This year, nearly 1.1 million Americas are expected to suffer “coronary events,” according to an American Heart Association report released earlier this year. The good news is that the number of deaths caused by cardiovascular heart failure or coronary heart disease has been falling steadily over the past several years.
That decline corresponds with the growth of heart failure clinics that have been popping up across the country, not only on academic campuses such as Stanford, Northwestern, Johns Hopkins, the University of Iowa and the University of Michigan, but also at major medical centers like Mayo Clinic (which has heart failure clinics in Arizona, Florida, and Minnesota), NYU|Langone Medical Center, and Cleveland Clinic.
Also see: 2019 Healthcare Giants Report: The ‘smart hospital’ is on the horizon
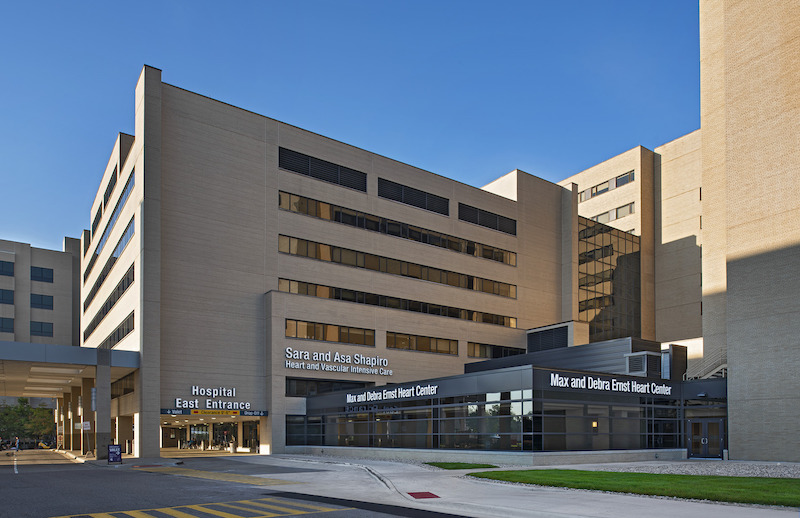
Add to that list the Max and Debra Ernst Heart Center, a $9 million, 14,000-sf facility that opened last month at Beaumont Hospital in Royal Oak, Mich. This addition, which is set up to treat 100 visitors per day, includes 12 patient care rooms, an echocardiogram room, a vascular room, a stress testing room, and two treatment rooms designed for outpatient medication infusion services.
The clinic is named after Max Ernst, the former Arbor Drugs COO, and his wife, who last year donated $5 million to the construction of the new heart failure center.
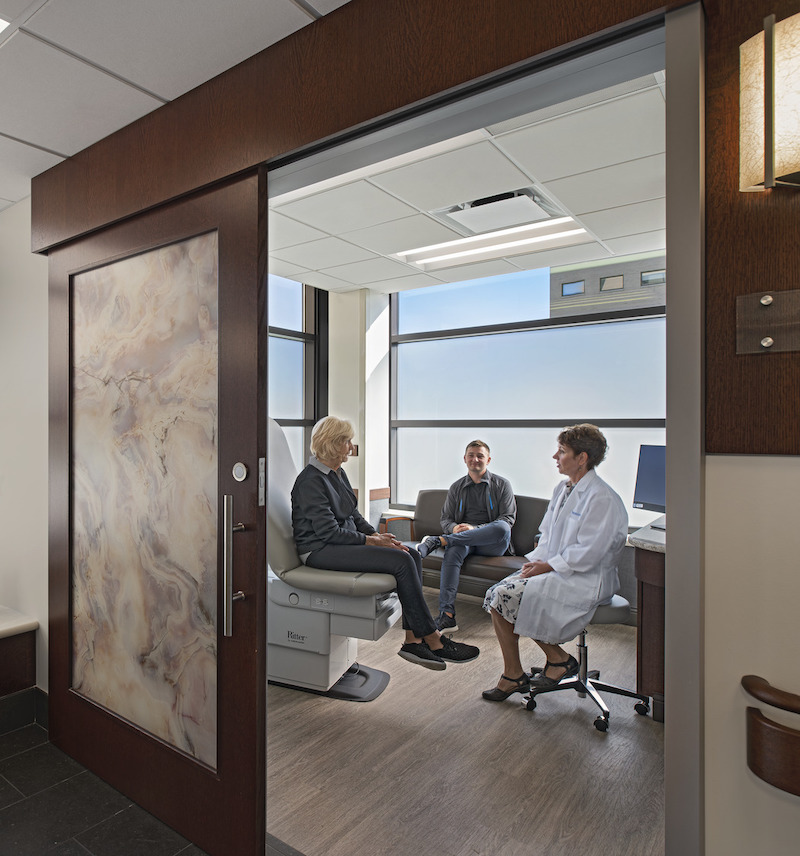 The clinic, with 12 patient rooms, is set up to treat up to 100 visitors per day.
The clinic, with 12 patient rooms, is set up to treat up to 100 visitors per day.
David Jaeger, Principal, Healthcare Studio Leader, Harley EIllis Devereaux (HED), this project’s primary design architect, talked about the “scalability” of the clinics for treating heart failure. “That’s been the case for Beaumont for many years,” adding that the new clinic is about expansion and branding.
He says his firm has had a “longstanding relationship” with Beaumont, dating back to 1997. HED has also done a number of heart centers for other clients; Jaeger says this has become something of a specialty for the firm. On the Beaumont project, HED was also the SE, ME, EE, and landscape architect. PEA Inc. was the CE. And Kasco Construction was the CM.
Heart failure clinics: More than a heart hospital
The goal of heart failure clinics, he explains, is to keep more patients out of emergency rooms. He made the point, however, that cardiology in general is not a growing service anymore for hospitals. “You rarely hear about open-heart surgery anymore,” he says, noting the clinicians are doing a much better job, and have better tools, to treat patients so they don’t need major surgery. “Cardiovascular clinicians have to think about population health in a different what to grow and expand their businesses.”
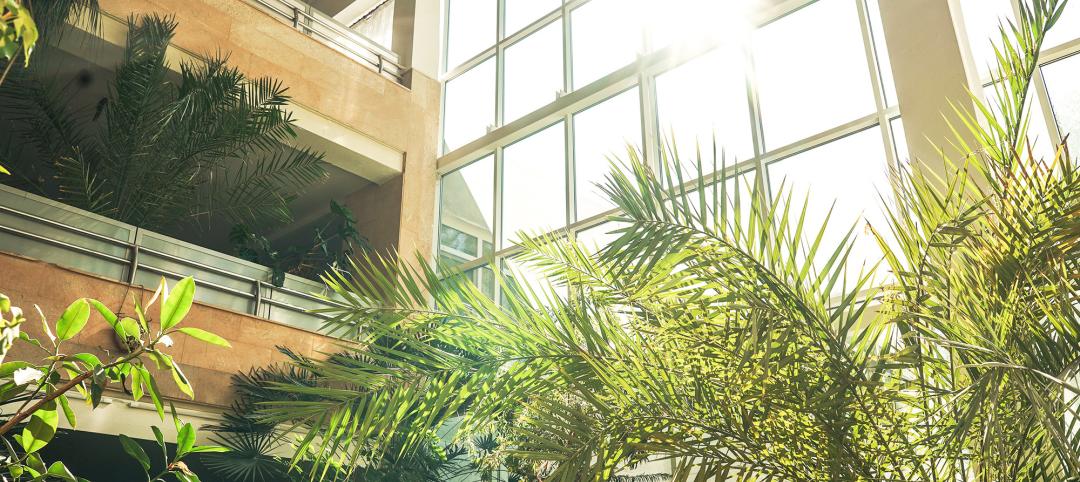
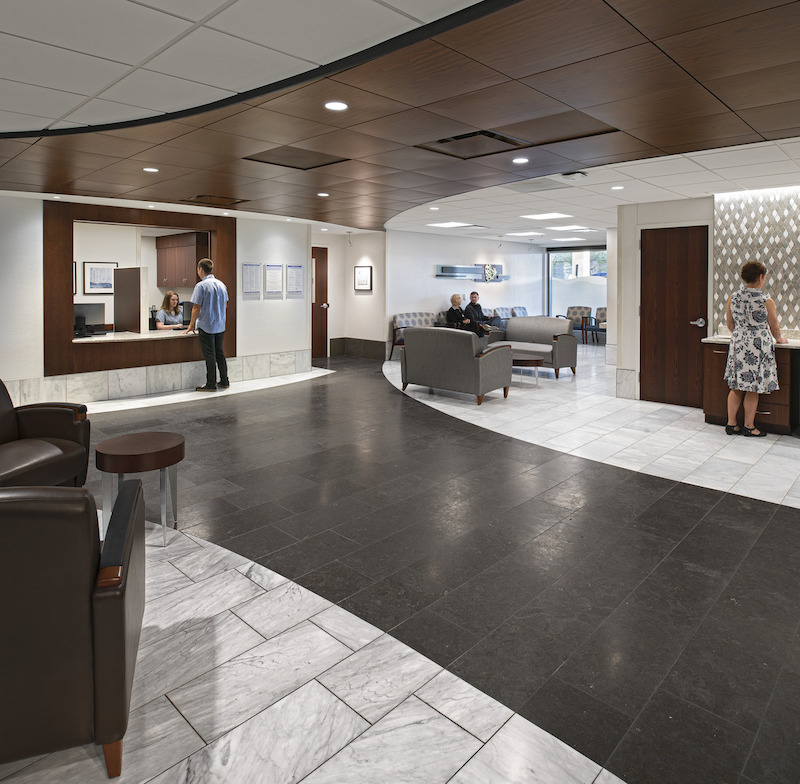 The clinic's glass facade lets in more natural light.
The clinic's glass facade lets in more natural light.
Jaeger says that this project was a challenge because the clinic needed to be wedged within five existing buildings on campus. It also needed to mediate radiation services below.
The precedent for heart failure clients that HED turned toward for its design, says Jaeger, was Duke University, which operates an advanced heart and lung failure clinic, a cardiology consult clinic, and a clinical research unit.
Beaumont is a 3 million-sf hospital, so patient access to the clinic was imperative. Located adjacent to the East Tower entrance of the hospital near the Ernst Cardiovascular Center that opened eight years ago, the clinic has its own entryway in close proximity to parking.
Jaeger also points out that, even though this campus’ buildings are mostly made from brick, HED specified a glass façade that wraps around the clinic addition, providing more natural light to patients and visitors.
Related Stories
Design Innovation Report | Apr 27, 2023
BD+C's 2023 Design Innovation Report
Building Design+Construction’s Design Innovation Report presents projects, spaces, and initiatives—and the AEC professionals behind them—that push the boundaries of building design. This year, we feature four novel projects and one building science innovation.
Sustainability | Apr 20, 2023
13 trends, technologies, and strategies to expect in 2023
Biophilic design, microgrids, and decarbonization—these are three of the trends, technologies, and strategies IMEG’s market and service leaders believe are poised to have a growing impact on the built environment.
Design Innovation Report | Apr 19, 2023
HDR uses artificial intelligence tools to help design a vital health clinic in India
Architects from HDR worked pro bono with iKure, a technology-centric healthcare provider, to build a healthcare clinic in rural India.
Healthcare Facilities | Apr 17, 2023
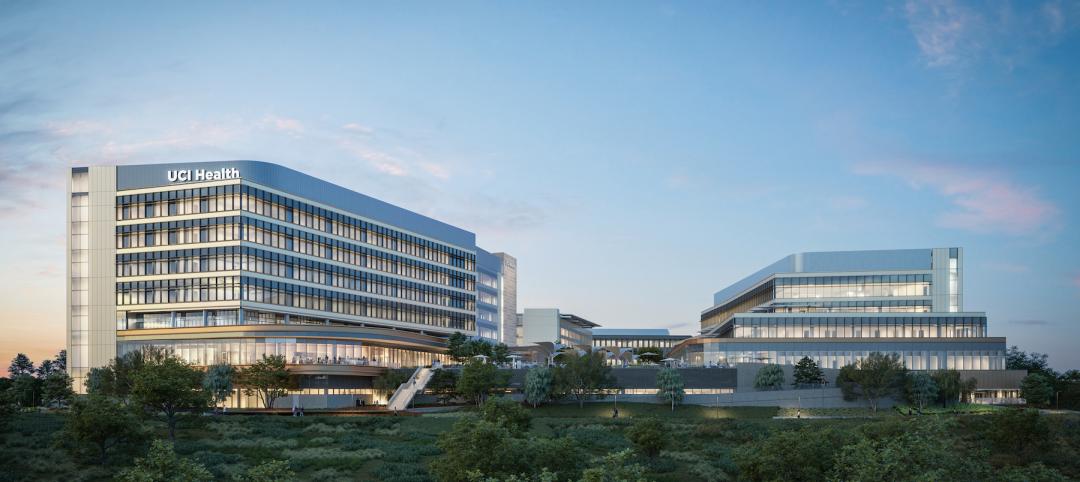
UC Irvine takes sustainability to new level with all-electric medical center
The University of California at Irvine (UCI) has a track record for sustainability. Its under-construction UCI Medical Center is designed, positioned, and built to preserve the nearby San Joaquin Marsh Reserve, to reduce the facility’s solar gain by 85%, and to be the first medical center in the country to operate on an all-electric central plant.
Healthcare Facilities | Apr 13, 2023
Healthcare construction costs for 2023
Data from Gordian breaks down the average cost per square foot for a three-story hospital across 10 U.S. cities.
Healthcare Facilities | Apr 13, 2023
Urgent care facilities: Intentional design for mental and behavioral healthcare
The emergency department (ED) is the de-facto front door for behavior health crises, and yet these departments are understaffed, overwhelmed, and ill-equipped to navigate the layered complexities of highly demanding physical and behavioral health needs.
Urban Planning | Apr 12, 2023
Watch: Trends in urban design for 2023, with James Corner Field Operations
Isabel Castilla, a Principal Designer with the landscape architecture firm James Corner Field Operations, discusses recent changes in clients' priorities about urban design, with a focus on her firm's recent projects.
Market Data | Apr 11, 2023
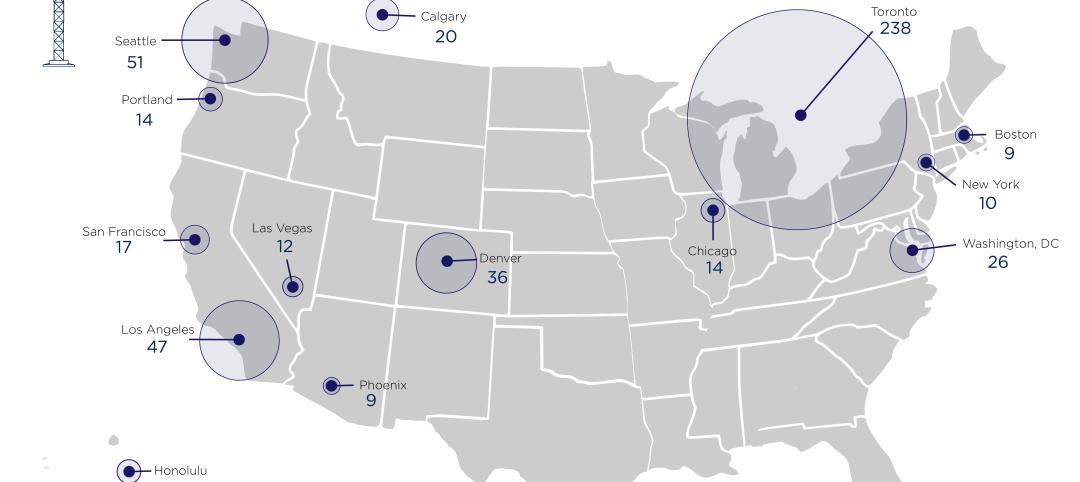
Construction crane count reaches all-time high in Q1 2023
Toronto, Seattle, Los Angeles, and Denver top the list of U.S/Canadian cities with the greatest number of fixed cranes on construction sites, according to Rider Levett Bucknall's RLB Crane Index for North America for Q1 2023.
Contractors | Apr 10, 2023
What makes prefabrication work? Factors every construction project should consider
There are many factors requiring careful consideration when determining whether a project is a good fit for prefabrication. JE Dunn’s Brian Burkett breaks down the most important considerations.
Architects | Apr 6, 2023
New tool from Perkins&Will will make public health data more accessible to designers and architects
Called PRECEDE, the dashboard is an open-source tool developed by Perkins&Will that draws on federal data to identify and assess community health priorities within the U.S. by location. The firm was recently awarded a $30,000 ASID Foundation Grant to enhance the tool.