After a 20% falloff in 2013, the global wind power industry made a strong comeback in 2014, with a record 51.2 gigawatts (GW) installed, representing a 42% increase over the previous year, according to the BTM Consult arm of Navigant Research in its latest World Wind Energy Market Update 2015.
China alone installed a record 23.2 GW of new wind power last year. All told, the global five-year average growth rate was 7.8%, and cumulative installed capacity rose to 373 GW by the end of last year
However, Navigant projects a curtailment in the growth of annual new installations through 2019. Over that forecast period, installations are expected to increase by only 0.3% per year, and that includes an 8.9% growth in 2015. A total of 245,547 megawatts of wind power will be added over the forecast period, increasing cumulative capacity by 13.2% per year.
China will continue to lead the world in installation activity for the foreseeable future. But Navigant doesn’t expect that country to add more than 17 GWs in any given year.
Navigant foresees a “substantial” drop in installations in Germany due to changes in incentive structures after 5.1 GW of wind power were installed last year, which was higher than anticipated.
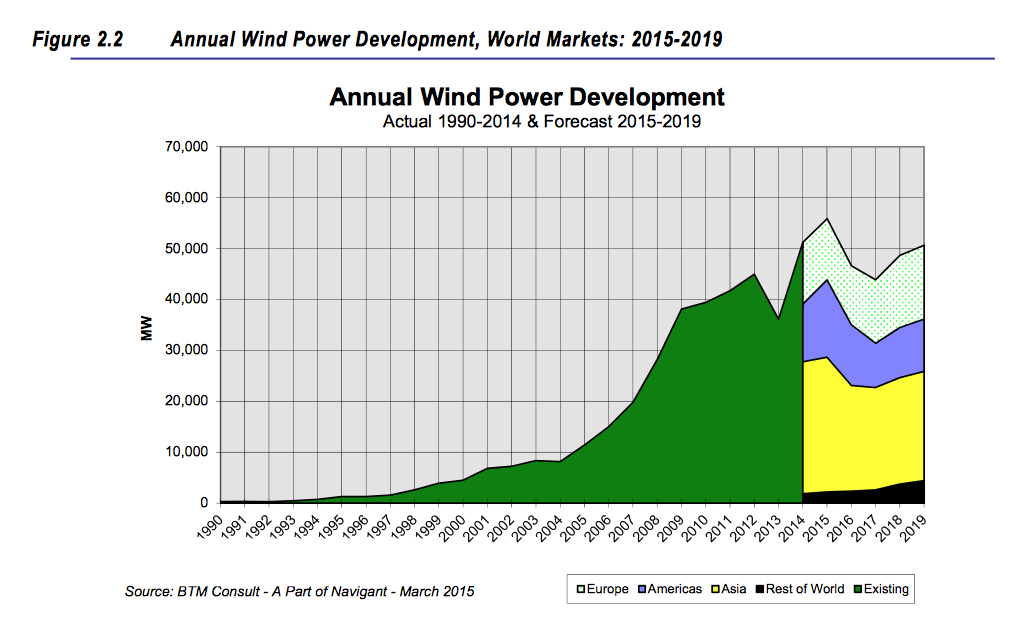 Chart from Navigant Research's wind power outlook
Chart from Navigant Research's wind power outlook
The U.S. wind power market has been recovering, thanks to the 2013 extension of the Production Tax Credit/Investment Tax Credit, as well as new safe-harbor guidance from the Internal Revenue Service about tax-credit eligibility. Navigant projects 14.8 GW will be installed in the U.S. in the years 2015 and 2016 combined.
In its 227-page report, Navigant notes that the average size of wind turbines increased only slightly in 2014, to 1,958 kilowatts (kW). The global market for direct-drive turbines grew 30% to 13,740 megawatts (MW), and represented 27% of all installations. In contrast, offshore wind grid connection and weather-related delays halved new offshore installations to 852 MWs in 2014.
Navigant notes that OEM sources are focusing more on product diversification, and are designed machines for maximum energy production in low wind speed areas, for operations in high altitudes or in cold climates, or for areas with blade-tip height restrictions. The evolution of larger rotor machines is leading to new blade designs, manufacturing processes, sourcing strategies, and supplier partnerships.
Interestingly, Navigant is seeing the hegemony of bigger players loosening a bit. Last year, the top 15 operator-owners controlled 29.3% of the market, or two percentage points lower than in 2013. “This exemplifies a trend of commercial acceptance in the utility marketplace. Demand for wind plants continues to move beyond the traditional owners that are historically comfortable with wind to new owners that are now convinced of the value wind plants bring to their portfolios,” Navigant reports.
Related Stories
| Nov 9, 2010
Turner Construction report: Green buildings still on the agenda
Green buildings continue to be on the agenda for real estate owners, developers, and corporate owner-occupants, according to the Turner 2010 Green Building Market Barometer. Key findings: Almost 90% of respondents said it was extremely or very likely they would incorporate energy-efficiency improvements in their new construction or renovation project, and 60% expected to incorporate improvements to water efficiency, indoor environmental quality, and green materials.
| Nov 2, 2010
11 Tips for Breathing New Life into Old Office Spaces
A slowdown in new construction has firms focusing on office reconstruction and interior renovations. Three experts from Hixson Architecture Engineering Interiors offer 11 tips for office renovation success. Tip #1: Check the landscaping.
| Nov 2, 2010
A Look Back at the Navy’s First LEED Gold
Building Design+Construction takes a retrospective tour of a pace-setting LEED project.
| Nov 2, 2010
Yudelson: ‘If It Doesn’t Perform, It Can’t Be Green’
Jerry Yudelson, prolific author and veteran green building expert, challenges Building Teams to think big when it comes to controlling energy use and reducing carbon emissions in buildings.
| Nov 1, 2010
Sustainable, mixed-income housing to revitalize community
The $41 million Arlington Grove mixed-use development in St. Louis is viewed as a major step in revitalizing the community. Developed by McCormack Baron Salazar with KAI Design & Build (architect, MEP, GC), the project will add 112 new and renovated mixed-income rental units (market rate, low-income, and public housing) totaling 162,000 sf, plus 5,000 sf of commercial/retail space.
| Nov 1, 2010
Vancouver’s former Olympic Village shoots for Gold
The first tenants of the Millennium Water development in Vancouver, B.C., were Olympic athletes competing in the 2010 Winter Games. Now the former Olympic Village, located on a 17-acre brownfield site, is being transformed into a residential neighborhood targeting LEED ND Gold. The buildings are expected to consume 30-70% less energy than comparable structures.
| Oct 21, 2010
GSA confirms new LEED Gold requirement
The General Services Administration has increased its sustainability requirements and now mandates LEED Gold for its projects.
| Oct 13, 2010
Editorial
The AEC industry shares a widespread obsession with the new. New is fresh. New is youthful. New is cool. But “old” or “slightly used” can be financially profitable and professionally rewarding, too.
| Oct 12, 2010
University of Toledo, Memorial Field House
27th Annual Reconstruction Awards—Silver Award. Memorial Field House, once the lovely Collegiate Gothic (ca. 1933) centerpiece (along with neighboring University Hall) of the University of Toledo campus, took its share of abuse after a new athletic arena made it redundant, in 1976. The ultimate insult occurred when the ROTC used it as a paintball venue.
| Oct 12, 2010
Cell and Genome Sciences Building, Farmington, Conn.
27th Annual Reconstruction Awards—Silver Award. Administrators at the University of Connecticut Health Center in Farmington didn’t think much of the 1970s building they planned to turn into the school’s Cell and Genome Sciences Building. It’s not that the former toxicology research facility was in such terrible shape, but the 117,800-sf structure had almost no windows and its interior was dark and chopped up.















