on a new multifamily high-rise called The Oliver. The 19-story, 351-unit apartment building will be located within The Central, a 27-acre mixed-use development near the Knox/Henderson neighborhood north of downtown Dallas.