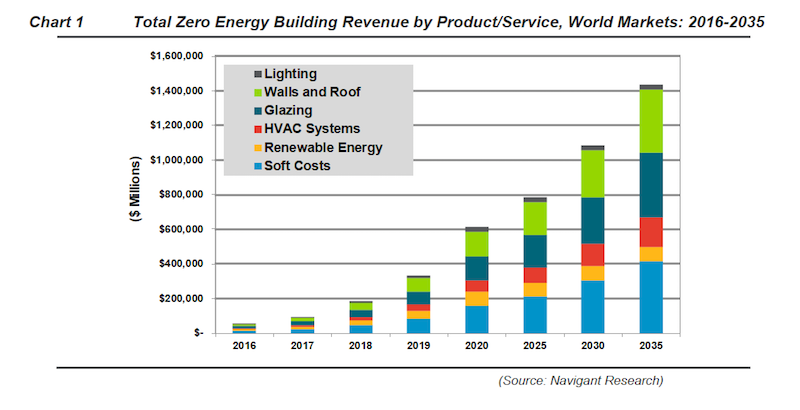
The global market for products and services related to achieving net zero energy in residential and commercial construction and renovation is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate of 44.5% between 2014 and 2035, and exceed $1.4 trillion in that last year, according to the latest estimates in a new 24-page report, titled Net Zero Energy Buildings, published by Navigant Research.
In North America alone, that market is projected to increase annually at a rate of 38.4% during that timeframe, reaching more than $127 billion in 2035.
Once confined mostly to single-family home and one-story office construction, net zero energy (ZNE) is penetrating a nonresidential sector that is placing greater emphasis on efficiency, renewable energy, and consumption. The Navigant report contends that the technology needed to achieve net zero energy is available for almost any building type.
Benjamin Freas, Navigant’s Principal Research Analyst in Washington, D.C., tells BD+C that the regulatory climate, both in North America and worldwide, is leaning in directions that favor ZNE construction practices. He points specifically to California’s Title 24, which went into effect on January 1 and sets minimum energy saving requirements for new buildings and renovations. By 2030, all new commercial construction in California must be ZNE, meaning that those buildings produce at least as much energy onsite as they consume.
Freas concedes that commercial ZNE so far is in the “pilot program phase” and is being being adopted “jurisdiction by jurisdiction, state by state.” But he’s convinced that the actions of “forward-thinking” states such as California, Massachusetts, and New York will ultimately result in regional and national code changes.
Freas also points to the Paris Climate agreement, which takes effect on November 4, 2017, as a possible turning point for ZNE construction. The pact, with 197 signatories, requires governments to present national plans to reduce emissions to limit global temperature rise to well below 3.6 degrees Fahrenheit. (While President-elect Donald Trump has threatened to pull the U.S. out of that accord, there is less certainty about what impact his administration will have on America’s push toward greater energy efficiency and reducing carbon emissions.)
Another factor in Navigant’s projections is the advocacy of groups like U.S. Green Building Council and the New Buildings Institute that are pressing developers and their AEC partners to entertain ZNE as an option in their design and construction plans.
Freas observes that ZNE is starting to seep into AEC continuing education programming. However, he admits that educating the industry about the benefits of ZNE remains “a challenge,” in part because the costs related to making buildings net zero energy are “currently not acceptable to most building owners.”
That being said, Navigant’s research paints a picture of a global market in which ZNE is inevitable and, eventually, ubiquitous.
Glazing, walls and roofs are the biggest potential ZNE areas. Navigant estimates that the value of ZNE products and services for wall and roof construction and renovation will expand to $366.3 billion in 2035, from a mere $134.1 million in 2014. ZNE-related glazing products and services will increase to $369.9 billion from $132.4 million over that same period.
Another big gainer could be ZNE HVAC products and services, which are expected to grow at an annualized rate of 45.8%, to $172.6 billion in 2035.
All told, the global ZNE products and services market is projected to hit $1.436 trillion in 2035, compared to only $629.3 million in 2014.
The North American ZNE market will reach $127.1 billion in 2035, nearly 1,000 times larger than the 137.4 million market at 2014. The walls and roofs sector is expected to increase at an annual rate of 39.6% to $32.3 billion; and ZNE products and services for glazing should increase annually by 39.8% to $32.9 billion.
Related Stories
| May 10, 2011
Solar installations on multifamily rooftops aid social change
The Los Angeles Business Council's study on the feasibility of installing solar panels on the city’s multifamily buildings shows there's tremendous rooftop capacity, and that a significant portion of that rooftop capacity comes from buildings in economically depressed neighborhoods. Solar installations could therefore be used to create jobs, lower utility costs, and improve conditions for residents in these neighborhood.
| May 3, 2011
North Carolina State University partners with Schneider Electric, targets energy efficiency
Schneider Electric is partnering with North Carolina State University on energy efficiency projects for 1.6 million square feet of building space across 13 campus facilities. As part of the $20 million project, the university will implement 89 separate energy conservation measures that will save the school approximately 10,137,668 kilowatt hours of electricity and 68,785 decatherms of natural gas annually.
| Apr 19, 2011
America’s energy use, in one handy chart
The Grist takes a look at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory's famed energy flow charts and tells us what we’re wasting and what we’re doing well. Turns out, commercial buildings account for the smallest amounts of energy use.
| Apr 11, 2011
Wind turbines to generate power for new UNT football stadium
The University of North Texas has received a $2 million grant from the State Energy Conservation Office to install three wind turbines that will feed the electrical grid and provide power to UNT’s new football stadium.
| Mar 17, 2011
Carbon footprint of public sector buildings in England and Wales to be released
The energy usage of 40,146 public buildings—including schools, hospitals, and offices—in England and Wales is being released to the public.
| Mar 8, 2011
Building, energy performance rating site launched
The Institute for Market Transformation and the Natural Resources Defense Council announced the launch of BuildingRating.org, the world’s first comprehensive resource on energy performance rating and disclosure policies for commercial buildings and homes.
| Mar 2, 2011
New ASHRAE standard may be too broad for the Canadian market
New Standard 189.1 from the American Society of Heating, Refrigeration, and Air-conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE), which goes beyond energy efficiency to include provisions that affect construction, post-occupancy monitoring, and site control, may be too much for the Canadian market—at least for now.
| Mar 1, 2011
Honeywell to implement China’s first smart grid project for managing energy use in commercial buildings
Honeywell announced it was selected to develop and implement China’s first smart grid pilot project and feasibility study for managing energy use in commercial buildings, also known as demand-side management. The project is part of a grant agreement signed today between the U.S. Trade and Development Agency (USTDA) and State Grid Electric Power Research Institute (SGEPRI), sponsor of the project and a subsidiary of State Grid Corp. of China.