Two leading consulting firms that focus on data centers and other mission-critical facilities have released a white paper on data center sustainability, the first in a series of reports that will provide technical analysis for data center operators to help lower their centers’ carbon footprints in line with regulations targeting carbon neutrality by 2030.
The authors of the white paper—which earlier this year formed a Greenhouse Gas Abatement Group—are i3 Solutions Group, a globally recognized data center MEP consulting engineering firm; and New York-based EYP Mission Critical Facilities, which performs MEP design and commissioning, operational procedures. multi-cloud and data center strategy, due diligence and site evaluation.
To download the first white paper and sign-up to receive alerts for future publications, click here.
CARBON NEUTRALITY AND REVENUE GENERATION AREN’T MUTUALLY EXCLUSIVE
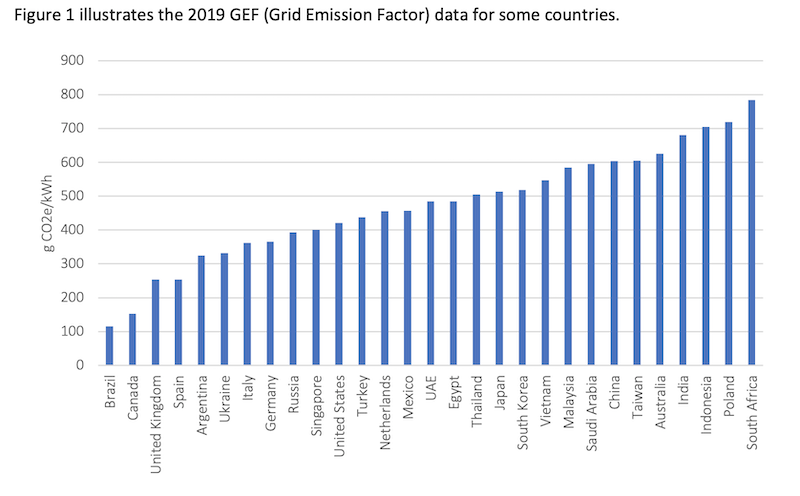
Greenhouse gas emissions from data centers vary widely by country. Chart: Greenhouse Gas Abatement Group
By almost every measure, data center demand is growing steadily and rapidly. Apex Market Research, for one, estimates that construction spending will increase by 7.7% annually and reach nearly $32 billion by 2025. To a greater extent than ever, operators are seeking ways to mitigate their facilities’ environmental effects, either voluntarily or in response to government mandates.
Titled “Infrastructure Sustainability Options and Revenue Opportunities for Data Centers,” the first white paper covers how targets for reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and increasing revenue-generating opportunities are not mutually exclusive objectives. “The falling costs of low-carbon distributed energy systems provide data center operators with opportunities to satisfy the requirements of hyperscale end-users with ambitions for a Zero Carbon Solution,” the white paper states.
Indeed, the energy sector has been moving in this direction for a while. Figures released in February by the International Energy Agency (IEA) reveal that global emissions from the electricity sector dropped by 450 million tons last year. This decline resulted partly from lower electricity demand but also from increases in electricity generation by solar PV and wind.
However, IEA also estimates that emissions in China increased last year by 0.8%. And while emissions in the U.S. fell by 10%, they started to bounce back in the later stages of 2020.
The white paper provides in-depth technical insight into areas where operators might reduce their facilities’ environmental impacts and monetize the process to boot. These areas include Demand Side Response, Data Center Power Generation, Energy Storage and Sustainable Energy Trading, as well as System Selection criteria such as Sustainability Performance Indices.
The white paper cautions there are no quick fixes to this problem of greenhouse gas emissions. For example, it postulates that when a company buys renewable energy from a private utility as a way of reducing its carbon footprint, it actually doesn’t improve its sustainability unless that purchase is coupled with a higher ratio of additional renewable energy and a reduction in the national grid emission factor (GEF).
NINE METRICS TO CONSIDER
Most data centers have excess energy capacities. Image: Greenhouse Gas Abatement Group
Other ways of reducing a data center’s carbon footprint might include energy trading that provides additional power to a grid from intermittent sources like wind energy. Data center operators might also benefit financially from exporting power to the grid from distributed generation systems, which in some scenarios also reduces the center’s GHGs.
“Practically all data centers have some excess capacity,” the white paper states. “Data center owners should consider whether it is possible to increase the utilization of standby and redundant generation and energy storage assets for DSR [demand-side response] or, indeed, configuring low-carbon generation assets to be the primary source of power to the data center.” The sources of this potentially exportable energy capacity are typically mechanical generators, and hot or cold fuel cells.
In terms of sustainability, the white paper asserts there are at least nine metrics to consider, including product carbon footprint, water use, volatile organic compounds, carbon payback, embodied energy, recycling, source material environmental impact, electrical and thermal system efficiency. The paper points out that location, and specific national- and state-related conditions, invariably affect the selection of an appropriate low-carbon technology, in part due to resource availability.
Subsequent white papers will touch on a range of topics that include:
- Assessment and application of gas reciprocating engines and turbines
- Assessment and application of fuel cells to data centers
- Demand response opportunities for data center embedded generation and storage systems
- GHG reduction with blended hydrogen and natural gas generation
Related Stories
Giants 400 | Oct 2, 2023
Top 60 Data Center Engineering Firms for 2023
Jacobs, Burns & McDonnell, WSP, EXP, and Alfa Tech head BD+C's ranking of the nation's largest data center sector engineering and engineering/architecture (EA) firms for 2023, as reported in Building Design+Construction's 2023 Giants 400 Report.
Giants 400 | Oct 2, 2023
Top 30 Data Center Architecture Firms for 2023
Corgan, HDR, Gensler, Page Southerland Page, and HED top BD+C's ranking of the nation's largest data center sector architecture and architecture/engineering (AE) firms for 2023, as reported in Building Design+Construction's 2023 Giants 400 Report.
Data Centers | Sep 21, 2023
North American data center construction rises 25% to record high in first half of 2023, driven by growth of artificial intelligence
CBRE’s latest North American Data Center Trends Report found there is 2,287.6 megawatts (MW) of data center supply currently under construction in primary markets, reaching a new all-time high with more than 70% already preleased.
Data Centers | Sep 15, 2023
Power constraints are restricting data center market growth
There is record global demand for new data centers, but availability of power is hampering market growth. That’s one of the key findings from a new CBRE report: Global Data Center Trends 2023.
Giants 400 | Aug 22, 2023
Top 115 Architecture Engineering Firms for 2023
Stantec, HDR, Page, HOK, and Arcadis North America top the rankings of the nation's largest architecture engineering (AE) firms for nonresidential building and multifamily housing work, as reported in Building Design+Construction's 2023 Giants 400 Report.
Giants 400 | Aug 22, 2023
2023 Giants 400 Report: Ranking the nation's largest architecture, engineering, and construction firms
A record 552 AEC firms submitted data for BD+C's 2023 Giants 400 Report. The final report includes 137 rankings across 25 building sectors and specialty categories.
Giants 400 | Aug 22, 2023
Top 175 Architecture Firms for 2023
Gensler, HKS, Perkins&Will, Corgan, and Perkins Eastman top the rankings of the nation's largest architecture firms for nonresidential building and multifamily housing work, as reported in Building Design+Construction's 2023 Giants 400 Report.
Market Data | Aug 1, 2023
Nonresidential construction spending increases slightly in June
National nonresidential construction spending increased 0.1% in June, according to an Associated Builders and Contractors analysis of data published today by the U.S. Census Bureau. Spending is up 18% over the past 12 months. On a seasonally adjusted annualized basis, nonresidential spending totaled $1.07 trillion in June.
Data Centers | Apr 14, 2023
JLL's data center outlook: Cloud computing, AI driving exponential growth for data center industry
According to JLL’s new Global Data Center Outlook, the mass adoption of cloud computing and artificial intelligence (AI) is driving exponential growth for the data center industry, with hyperscale and edge computing leading investor demand.
Sustainability | Apr 4, 2023
NIBS report: Decarbonizing the U.S. building sector will require massive, coordinated effort
Decarbonizing the building sector will require a massive, strategic, and coordinated effort by the public and private sectors, according to a report by the National Institute of Building Sciences (NIBS).

















