A new software program that’s been more than five years in the making addresses one of the missing pieces in LEED certification—quantifying the value of going through the process.
At the Greenbuild convention in Los Angeles on Wednesday, Impact Infrastructure, a New York-based software supplier; and Autodesk, an investor in that company, introduced a beta version of Autocase for Sustainable Buildings, a web- and research-based software tool that can show building owners and their AEC teams the financial, social, and environmental returns from green strategies and practices, all in real time.
In addition, the U.S. Green Building Council (USGBC) has created a pilot credit under LEED v.4, called “Informing Design Using Triple Bottom Line Analysis,” that awards cost-benefit evaluations using Autocase that help users determine solutions for optimal returns from earning LEED points.
“What is the value of being green?” asked Mahesh Ramanujam, COO and incoming CEO of USGBC, during the press conference. He answered his own question by pointing out that in a nonresidential sector averse to sharing data, Autocase provides a much-needed measuring stick that is simple and affordable to use, and is informed by LEED’s vision.
Ramanujam framed Autocase as giving more ammunition to users that are weighing the pros and cons of LEED certification, at a time when LEED finds itself competing with several other certification programs, some of which are more focused on wellness and post-occupancy comfort and efficiency. Ramanujam suggested as well that Autocase “raises the bar” for any subsequent versions of LEED.
John Williams, CEO of Impact Infrastructure, recounted how his company and its strategic partners, which include the third-party certifier Green Business Certification Inc. (GBCI), had been working on this tool since the beginning of this decade. Early versions were too expensive, so Impact Infrastructure went back to the drawing board to refine the software so that it was not only more affordable to a broader customer base, but also much quicker to use.
“What would have cost $250,000 for a custom analysis now costs virtually nothing,” he said. “We’re filling the gap and showing value.” And an analysis that would have taken months to complete is now automated with a few keystrokes for speedy information delivery.
Ryan Meyers, Impact’s Chief Technology Officer, and the principal architect of Autocase, gave a brief demonstration of the product, showing how users plug in their own market-specific data, which Autocase applies to its analysis for calculating the savings for owners, occupants, and other stakeholders, based on a raft of existing research and case studies.
Much like Turbo Tax, Autocase has an icon at the top of its home page that tells uses how much they gain from green building. For example, if you want to know the value of sustainable water practices or how green building benefits the long-term health of occupants, Autocase can provide a dollar estimate that changes as new data are introduced.
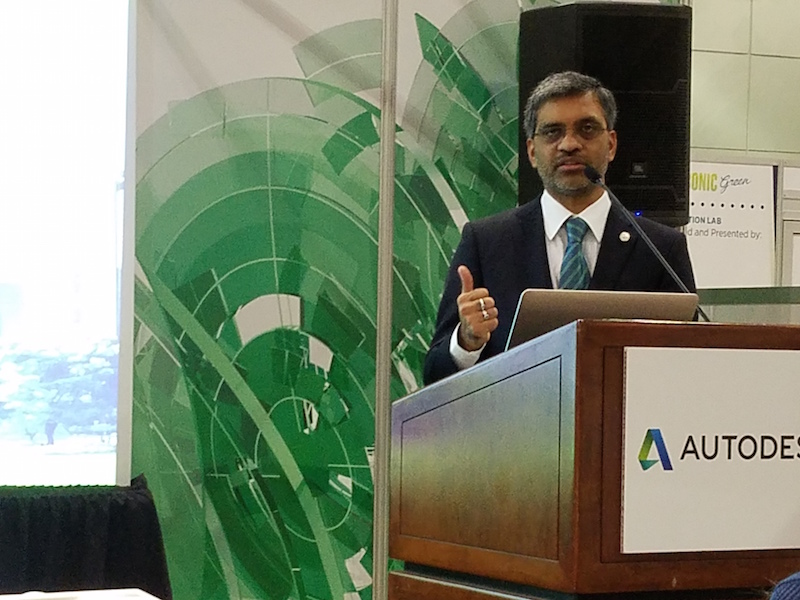

Mahesh Ramanujam, the incoming CEO of the U.S. Green Building Council, which created a pilot credit in LEED certtification for analyses that derive from Autocase software. Image: BD+C
For Johns Hopkins University’s Sustainable Campus Initiative LEED Existing Buildings certification, Autocase was used to analyze energy and water conversation practices—such as efficient lighting, heat recovery, and graywater systems—and prioritized investments in order to build a case that was used to get budgetary approval.
Dewberry is using this tool for the renovation of its corporate headquarters, said Lidia Berger, MEM, LEED Fellow, LEED AP BD+C, LEED O+M, the engineering firm’s sustainability director.
Sometime in the first quarter of 2017, Impact Infrastructure plans to release a production version of Autocase, along with a similar tool for analyzing and quantifying green infrastructure practices, said Meyers.
Related Stories
Augmented Reality | May 30, 2018
HoloLens used as wayfinding device to guide blind people through complex buildings
Neither training nor modification of the physical environment are required to use the system.
Architects | May 14, 2018
4 tactics for our digital transformation
While our technology is becoming more advanced, the fundamental processes at the core of design and construction businesses have largely remained unchanged for decades.
Virtual Reality | May 8, 2018
‘Bespoke’ VR apps give Woods Bagot an edge in presenting design ideas
The architectural firm is finding that some clients respond quicker to proposals as a result.
Architects | Apr 16, 2018
Is the AEC industry ready to shake off its retrograde image?
Technology has been and always will be perceived as a source for wonder and worry.
Building Technology | Apr 10, 2018
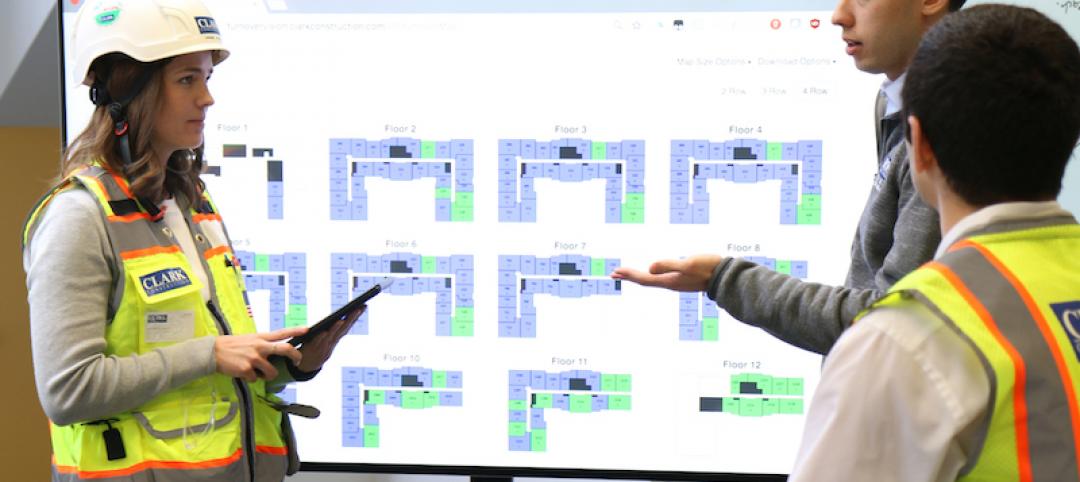
A jobsite dashboard is helping Clark Construction take the drudgery out of managing punch lists
Turnover Vision is the latest example of Clark digitizing its construction management process.
Contractors | Apr 9, 2018
Tech Report 5.0: Smart(er) Jobsites
Real-time construction analysis, just-in-time materials delivery, digital production planning systems—these are just a few of the novel approaches construction firms are implementing to take control of their jobsites.
Building Technology | Apr 9, 2018
Autodesk opens its Forge platform, encouraging more suppliers to build onto it
The goal is to further streamline the construction process, from design to commissioning.
Architects | Apr 5, 2018
Tech Report 5.0: The Human Touch
Can studying humans at a behavioral level produce better buildings? Cognitive architecture experts are working to find out.
Building Technology | Apr 4, 2018
Tech Report 5.0: Digital Immersion
Indoor digital media changes the identities of buildings by stimulating occupant interaction.
Building Technology | Apr 3, 2018
Tech Report 5.0: AI Arrives
From construction scheduling to risk management, AEC firms see promise in budding artificial intelligence platforms geared for commercial building projects.