|
14. Mod Pod A Nod to Flex Biz
Designed by the British firm Tate + Hindle, the OfficePOD is a flexible office space that can be installed, well, just about anywhere, indoors or out. The self-contained modular units measure about seven feet square and are designed to serve as dedicated space for employees who work from home or other remote locations. Construction of the modular pods includes natural, recycled, and recyclable materials, as well as insulation and a high-efficiency HVAC system. The pods are plug-in powered; the fully wired units connect to an existing structure (home, garage, office building, um...Starbucks?) while IT and phone connectivity is wireless, but can also be cabled in. Delivery takes approximately 12 weeks. |
15. Transform any Work Surface into A Charging Station
 |
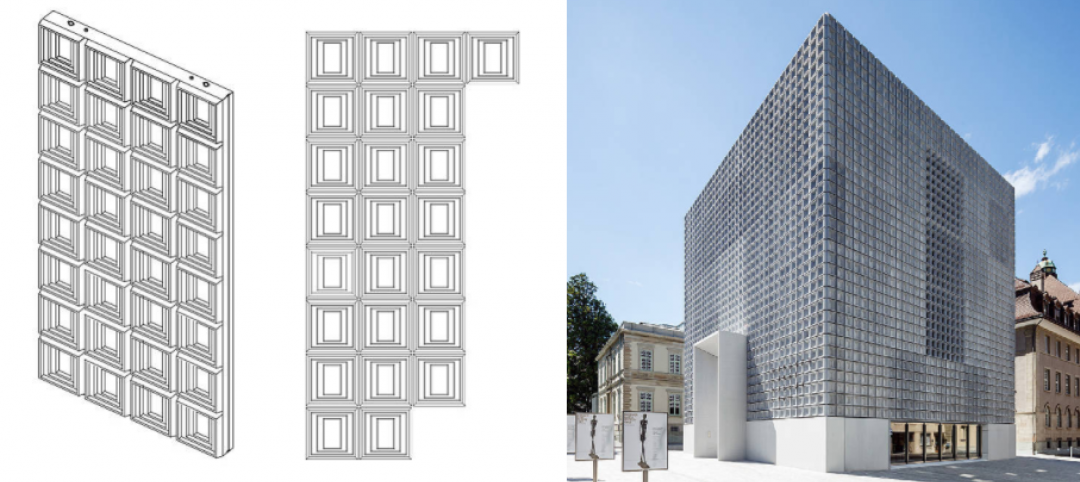
16. Concrete Slabs Plays up Rubber Ball Technology
17. Brown Rice for Greener Concrete
While slag from steel mills, fly ash, and silica fume are being added to concrete to reduce the material's greenhouse gas emissions and make it stronger and more resistant to corrosion, rice husks (the small cases around edible rice kernels) have so far proved an unsuitable additive because when burned, its ash is too contaminated with carbon. However, scientists were focused on finding ways to utilize rice husks because they are very rich in silicon dioxide, a core concrete ingredient. A breakthrough has come from researchers at Plano, Texas-based ChK Group, who discovered that superheating the husks to almost 1500 °F in an oxygen-free furnace produces pure, nearly carbon-free silica. ChK researchers, who are still refining their production processes, speculate a single full-size furnace could produce 15,000 tons of rice husk ash annually, which can be used to replace up to 20% of cement used in concrete production. |
18. Killer Beetles Lead to Concrete Plywood
The mountain pine beetle is devastating British Columbia's conifer forests, and while some researchers focused on controlling the destruction, others focused on salvaging the billions of dead trees. The University of Northern British Columbia's professor Ron Thring and graduate student Sorin Pasca focused on salvaging efforts and discovered that dead wood from lodgepole pine trees is an excellent ingredient for cement production. While cement typically repels organic material, the beetles "enhanced" the wood in such a way that it sticks to cement and act as a substitute for typical aggregates like stones and rocks. Researchers say the concrete plywood hybrid board (above), which they call MPB (for mountain pine beetle), is water resistant and can be used in place of drywall and gypsum board or as flooring and countertop surfacing. Boards can be cut with regular woodworking tools and nailed without pre-drilling.
Related Stories
Concrete | Aug 11, 2010
8 Innovations That Will Rock Your Next Concrete Project
If you think you've seen it all when it comes to concrete construction, then you haven't sat down with Blaine Brownell. The architect-turned-blogger-turned-author has become the industry's foremost expert in everything that is unconventional and provocative in the building products field. For the past eight years, this LEED Accredited Professional, BD+C “40 Under 40” winner, and vis...
| Aug 11, 2010
Let There Be Daylight
The new public library in Champaign, Ill., is drawing 2,100 patrons a day, up from 1,600 in 2007. The 122,600-sf facility, which opened in January 2008, certainly benefits from amenities that the old 40,000-sf library didn't have—electronic check-in and check-out, new computers, an onsite coffeehouse.
| Aug 11, 2010
BIM school, green school: California's newest high-performance school
Nestled deep in the Napa Valley, the city of American Canyon is one of a number of new communities in Northern California that have experienced tremendous growth in the last five years. Located 42 miles northeast of San Francisco, American Canyon had a population of just over 9,000 in 2000; by 2008, that figure stood at 15,276, with 28% of the population under age 18.
| Aug 11, 2010
Platinum Award: The Handmade Building
When Milwaukee's City Hall was completed in 1896, it was, at 394 feet in height, the third-tallest structure in the United States. Designed by Henry C. Koch, it was a statement of civic pride and a monument to Milwaukee's German heritage. It was placed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1973 and designated a National Historic Landmark in 2005.
| Aug 11, 2010
Special Recognition: Kingswood School Bloomfield Hills, Mich.
Kingswood School is perhaps the best example of Eliel Saarinen's work in North America. Designed in 1930 by the Finnish-born architect, the building was inspired by Frank Lloyd Wright's Prairie Style, with wide overhanging hipped roofs, long horizontal bands of windows, decorative leaded glass doors, and asymmetrical massing of elements.
| Aug 11, 2010
The pride of Pasadena
As a shining symbol of civic pride in Los Angeles County, Pasadena City Hall stood as the stately centerpiece of Pasadena's Civic Center since 1927. To the casual observer, the rectangular edifice, designed by San Francisco Classicists John Bakewell, Jr., and Arthur Brown, Jr., appeared to be aging gracefully.
| Aug 11, 2010
Great Solutions: Technology
19. Hybrid Geothermal Technology The team at Stantec saved $800,000 in construction costs by embedding geothermal piping into the structural piles at the WestJet office complex in Calgary, Alb., rather than drilling boreholes adjacent to the building site, which is the standard approach. Regular geothermal installation would have required about 200 boreholes, each about four-inches in diameter ...