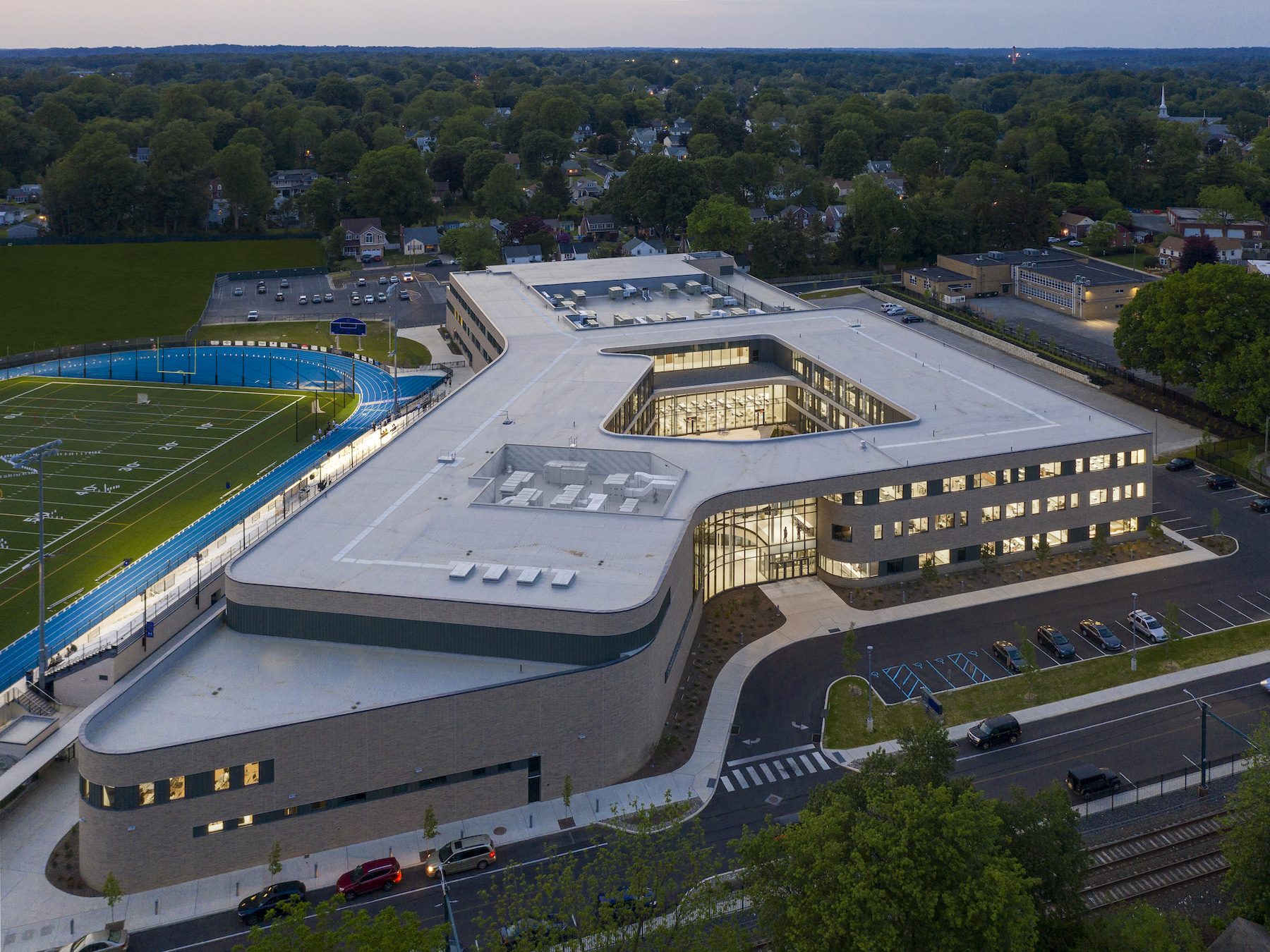
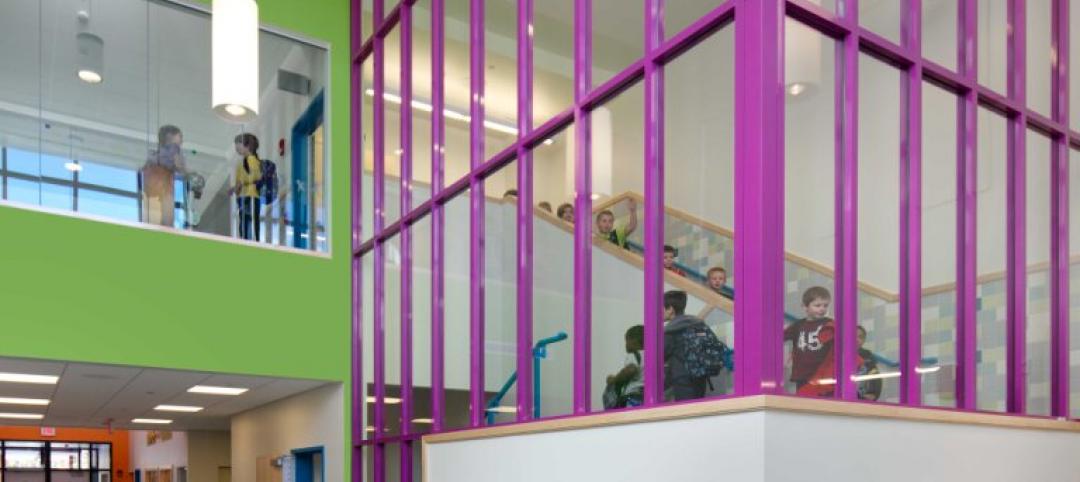
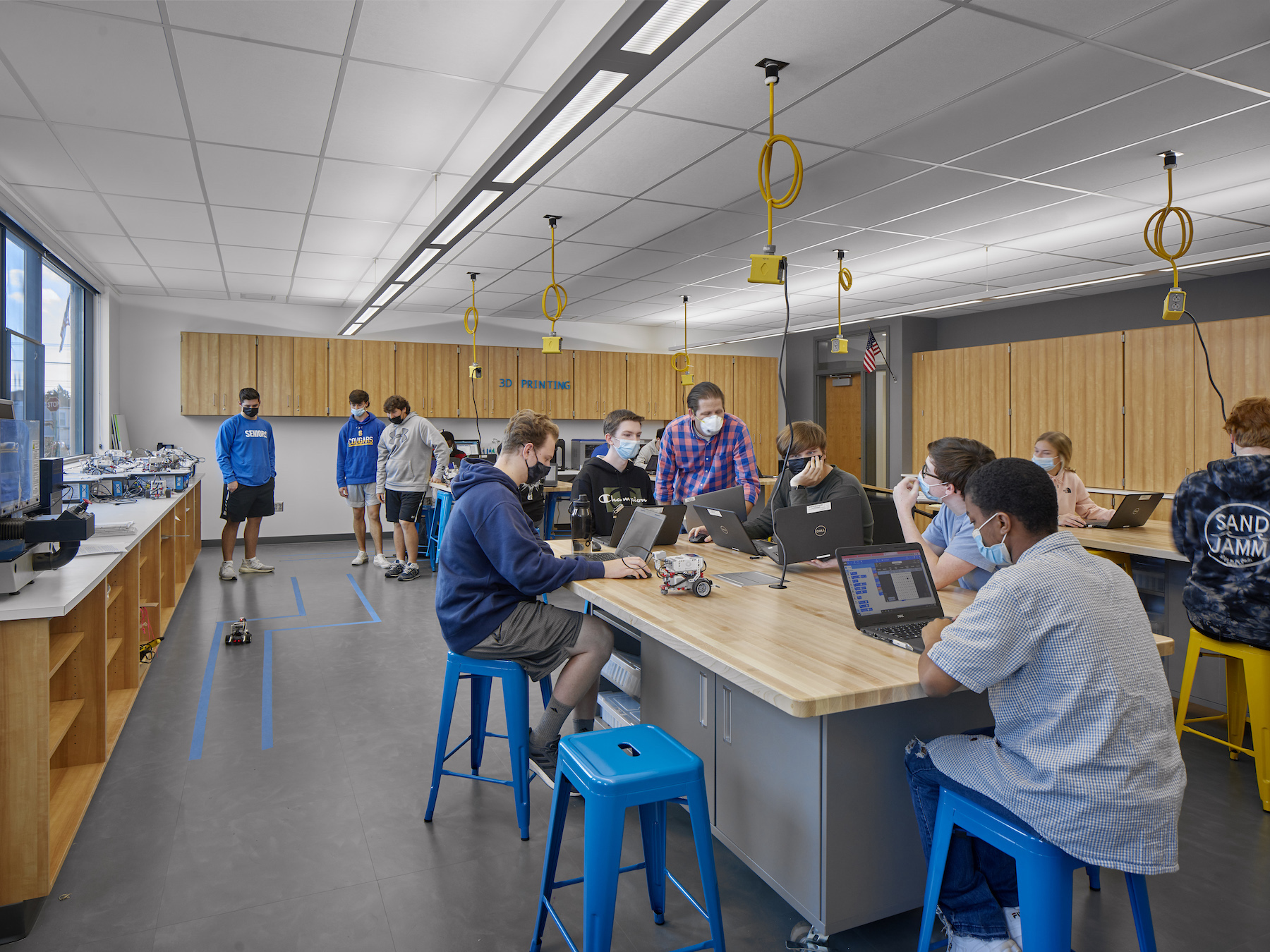
Springfield High School, in the suburbs of Philadelphia, dated back to 1953, was well passed its expiration date. To replace that aging building, Springfield’s school board called upon architect Perkins & Will to design a new, 230,000-sf facility that is separated into three zones—academic, physical education, and visual and performing arts—within somewhat smaller footprint.
Construction of this three-story project—which sits on a former baseball field and had been in the works since 2009—began in 2018, at an estimated cost of $130 million, and opened for 1,500 students in 2021. The project’s Building Team included E.R. Stuebner (GC), Boro Construction (ME and EE), and Stan-Roch Plumbing (PE).
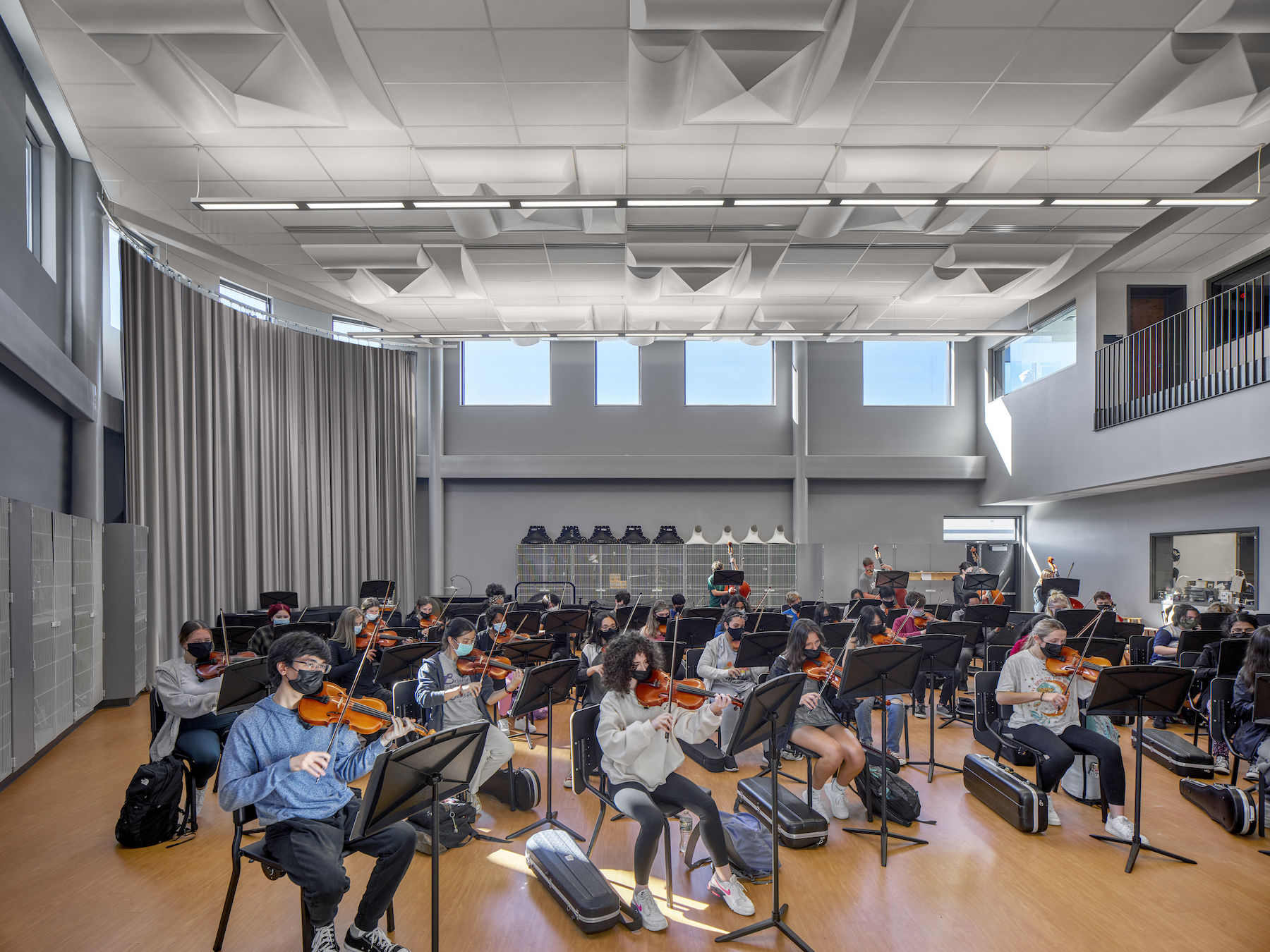
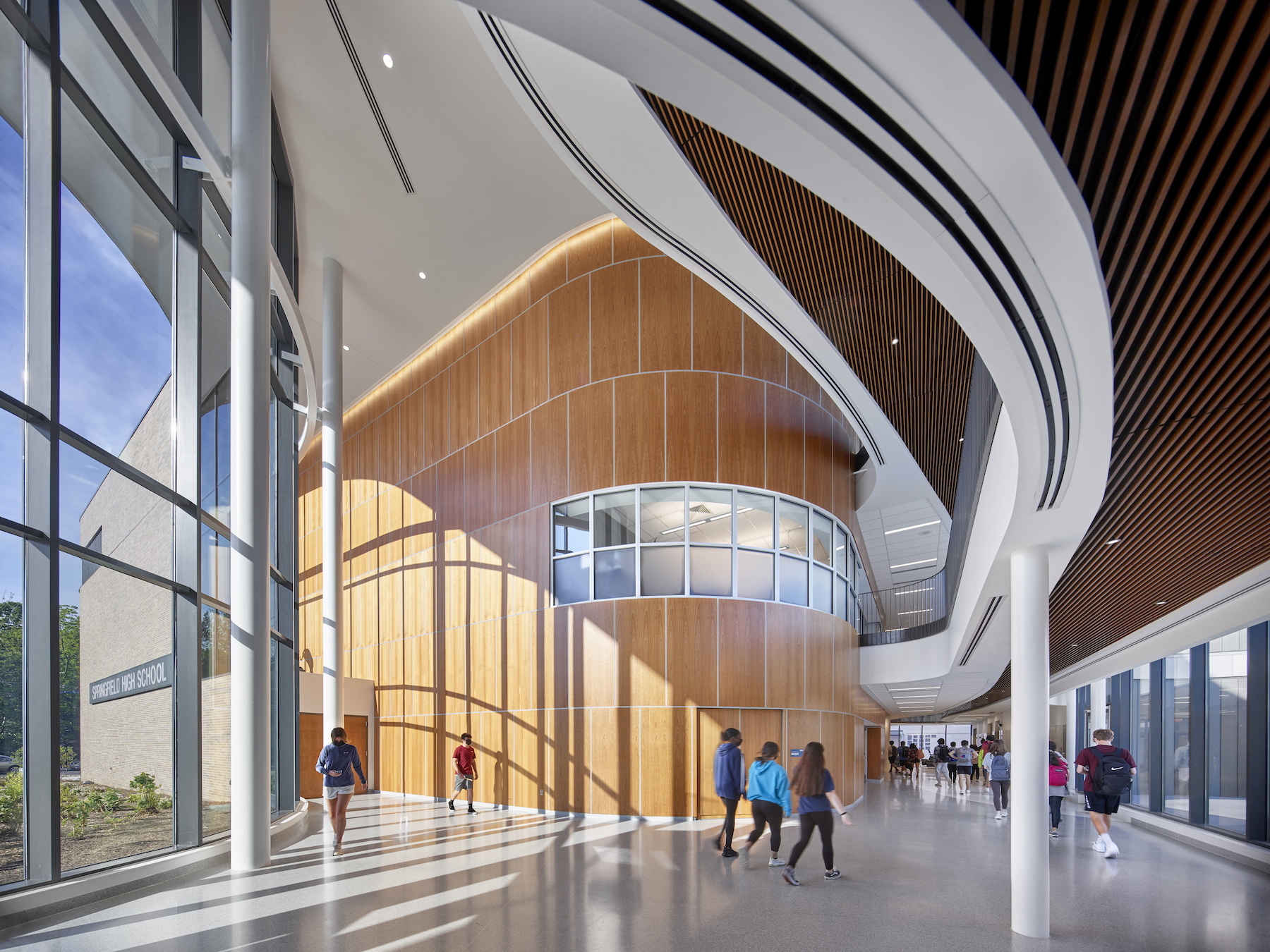
The exterior design of the new school is distinguished by an outer shell of curving beige brick and glass. Daylight fills the school’s wood-paneled hallways and ceilings, as well as its open learning commons that are placed strategically throughout the academic zone to allow for informal student interactions.
The school highlights a popular recent design trend by allowing its library to “spill” into its cafeteria, thereby creating another informal learning area. (The cafeteria and auditorium can be used for public events, too.
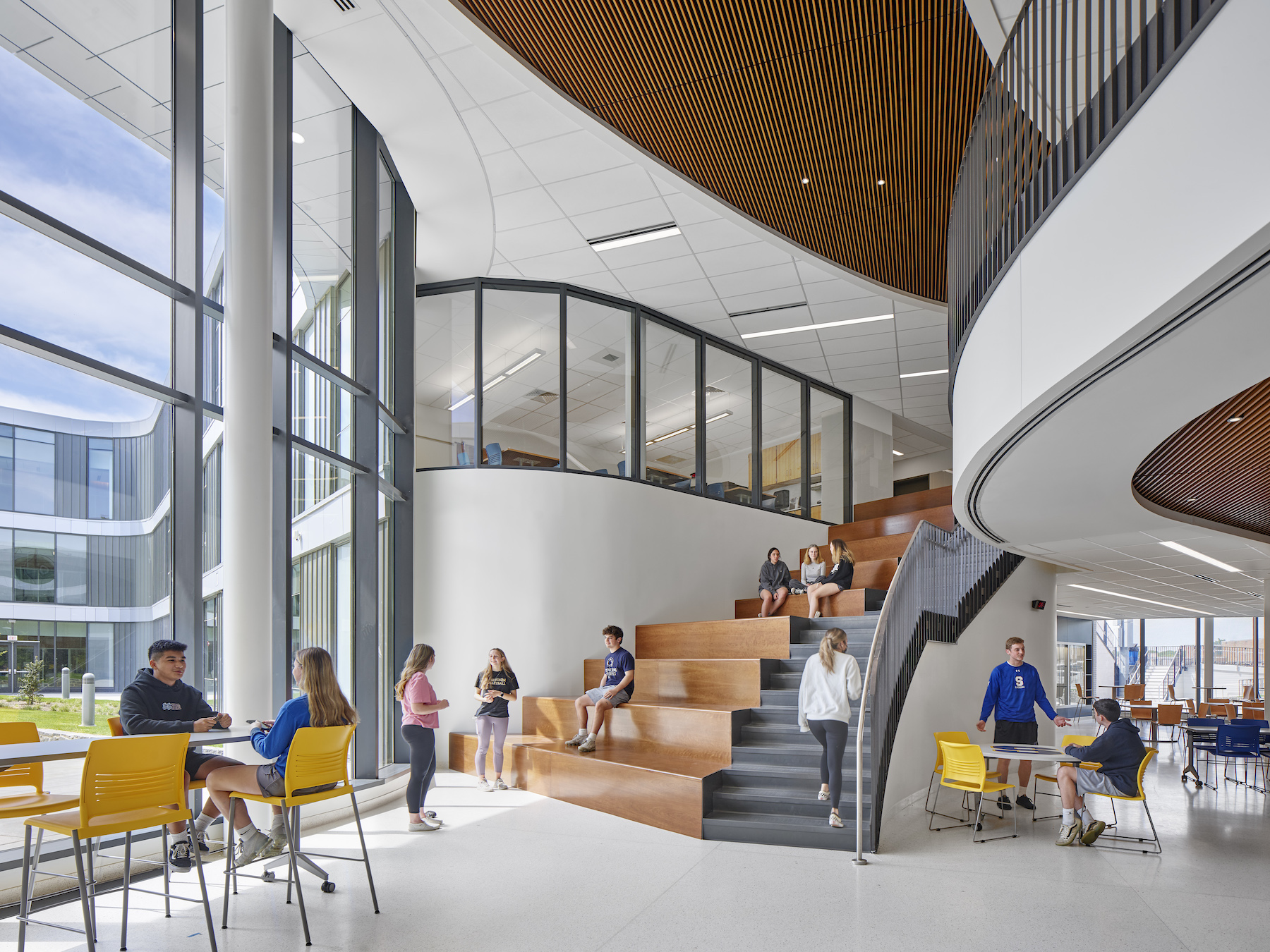

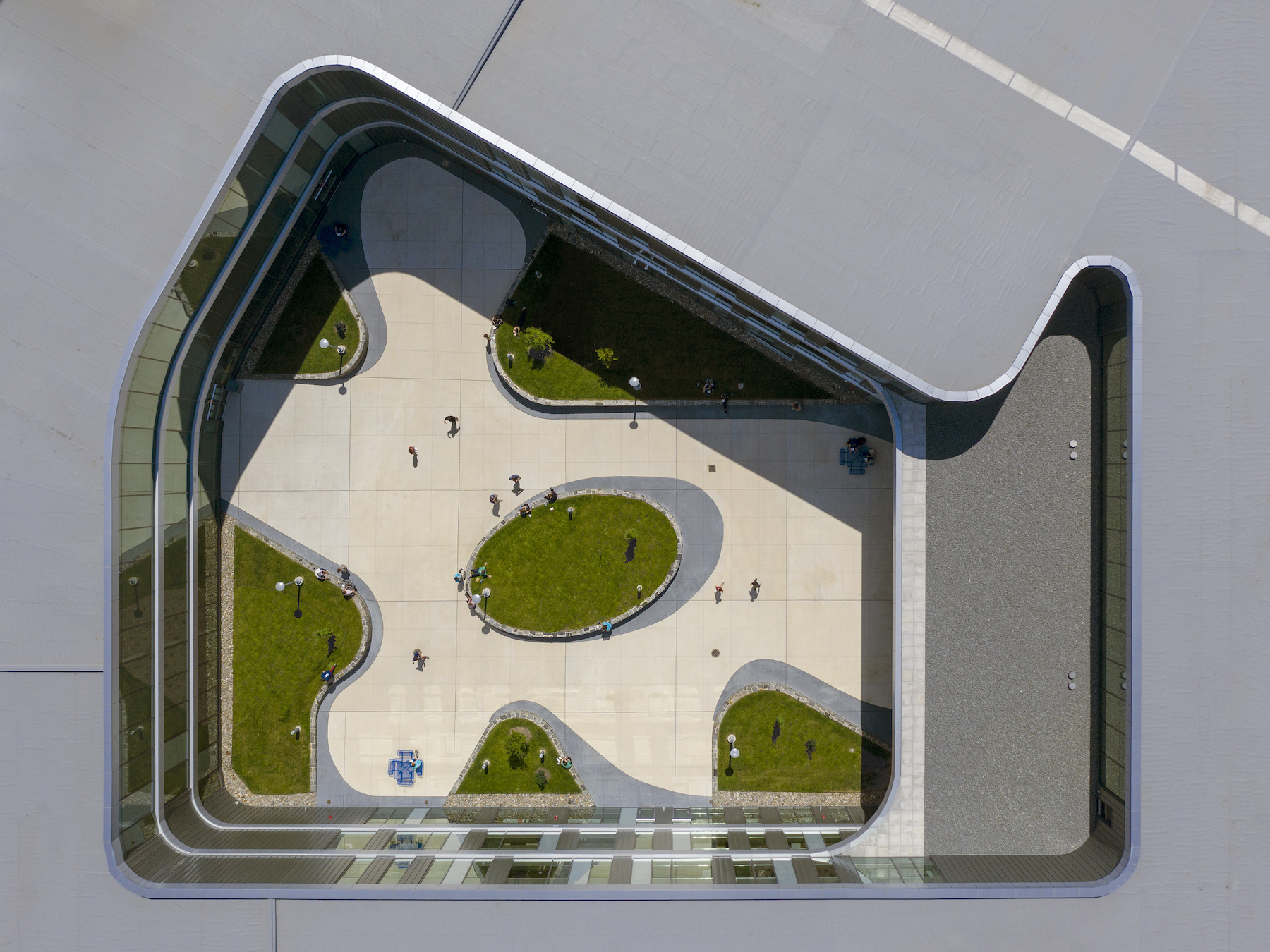
Common spaces open directly onto the large courtyard, whose inner periphery is made up of glass and metal panels that separate it from the outer space. This flexibility accommodates a range of activities, and connects the facility to the surrounding community.
MULTIFUNCTIONAL SPACES
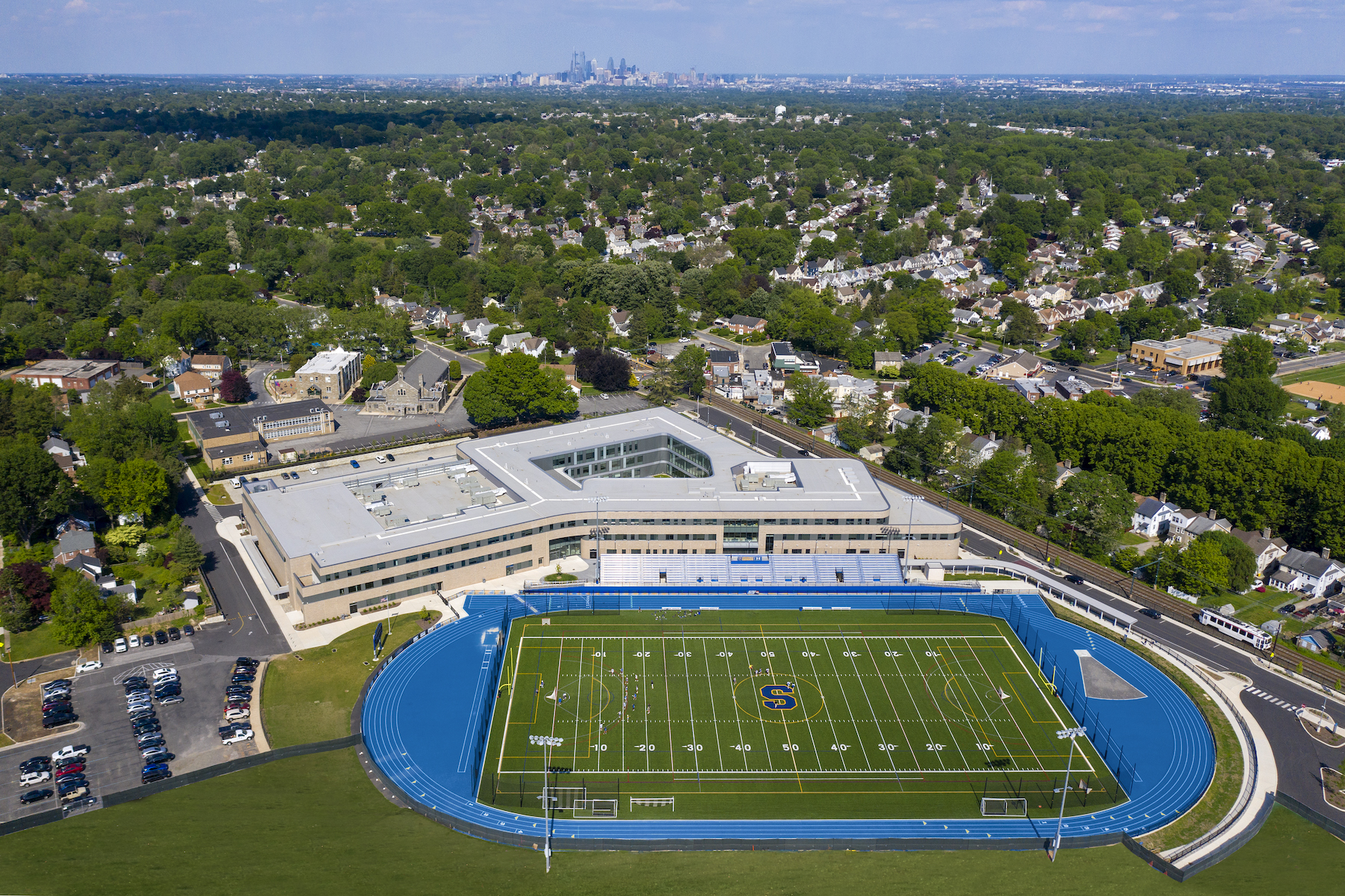

Because of its smaller footprint, the school’s most heavily used spaces—such as its lobby, cafeteria, and courtyard—are set up for greater efficiency. For example, the cafeteria can serve as “pre-function” space for the gym and for community space during evening hours. The school’s gyms open to each other, and therefore can handle overflow seating during events.
The smaller building is also more energy efficient, and allows for easier sharing of amenities. And by focusing density closer to the town’s urban core, the school’s playfields are positioned as virtual extensions of nearby Whiskey Run Creek and Spring Valley Park.


The new school is within walking distance of the town, and adjacent to public transportation. Indeed, the school is organized to provide access to the public: the auditorium, for example, is located off the main entrance so it can be used by the community for non-school events. Practice fields are open to the public. And in phase two of this redevelopment, the site of the old school will become a green space in the heart of the town’s residential area.


Related Stories
| Oct 26, 2014
Study asks: Do green schools improve student performance?
A study by DLR Group and Colorado State University attempts to quantify the student performance benefits of green schools.
| Oct 21, 2014
Check out BD+C's GreenZone Environment Education Classroom debuting this week at Greenbuild
At the conclusion of the show, the modular classroom structure will be moved to a permanent location in New Orleans' Lower 9th Ward, where it will serve as a community center and K-12 classroom.
| Oct 16, 2014
Perkins+Will white paper examines alternatives to flame retardant building materials
The white paper includes a list of 193 flame retardants, including 29 discovered in building and household products, 50 found in the indoor environment, and 33 in human blood, milk, and tissues.
Sponsored | | Oct 16, 2014
Mill Brook Elementary School colors outside the lines with creative fire-rated framing solution
Among the building elements contributing to the success of the elementary school’s public learning areas is a fire-rated stairwell that supports the school’s vision for collaboration. HMFH Architects designed the stairwell to be bright and open, reflecting the playful energy of students. SPONSORED CONTENT
| Oct 15, 2014
Harvard launches ‘design-centric’ center for green buildings and cities
The impetus behind Harvard's Center for Green Buildings and Cities is what the design school’s dean, Mohsen Mostafavi, describes as a “rapidly urbanizing global economy,” in which cities are building new structures “on a massive scale.”
| Oct 12, 2014
AIA 2030 commitment: Five years on, are we any closer to net-zero?
This year marks the fifth anniversary of the American Institute of Architects’ effort to have architecture firms voluntarily pledge net-zero energy design for all their buildings by 2030.
| Oct 9, 2014
Regulations, demand will accelerate revenue from zero energy buildings, according to study
A new study by Navigant Research projects that public- and private-sector efforts to lower the carbon footprint of new and renovated commercial and residential structures will boost the annual revenue generated by commercial and residential zero energy buildings over the next 20 years by 122.5%, to $1.4 trillion.
| Sep 29, 2014
Living Building vs. LEED Platinum: Comparing the first costs and savings
Skanska USA's Steve Clem breaks down the costs and benefits of various ultra-green building standards and practices.
| Sep 24, 2014
Architecture billings see continued strength, led by institutional sector
On the heels of recording its strongest pace of growth since 2007, there continues to be an increasing level of demand for design services signaled in the latest Architecture Billings Index.
| Sep 22, 2014
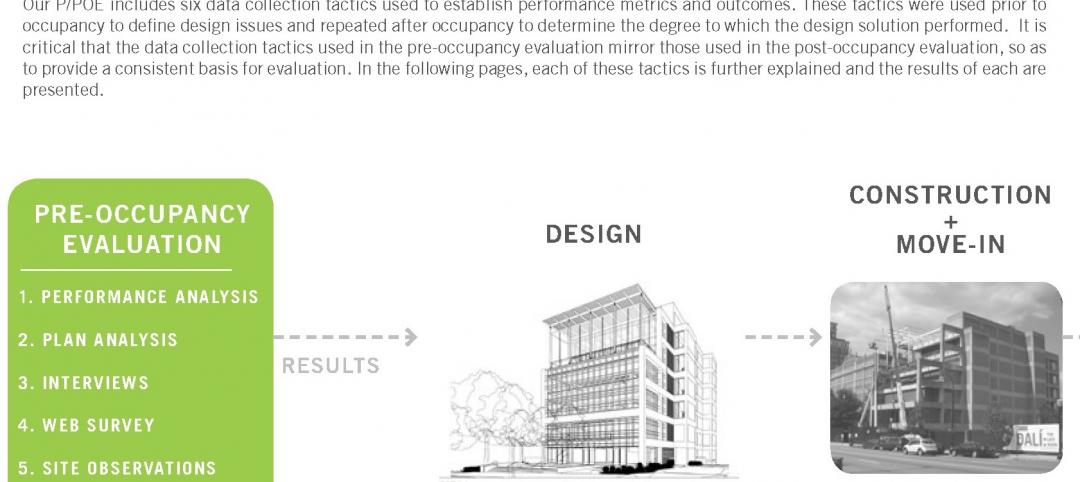
4 keys to effective post-occupancy evaluations
Perkins+Will's Janice Barnes covers the four steps that designers should take to create POEs that provide design direction and measure design effectiveness.