The benefits of having a sports facility in a community are many—from a shared sense of public pride to increased job opportunities to enhanced real estate values—but perhaps surprisingly, immediate profitability is not among them. Whether minor league ballpark or Olympic-caliber stadium, the economics of athletic facilities is an intricate business, involving franchise fees, broadcast agreements, sponsorships, public funding, licensing issues, and more. Because of this complicated scenario, a realistic understanding of the budget is critical, and must be determined well before the architectural design phase begins.
Cost modeling, an algorithm-based process of estimating the complex expenses of a construction project by analyzing fixed and variable factors, can provide the clarity and direction that get a project off on the right financial foot, putting the facility development on the road to profitability. While there are two established approaches to this—one focuses on cost-per-seat, the other on cost-per-square-foot—there are compelling arguments why relying on just one of these methods may lead to inaccurate conclusions.
While there are two established approaches to this—one focuses on cost-per-seat, the other on cost-per-square-foot—there are compelling arguments why relying on just one of these methods may lead to inaccurate conclusions.
The reason for this is apparent to anyone who has walked through an arena turnstile in the past five years: Modern athletic facility design is far from standardized. What was once simply a playing field surrounded by bleachers, today’s facilities have evolved into entertainment destinations where the competition is not just between teams on the gridiron, diamond, or rink, but also for customers at the multitude of concessions that now populate these venues.
Restaurants and bars, luxury suites, and fan-experience features all make significant contributions to the bottom line of the facility’s business. Such diverse amenities frequently require sophisticated technologies that go beyond the normal parameters of design, so it follows that they also defy conventional cost-modeling techniques.
As sports seasons are limited in length, facility operators look to supplement their income by scheduling revenue-generating events throughout the entire year. To do so, the venue must be designed to accommodate a variety of activities, from concerts to conventions. When a building is multi-functional and doesn’t fit a well-defined profile of a single-purpose structure, using cost-modeling with a narrow focus simply isn’t a suitable approach.
It’s not just the bells and whistles aspects of arenas that keep cost-modeling experts on their toes; the basic building program can prove resistant to seat- or square-foot-based study, as well. Something as fundamental as the location of a facility can dictate certain architectural measures that disrupt strictly formulaic analysis. Examples of such circumstances abound: facilities in earthquake-prone regions will require seismic engineering; those in northern climes must contend with snow loads on the roof; where extreme heat and humidity prevail, solar control might take the form of an expensive retractable roof or a more affordable passive shading system. All these present estimating challenges which cannot be resolved though a single mode of cost-modeling without risk.
Paradoxically, even the seating plan may confound traditional cost-modeling practices. Particularly with the increasing emphasis on luxury boxes as a source of revenue, the amount of general admission seating has become an economically fraught issue.
Responsive cost models are key
As early as possible during conceptual design stages, a responsive cost model should be assembled so that building elements can be isolated, interrogated, and priced individually. Fortunately, most facility designers will have sufficient experience to be able to respond constructively to detailed design questions asked early on in the process. Accordingly, an effective cost model should be organized by building elements—from foundations systems to interior finishes to A/V and special tech systems—in order to create comprehensive cost scenarios.
There are significant advantages to implementing a more detailed cost modeling technique. Unique facility design and cost challenges, which are often overlooked in comparative cost modeling, can be illuminated and addressed early on. At early stages, the conceptual design is still quite flexible and malleable and responses to cost issues can be modelled and priced in relatively short order if the baseline cost model has been properly prepared. And, perhaps most important, conversations about the facility costs can be addressed with specific data rather than conjecture and biased opinions.
Obviously this process places demands on design and project teams, which are more commonly encountered at later stages of the process. However, an added virtue of implementing discovery early on is that it engages the entire team in an informed discussion about costs at a point in the design where changes can be affected with minimal effort and maximum impact.
Cost modeling is a powerful tool for planning sports facilities, but to reap the rewards it offers, it’s important to understand the limits, as well as the capabilities, of the process. With architects continuously upping the ante on facility designs, relying on per-square-foot methods can be a costly mistake. Responsive modeling is critical. Experience and strong relationships are key to engendering full “buy-in” for these methods with all stakeholders and team members. But when everyone is on board, this process can actually promote and improve trust, foster teamwork, and create a sense of shared responsibility to ensure a successful project outcome.
About Peter Knowles: Peter Knowles is executive vice president of Rider Levett Bucknall North America. Based in Denver, he is a member of Rider Levett Bucknall’s senior leadership team responsible for operations of the North American practice. Peter joined the firm in 1987. As a Chartered Quantity Surveyor with over 30 years of experience, he has particular expertise in healthcare and sports facilities, and has worked on aviation, commercial, educational, healthcare, hospitality, mission critical, research and technology, and public assembly projects in the United States, Asia, and Europe. Peter specializes in the management of construction cost and time of projects. A Fellow of the Royal Institution of Chartered Surveys, Peter is also a member of the Australian Institute of Quantity Surveyors and the Association for the Advancement of Cost Engineering.
About Steve Kelly: Steve Kelly is an associate principal at Rider Levett Bucknall and leads the firm’s Seattle office. With more than 29 years of experience in cost management, Steve has worked on behalf of building contractors and cost consulting firms providing his expertise in preparing bills of quantities, analyzing projects by functional component, evaluation of change orders and post construction management control. In addition to his specialized expertise in the sports sector, Steve has worked on numerous projects in sectors ranging from education and hospitality to healthcare infrastructure and commercial. He is also a Member of the Royal Institution of Chartered Surveyors (MRICS).
Related Stories
| Jun 12, 2014
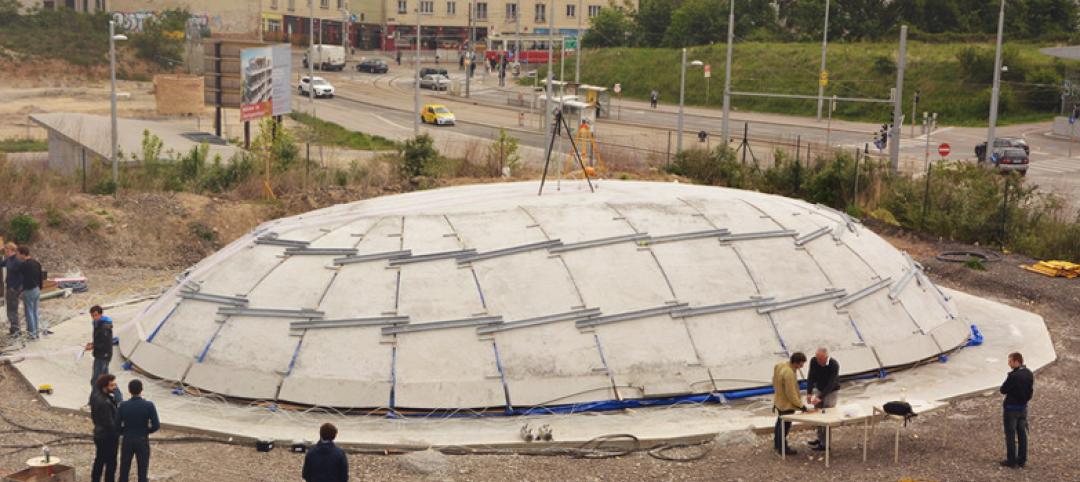
Austrian university develops 'inflatable' concrete dome method
Constructing a concrete dome is a costly process, but this may change soon. A team from the Vienna University of Technology has developed a method that allows concrete domes to form with the use of air and steel cables instead of expensive, timber supporting structures.
| Jun 11, 2014
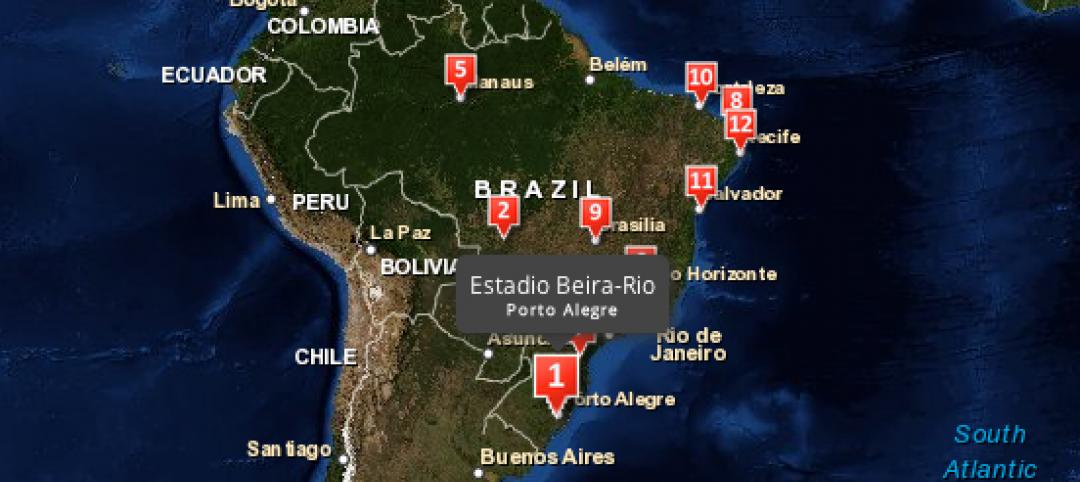
Esri’s interactive guide to 2014 World Cup Stadiums
California-based Esri, a supplier of GIS software, created a nifty interactive map that gives viewers a satellite perspective of Brazil’s many new stadiums.
| Jun 4, 2014
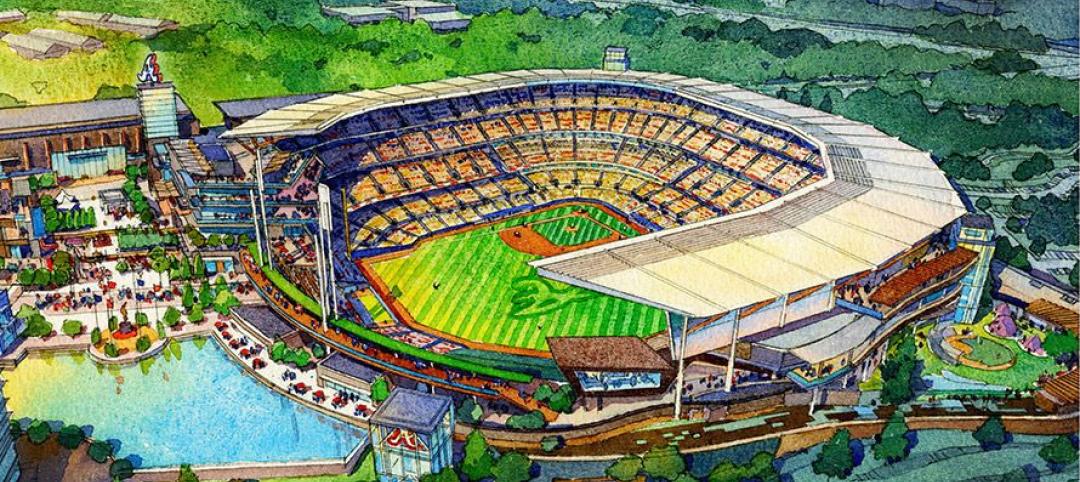
Construction team named for Atlanta Braves ballpark
A joint venture between Barton Malow, Brasfield & Gorrie, Mortenson Construction, and New South Construction will build the Atlanta Braves ballpark, which is scheduled to open in early 2017. Check out the latest renderings of the plan.
| Jun 2, 2014
Parking structures group launches LEED-type program for parking garages
The Green Parking Council, an affiliate of the International Parking Institute, has launched the Green Garage Certification program, the parking industry equivalent of LEED certification.
| May 29, 2014
7 cost-effective ways to make U.S. infrastructure more resilient
Moving critical elements to higher ground and designing for longer lifespans are just some of the ways cities and governments can make infrastructure more resilient to natural disasters and climate change, writes Richard Cavallaro, President of Skanska USA Civil.
| May 22, 2014
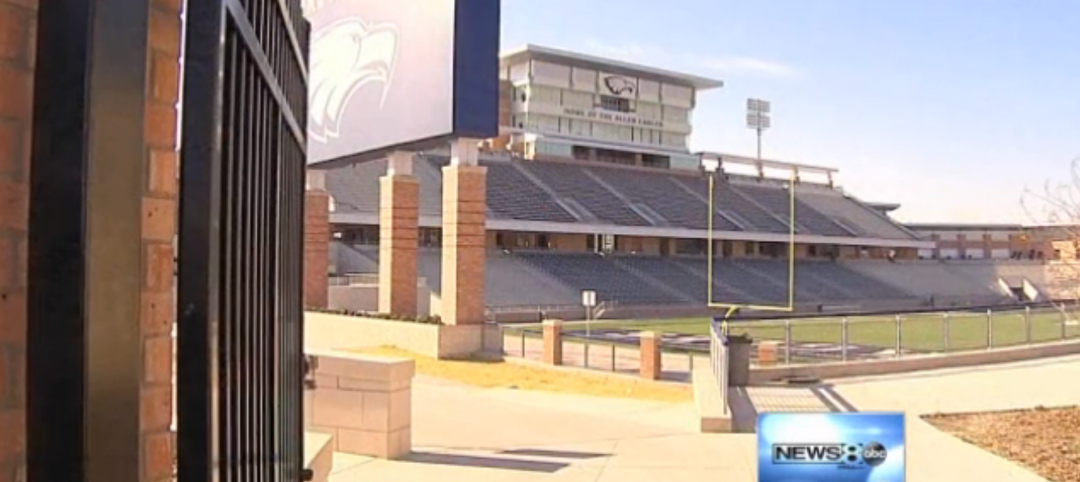
Just two years after opening, $60 million high school stadium will close for repairs
The 18,000-seat Eagle Stadium in Allen, Texas, opened in 2012 to much fanfare. But cracks recently began to appear throughout the structure, causing to the school district to close the facility.
| May 20, 2014
Kinetic Architecture: New book explores innovations in active façades
The book, co-authored by Arup's Russell Fortmeyer, illustrates the various ways architects, consultants, and engineers approach energy and comfort by manipulating air, water, and light through the layers of passive and active building envelope systems.
| May 19, 2014
What can architects learn from nature’s 3.8 billion years of experience?
In a new report, HOK and Biomimicry 3.8 partnered to study how lessons from the temperate broadleaf forest biome, which houses many of the world’s largest population centers, can inform the design of the built environment.
| May 16, 2014
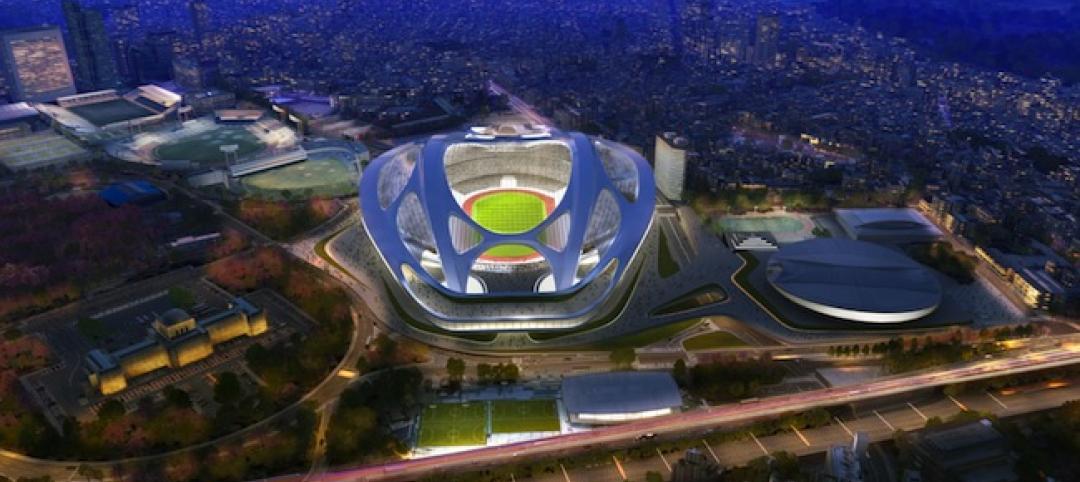
Toyo Ito leads petition to scrap Zaha Hadid's 2020 Olympic Stadium project
Ito and other Japanese architects cite excessive costs, massive size, and the project's potentially negative impact on surrounding public spaces as reasons for nixing Hadid's plan.
| May 13, 2014
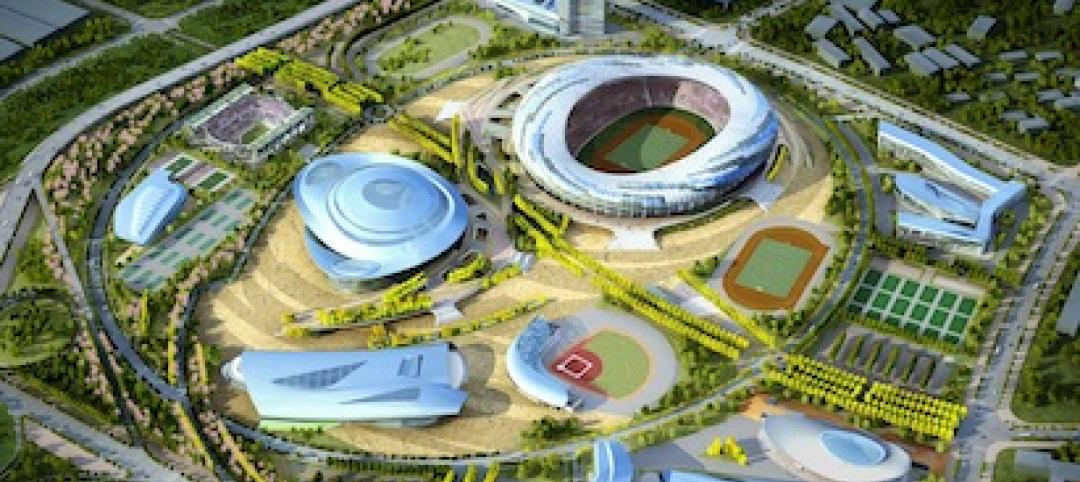
First look: Nadel's $1.5 billion Dalian, China, Sports Center
In addition to five major sports venues, the Dalian Sports Center includes a 30-story, 440-room, 5-star Kempinski full-service hotel and conference center and a 40,500-square-meter athletes’ training facility and office building.