During a recent investor and analyst conference call, George Oliver, chairman and CEO of Johnson Controls, revealed that his company is looking at potential building air-system upgrade projects valued at “a couple of hundred million” dollars in just the next year. Bloomberg reported that Honeywell International has more than $600 million worth of projects in its pipelines. Carrier Global Corp. estimates that the market for indoor-air quality improvements in buildings could eventually reach $10 billion.
However, these improvements won’t necessarily make buildings more energy efficient. Carbon Lighthouse, the energy savings as a service provider, recently surveyed its clients about how they were managing their buildings’ energy use during a pandemic that forced many employees to work remotely from home, leaving many buildings largely empty.
That poll found three-fifths of the clients’ building portfolios had lowered their energy consumptions by an average of only 23% (compared to an 80% average decline in occupancy most buildings experienced). In one-quarter of the clients’ buildings, there was no change in energy use during shelter-in-place.
These findings bring into sharp relief how COVID-19 has created a massive headwind against energy conservation and continues to pose a significant environmental challenge as building operators focus on HVAC upgrades and air-quality solutions. What’s more, some operators may be under the misconception that if buildings are empty, energy efficiency no longer needs to be a priority.
OCCUPANCY AND ENERGY USE DISCONNECT
Corroborating that assessment is Johnson Controls’ latest Energy Efficiency Indicator COVID-19 Pulse study, based on its survey last September of 150 commercial, institutional, and industrial facilities executives in the U.S. This survey included questions on coronavirus-related improvements, investments, and impacts.
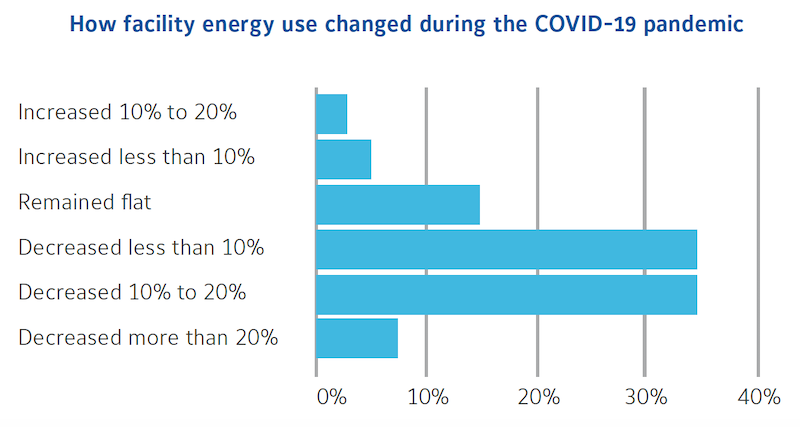
Few buildings altered their energy usage commensurate with reductions in their occupants. Image: Johnson Controls
Perhaps the most sobering finding in Johnson Controls’ study is that the virus had not substantively reduced building energy consumption, regardless of reduced occupancy rates. During the pandemic, less than 10% of the organizations surveyed reduced their energy use by more than 20%. More typical were buildings that decreased their energy consumption by between 0-20%. More than 7% of the surveyed companies increased their energy use.
There could be several reasons for this, explains Clay Nesler, Johnson Controls' Vice President of Global Sustainability. “Even buildings in New York City, where occupancy can be at around 10%, space is still being leased with service agreements that require buildings to maintain temperatures.” Nesler also points out that, typically, more than 50% of a building's energy load is under its tenants' control. “How many refrigerators, computers, and monitors are still plugged in? What's going on with the lights?” He adds that many tenants have big data closets, “and those IT loads aren't going down.”
e
Making environments safer quickly during a health event is where facilities managers say investment dollars are flowing. Image: Johnson Controls.
Most facilities managers saw a more pressing need for flexibility that can quickly respond to emergency conditions. There was a significant increase, compared to last year, of facilities managers who view occupant safety as a critical driver of investment. Another important driver, said 85% of those polled, was energy cost savings.
DID SOMEONE SAY ‘TOUCHLESS’?
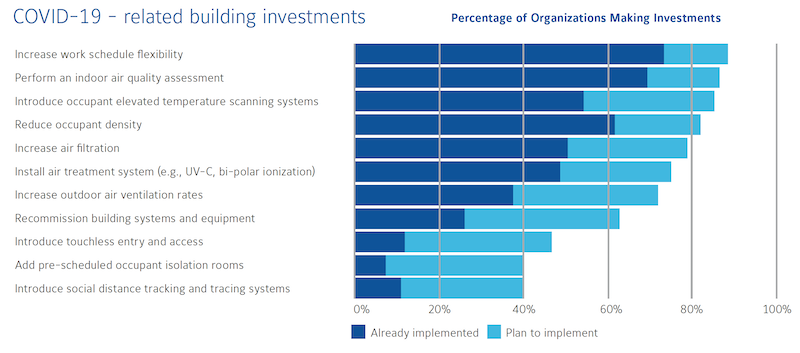
Improving indoor air quality is one of facilities managers' investment priorities. Image: Johnson Controls
When it came to actions in response to the virus’ spread, 60% of the survey’s participants said that plan to upgrade their HVAC and air filtration systems More than half had already conducted air-quality assessments, introduced elevated temperature scanning systems, and increased air filtration.
Nearly 90% of those polled by Johnson Controls said they had already implemented or planned to expand their employees’ work schedule flexibility. But there was less interest in such infection-control measures as introducing touchless entry and access, adding pre-scheduled occupant isolation rooms, or installed systems that track and trace social distancing.
Johnson Controls' Nesler acknowledges that energy efficiency can sometimes confliect with health and safe measures. But it doesn't have to be that way. He points specifically to Environmental, Social, and Governance assessments of sustainable buildings, conducted by the benchmarking firm GRESB, that found these buildings better able to regulate their energy uses, partly by giving tenants solutions to do so before an event hits.
“We believe the future is in control systems that go beyond “on” and “off” to include a pandemic mode” that would align with CDC and ASHRAE safety regulations, says Nesler. He adds that there might also be anther control for facilities managers that allow them to shut down a building's non-critical loads. “We think resilience will be a big thing going forward.”
Editor's note: Information from Clay Nesler of Johnson Controls was added to this story after its initial posting.
Related Stories
| Aug 11, 2010
Tall ICF Walls: 9 Building Tips from the Experts
Insulating concrete forms have a long history of success in low-rise buildings, but now Building Teams are specifying ICFs for mid- and high-rise structures—more than 100 feet. ICF walls can be used for tall unsupported walls (for, say, movie theaters and big-box stores) and for multistory, load-bearing walls (for hotels, multifamily residential buildings, and student residence halls).
| Aug 11, 2010
Integrated Project Delivery builds a brave, new BIM world
Three-dimensional information, such as that provided by building information modeling, allows all members of the Building Team to visualize the many components of a project and how they work together. BIM and other 3D tools convey the idea and intent of the designer to the entire Building Team and lay the groundwork for integrated project delivery.
| Aug 11, 2010
Great Solutions: BIM/Information Technology
4. Architectural Visualization through Gaming Technology Before 3D walkthroughs for client presentations were popular, HKS manager of Advanced Technologies Pat Carmichael and his team were working to marry gaming engines with 3D building models. "What's being tasked to us more and more is not just to show design, but to show function," Carmichael said.
| Aug 11, 2010
BIM school, green school: California's newest high-performance school
Nestled deep in the Napa Valley, the city of American Canyon is one of a number of new communities in Northern California that have experienced tremendous growth in the last five years. Located 42 miles northeast of San Francisco, American Canyon had a population of just over 9,000 in 2000; by 2008, that figure stood at 15,276, with 28% of the population under age 18.
| Aug 11, 2010
Great Solutions: Products
14. Mod Pod A Nod to Flex Biz Designed by the British firm Tate + Hindle, the OfficePOD is a flexible office space that can be installed, well, just about anywhere, indoors or out. The self-contained modular units measure about seven feet square and are designed to serve as dedicated space for employees who work from home or other remote locations.
| Aug 11, 2010
Special Recognition: Kingswood School Bloomfield Hills, Mich.
Kingswood School is perhaps the best example of Eliel Saarinen's work in North America. Designed in 1930 by the Finnish-born architect, the building was inspired by Frank Lloyd Wright's Prairie Style, with wide overhanging hipped roofs, long horizontal bands of windows, decorative leaded glass doors, and asymmetrical massing of elements.








