If it’s true that a picture is worth a thousand words, it’s not surprising that the construction industry loses an untold amount of dollars every year due to poor photo filing. Construction progress photos are worthless if they get filed away without an easy way to locate them, or if you don’t know when and where they were taken.
Commercial construction is extremely complex and becoming more so as we move to combine tens of thousands of supply chains in new synergistic ways—energy recovery systems, variable volume air distribution, and dynamic building controls being a few examples. With all of these moving parts, progress documentation has become essential to the construction process, thus requiring us to take lots of photos. Imagine you could see through walls, above ceilings, and underground, but had no idea where you were looking. That’s roughly the current status of construction progress digital photography.
Let me tell you a story that illustrates my point.
A month after moving a client into a beautiful laboratory building, I received a phone call from one of the facility managers telling me that the exterior lights were out—the breaker had been tripped. We checked the lighting loads and conductors, replaced the breaker, safely reset it, and—ta-da!—the lights worked.
Exactly 30 days later, the same phone call. In desperation I turned to the installation photos. What I found was a mind-numbing pile of digital photos, including one shown here labeled “BOB 005.” The entire collection lacked a meaningful file name, structure, or location. I had no clue as to where the photo belonged or when it was taken. In fact, all the photos had the exact same date, the day the project was closed out.
As it turns out sheer luck led me to the solution. I’ll give you a clue: grey conduit met white conduit and, magically, on the one day in the month when the trees on this desert property were watered, the site lighting would short out. The experience inspired me to find a way to organize digital construction photos so that they could be useful in situations like this.
'Simple isn't the same thing as 'easy'
My first instinct was to try to simplify the process. However, that meant requiring our construction field teams to: 1) take photos of anything that could not be seen after construction; 2) download the photos on a regular basis; 3) name and date the photos in such a way that a third party could find their way back to the point of reference where the photo was taken; and 4) make the photos truly searchable.
This first idea was to develop a complex file structure that was located on a project SharePoint site. The idea was that each folder would hold only photos of that specific room, product, or site location; anyone could post and use the library at any time in the future.
As you’ve probably guessed, my plan fell short at the implementation stage. The operations group members weren’t downloading photos on a regular basis, couldn’t remember where photos had been taken, and didn’t post them into the correct folder. As a fallback, I thought about hiring a couple of project interns whose only job would be to document photos, but that, too, would have been too labor intensive.
What we needed was a solution that didn’t add labor costs and would actually encourage our field staff to take construction progress photos. In short, we needed a tool that could see through walls, above ceilings, and underground—a tool where all the pertinent information could be automatically stored with the photo the moment it was taken.
Increasing the level of photo sophistication
I won’t keep you in suspense any longer. The solution turned out to be “geo-tagging,” which is the process of adding geographical identification metadata to images through a global positioning system (GPS) digital camera. Such cameras are all over the market. We tested Nikon’s P6000, Samsung’s CL65, and several models by Sony; we chose the Sony Cybershot DSC-HX5 for its reasonable cost, GPS accuracy, and the fact that it utilizes a nonproprietary memory card that could easy be removed to transfer photos onto our project servers.
The data-rich file itself is not the end-all; it’s what you can do with it that counts. To draw a parallel, a digital song file comes with the image of the album cover, the name of the song, the artist, and the date it was recorded. It doesn’t matter what kind of device you play a digital song on, you still have access to the data.
Similarly, a geo-tagged photo comes with its latitude, longitude, altitude, compass direction, date, and time recorded. Having all that data embedded in your geo-tagged photos allows you to create so-called “mashups.”
According to Wikipedia 2012, a mashup is “a Web page or application that uses and combines data, presentation, or functionality from two or more sources to create new services.” The main characteristics of mashups are “combination, visualization, and aggregation” that make existing data more useful for professional (or personal) use.
When a construction progress photo has been geo-tagged, it can be viewed in any of a number of mapping programs that recognize latitude and longitude; with a little work, it can even be viewed in programs that recognize x-y-z relationships to a given reference point.
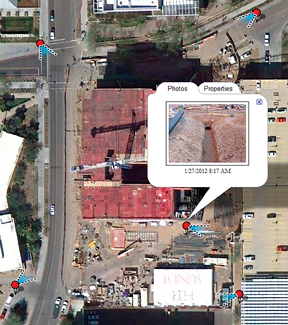
One of the simplest of these mapping programs is Google Maps. In the case of the geo-tagged photo and Google Maps mashup on page 21, the red pin represents the precise location where the photo was taken. The blue cone emanating from the pin is the image angle, indicating the direction of the photo. In other words, the person taking the photo was standing on the red pin and facing in the direction of the blue triangle.
Once your photos have been geo-tagged they can be paired (i.e., mashed) with any number of backgrounds through a variety of interfaces. The three primary interfaces that we use are: 1) the typical file view (sort by name or date); 2) a very useful calendar view; and 3) a map view.
Finding your construction progress photos now becomes much easier. If you know the approximate date, use the calendar view. If you know roughly the location, use the map view. Let’s say you are a supervisor of several construction projects, and you want to find a photo from your job in Phoenix. No problem: using the software that comes with the GPS camera, just zoom in to the location.
Moreover, you don’t necessarily need a GPS-enabled camera to geo-tag your photos. You can download freeware (e.g., Picasa 3, GeoSetter, Geolmgr) that will enable you to manually geo-tag your new (and old) photos that were taken with a non-GPS-enabled camera. Using the map view, you simply drag and drop your photos to the location you remember being at.
However, this method makes you do all the manual work yourself, which from a field perspective creates a disincentive for taking project progress photos
The most elegant solutions are often the simplest. In the brave new world of open source data and cloud computing, data sophistication is paramount. Thanks to GPS and digital cameras, now you can see through walls, above ceilings, and below ground, as if you were really there. +
Ryan Abbott (raabbott@sundt.com) is the Science & Technology Group Leader with SUNDT Construction, Inc.
Related Stories
| Aug 11, 2010
USGBC honors Brad Pitt's Make It Right New Orleans as the ‘largest and greenest single-family community in the world’
U.S. Green Building Council President, CEO and Founding Chair Rick Fedrizzi today declared that the neighborhood being built by Make It Right New Orleans, the post-Katrina housing initiative launched by actor Brad Pitt, is the “largest and greenest community of single-family homes in the world” at the annual Clinton Global Initiative meeting in New York.
| Aug 11, 2010
AIA report estimates up to 270,000 construction industry jobs could be created if the American Clean Energy Security Act is passed
With the encouragement of Senate majority leader Harry Reid (D-NV), the American Institute of Architects (AIA) conducted a study to determine how many jobs in the design and construction industry could be created if the American Clean Energy Security Act (H.R. 2454; also known as the Waxman-Markey Bill) is enacted.
| Aug 11, 2010
Architect Michael Graves to be inducted into the N.J. Hall of Fame
Architect Michael Graves of Princeton, N.J., being inducted into the N.J. Hall of Fame.
| Aug 11, 2010
Modest rebound in Architecture Billings Index
Following a drop of nearly three points, the Architecture Billings Index (ABI) nudged up almost two points in February. As a leading economic indicator of construction activity, the ABI reflects the approximate nine to twelve month lag time between architecture billings and construction spending.
| Aug 11, 2010
Architecture firms NBBJ and Chan Krieger Sieniewicz announce merger
NBBJ, a global architecture and design firm, and Chan Krieger Sieniewicz, internationally-known for urban design and architecture excellence, announced a merger of the two firms.
| Aug 11, 2010
Nation's first set of green building model codes and standards announced
The International Code Council (ICC), the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE), the U.S. Green Building Council (USGBC), and the Illuminating Engineering Society of North America (IES) announce the launch of the International Green Construction Code (IGCC), representing the merger of two national efforts to develop adoptable and enforceable green building codes.
| Aug 11, 2010
David Rockwell unveils set for upcoming Oscar show
The Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences and 82nd Academy Awards® production designer David Rockwell unveiled the set for the upcoming Oscar show.
| Aug 11, 2010
More construction firms likely to perform stimulus-funded work in 2010 as funding expands beyond transportation programs
Stimulus funded infrastructure projects are saving and creating more direct construction jobs than initially estimated, according to a new analysis of federal data released today by the Associated General Contractors of America. The analysis also found that more contractors are likely to perform stimulus funded work this year as work starts on many of the non-transportation projects funded in the initial package.