If it’s true that a picture is worth a thousand words, it’s not surprising that the construction industry loses an untold amount of dollars every year due to poor photo filing. Construction progress photos are worthless if they get filed away without an easy way to locate them, or if you don’t know when and where they were taken.
Commercial construction is extremely complex and becoming more so as we move to combine tens of thousands of supply chains in new synergistic ways—energy recovery systems, variable volume air distribution, and dynamic building controls being a few examples. With all of these moving parts, progress documentation has become essential to the construction process, thus requiring us to take lots of photos. Imagine you could see through walls, above ceilings, and underground, but had no idea where you were looking. That’s roughly the current status of construction progress digital photography.
Let me tell you a story that illustrates my point.
A month after moving a client into a beautiful laboratory building, I received a phone call from one of the facility managers telling me that the exterior lights were out—the breaker had been tripped. We checked the lighting loads and conductors, replaced the breaker, safely reset it, and—ta-da!—the lights worked.
Exactly 30 days later, the same phone call. In desperation I turned to the installation photos. What I found was a mind-numbing pile of digital photos, including one shown here labeled “BOB 005.” The entire collection lacked a meaningful file name, structure, or location. I had no clue as to where the photo belonged or when it was taken. In fact, all the photos had the exact same date, the day the project was closed out.
As it turns out sheer luck led me to the solution. I’ll give you a clue: grey conduit met white conduit and, magically, on the one day in the month when the trees on this desert property were watered, the site lighting would short out. The experience inspired me to find a way to organize digital construction photos so that they could be useful in situations like this.
'Simple isn't the same thing as 'easy'
My first instinct was to try to simplify the process. However, that meant requiring our construction field teams to: 1) take photos of anything that could not be seen after construction; 2) download the photos on a regular basis; 3) name and date the photos in such a way that a third party could find their way back to the point of reference where the photo was taken; and 4) make the photos truly searchable.
This first idea was to develop a complex file structure that was located on a project SharePoint site. The idea was that each folder would hold only photos of that specific room, product, or site location; anyone could post and use the library at any time in the future.
As you’ve probably guessed, my plan fell short at the implementation stage. The operations group members weren’t downloading photos on a regular basis, couldn’t remember where photos had been taken, and didn’t post them into the correct folder. As a fallback, I thought about hiring a couple of project interns whose only job would be to document photos, but that, too, would have been too labor intensive.
What we needed was a solution that didn’t add labor costs and would actually encourage our field staff to take construction progress photos. In short, we needed a tool that could see through walls, above ceilings, and underground—a tool where all the pertinent information could be automatically stored with the photo the moment it was taken.
Increasing the level of photo sophistication
I won’t keep you in suspense any longer. The solution turned out to be “geo-tagging,” which is the process of adding geographical identification metadata to images through a global positioning system (GPS) digital camera. Such cameras are all over the market. We tested Nikon’s P6000, Samsung’s CL65, and several models by Sony; we chose the Sony Cybershot DSC-HX5 for its reasonable cost, GPS accuracy, and the fact that it utilizes a nonproprietary memory card that could easy be removed to transfer photos onto our project servers.
The data-rich file itself is not the end-all; it’s what you can do with it that counts. To draw a parallel, a digital song file comes with the image of the album cover, the name of the song, the artist, and the date it was recorded. It doesn’t matter what kind of device you play a digital song on, you still have access to the data.
Similarly, a geo-tagged photo comes with its latitude, longitude, altitude, compass direction, date, and time recorded. Having all that data embedded in your geo-tagged photos allows you to create so-called “mashups.”
According to Wikipedia 2012, a mashup is “a Web page or application that uses and combines data, presentation, or functionality from two or more sources to create new services.” The main characteristics of mashups are “combination, visualization, and aggregation” that make existing data more useful for professional (or personal) use.
When a construction progress photo has been geo-tagged, it can be viewed in any of a number of mapping programs that recognize latitude and longitude; with a little work, it can even be viewed in programs that recognize x-y-z relationships to a given reference point.
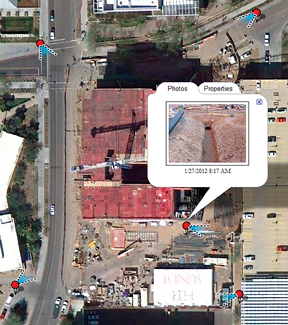
One of the simplest of these mapping programs is Google Maps. In the case of the geo-tagged photo and Google Maps mashup on page 21, the red pin represents the precise location where the photo was taken. The blue cone emanating from the pin is the image angle, indicating the direction of the photo. In other words, the person taking the photo was standing on the red pin and facing in the direction of the blue triangle.
Once your photos have been geo-tagged they can be paired (i.e., mashed) with any number of backgrounds through a variety of interfaces. The three primary interfaces that we use are: 1) the typical file view (sort by name or date); 2) a very useful calendar view; and 3) a map view.
Finding your construction progress photos now becomes much easier. If you know the approximate date, use the calendar view. If you know roughly the location, use the map view. Let’s say you are a supervisor of several construction projects, and you want to find a photo from your job in Phoenix. No problem: using the software that comes with the GPS camera, just zoom in to the location.
Moreover, you don’t necessarily need a GPS-enabled camera to geo-tag your photos. You can download freeware (e.g., Picasa 3, GeoSetter, Geolmgr) that will enable you to manually geo-tag your new (and old) photos that were taken with a non-GPS-enabled camera. Using the map view, you simply drag and drop your photos to the location you remember being at.
However, this method makes you do all the manual work yourself, which from a field perspective creates a disincentive for taking project progress photos
The most elegant solutions are often the simplest. In the brave new world of open source data and cloud computing, data sophistication is paramount. Thanks to GPS and digital cameras, now you can see through walls, above ceilings, and below ground, as if you were really there. +
Ryan Abbott (raabbott@sundt.com) is the Science & Technology Group Leader with SUNDT Construction, Inc.
Related Stories
Lighting | Mar 4, 2024
Illuminating your path to energy efficiency
Design Collaborative's Kelsey Rowe, PE, CLD, shares some tools, resources, and next steps to guide you through the process of lighting design.
MFPRO+ News | Mar 1, 2024
Housing affordability, speed of construction are top of mind for multifamily architecture and construction firms
The 2023 Multifamily Giants get creative to solve the affordability crisis, while helping their developer clients build faster and more economically.
Multifamily Housing | Feb 29, 2024
Manny Gonzalez, FAIA, inducted into Best in American Living Awards Hall of Fame
Manny Gonzalez, FAIA, has been inducted into the BALA Hall of Fame.
K-12 Schools | Feb 29, 2024
Average age of U.S. school buildings is just under 50 years
The average age of a main instructional school building in the United States is 49 years, according to a survey by the National Center for Education Statistics (NCES). About 38% of schools were built before 1970. Roughly half of the schools surveyed have undergone a major building renovation or addition.
MFPRO+ Research | Feb 28, 2024
New download: BD+C's 2023 Multifamily Amenities report
New research from Building Design+Construction and Multifamily Pro+ highlights the 127 top amenities that developers, property owners, architects, contractors, and builders are providing in today’s apartment, condominium, student housing, and senior living communities.
AEC Tech | Feb 28, 2024
How to harness LIDAR and BIM technology for precise building data, equipment needs
By following the Scan to Point Cloud + Point Cloud to BIM process, organizations can leverage the power of LIDAR and BIM technology at the same time. This optimizes the documentation of existing building conditions, functions, and equipment needs as a current condition and as a starting point for future physical plant expansion projects.
Data Centers | Feb 28, 2024
What’s next for data center design in 2024
Nuclear power, direct-to-chip liquid cooling, and data centers as learning destinations are among the emerging design trends in the data center sector, according to Scott Hays, Sector Leader, Sustainable Design, with HED.
Windows and Doors | Feb 28, 2024
DOE launches $2 million prize to advance cost-effective, energy-efficient commercial windows
The U.S. Department of Energy launched the American-Made Building Envelope Innovation Prize—Secondary Glazing Systems. The program will offer up to $2 million to encourage production of high-performance, cost-effective commercial windows.
AEC Innovators | Feb 28, 2024
How Suffolk Construction identifies ConTech and PropTech startups for investment, adoption
Contractor giant Suffolk Construction has invested in 27 ConTech and PropTech companies since 2019 through its Suffolk Technologies venture capital firm. Parker Mundt, Suffolk Technologies’ Vice President–Platforms, recently spoke with Building Design+Construction about his company’s investment strategy.
Performing Arts Centers | Feb 27, 2024
Frank Gehry-designed expansion of the Colburn School performing arts center set to break ground
In April, the Colburn School, an institute for music and dance education and performance, will break ground on a 100,000-sf expansion designed by architect Frank Gehry. Located in downtown Los Angeles, the performing arts center will join the neighboring Walt Disney Concert Hall and The Grand by Gehry, forming the largest concentration of Gehry-designed buildings in the world.