The U.S. General Services Administration (GSA), and the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) will invest $30 million from the Inflation Reduction Act to increase the sustainability of federal buildings by testing novel technologies.
The vehicle for that effort, the Green Proving Ground (GPG) program, will invest in American-made technologies to help increase federal electric vehicle supply equipment, protect air quality, reduce climate pollution, and enhance building performance. This year the GPG program has selected 20 emerging and sustainable technologies for real-world evaluation in GSA’s real-estate portfolio.
The number of technologies tested this year increased four-fold increase over previous years with added funding from the Inflation Reduction Act.
This year’s GPG program focuses on seven technology areas:
- Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment: Turnkey electric vehicle charging infrastructure from Loop Global, optimized charging through charge management software from bp pulse, a battery-buffered DC fast charger from ADS-TEC Energy, and vehicle grid integration (VGI) technology from General Motors LLC.
- Germicidal Ultraviolet technologies: Next-generation LEDs and Far-UVC light to disinfect air without increasing ventilation. The GPG program will evaluate technologies that support healthier buildings while reducing energy use from Far UV Technologies, R-Zero, and PURO (subsidiary of Applied UV Inc.) with the Academy Energy Group.
- Greenhouse Gas Accounting: Technologies essential to achieving 24/7 carbon-free electricity and net zero operational emissions. Cambio AI and nZero will aim to go beyond annual greenhouse gas reporting to operationally focused carbon management, including near-real-time 24/7 carbon-free electricity insights and impacts.
- Grid-Interactive Efficient Buildings: Delivering cost savings by leveraging technologies and strategies that provide continuous demand management and load flexibility. The energy management platform from COI Energy aims to optimize energy use through machine learning.
- High-Performance technologies: Helping reduce operational and embodied carbon emissions by evaluating automated aerosol-based duct sealing from Aeroseal; an Internet-of-Things (IoT) lighting system from Signify North America Corporation; and bio-engineered, low-embodied-carbon concrete from Biomason. DOE will seek commercial partners to validate Toggled, a plug load control solution, and a thermostatic radiator cover and hybrid electrification solution from Kelvin.
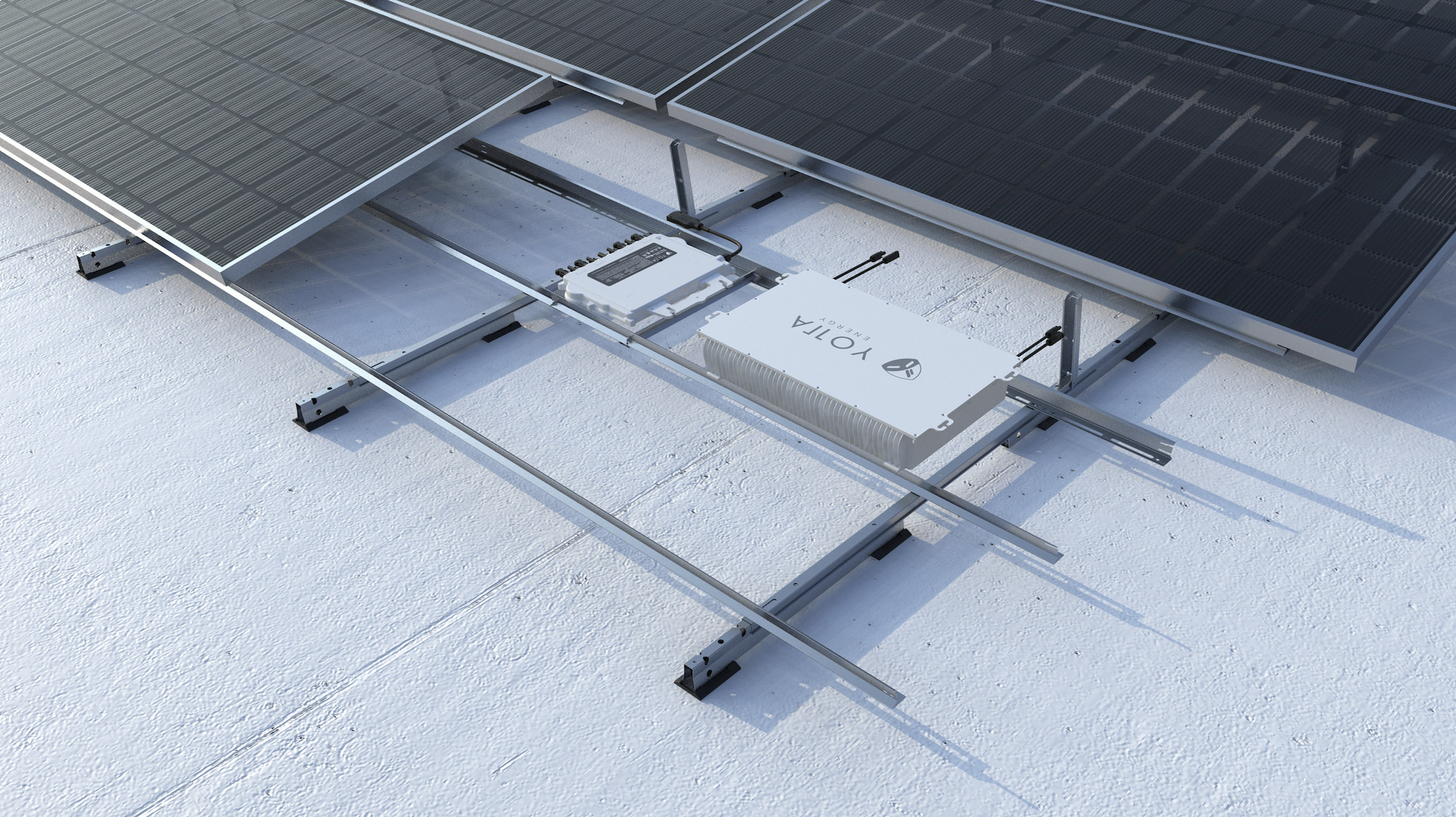
- Onsite Renewables: Technology essential to meeting the Administration’s net zero operational emission goals. The GPG program will evaluate an energy storage technology from Yotta Energy that is the size of a large laptop and installed in place of ballast beneath a rooftop photovoltaic system. The program will also pilot a wind turbine from Accelerate Wind that can be installed at the edge of the building roof and complement rooftop solar.
- Window Retrofit technologies: Help improve the performance of a building’s exterior envelope by evaluating three technologies: vacuum-insulated glazing from Pilkington; R14 interior window retrofit system from Vitro Architectural Glass; and, a secondary window framing system from Indow.
Some of these technologies will be tested at GSA’s Applied Innovation Learning Labs to identify replicable combinations of technologies that deliver net-zero operational emissions.
Related Stories
Green | Apr 20, 2015
USGBC opens public comment period for LEED for existing multifamily buildings
The new LEED Operations and Maintenance: Multifamily program will offer solutions for existing multifamily projects with at least 20 units.
Cultural Facilities | Apr 16, 2015
Milwaukee’s Lakeshore State Park visitor center will be ‘off the grid’
The plans also include a built-in wastewater treatment system and rainwater collection.
Green | Apr 16, 2015
Passive House Institute introduces new categories for building certification
The new evaluation procedure considers the building in an environment where only renewable energy is used. Sun and wind provide the primary electricity.
Green | Apr 16, 2015
New version of Building Energy Data Exchange Specification launched
BEDES is a dictionary that facilitates consistent exchange of building characteristics and energy use data between tools and databases in the building energy efficiency sector.
Green | Apr 14, 2015
USGBC will recognize energy and water standards for the Living Building Challenge
This move means that projects achieving the energy and water requirements in Living Building Challenge will be considered as technically equivalent to LEED.
Green | Apr 7, 2015
USGBC survey shows Fortune 200 companies prioritize green building
The world’s top-performing companies are prioritizing sustainability as part of their corporate social responsibility efforts, and a majority of them are using LEED to achieve their goals, according to the new survey.
Codes and Standards | Apr 6, 2015
DOE releases Better Buildings Workforce Guidelines
The guidelines are aimed at strengthening and streamlining commercial building workforce training and certification programs for workers in energy auditing, building commissioning, building operations, and energy management.
Green | Apr 3, 2015
Georgia may ban use of LEED on state buildings
Georgia's state legislature is considering a measure to require all state buildings to only use green building standards that permit the use of Georgia's lumber.
Green | Apr 3, 2015
Energy benchmarking law helps make D.C. top ranked Energy Star city
First-in-the-nation law requires public reporting of annual energy performance
Green | Apr 1, 2015
Global wind power installations expected to slow through 2019
After a 20% falloff in 2013, the global wind power industry made a strong comeback in 2014, with a record 51.2 gigawatts installed. But a new report from Navigant Research forecasts a curtailment in growth.