On March 29, Cushman & Wakefield brokered the $14.7 million sale of a two-story, 24,600-sf medical building in North Hills, N.Y., which traded at a 6% cap rate. Around the same time, an affiliate of Inland Real Estate Acquisitions sold four newly constructed medical buildings totaling 119,000 sf in the Houston, Raleigh, N.C., and Salt Lake City markets. And early this month in Scottsdale, Ariz., Helix Properties sold two Class A medical offices totaling 42,183 sf for $12.13 million.
The market for quality healthcare-related buildings remains robust. A recent poll found the majority of real estate investors and developers expect to be “net buyers” of medical office buildings in 2017, and many believe health systems’ development requests for proposals would be higher this year than in 2016.
Those are some of the findings from a just-released 2017 Healthcare Real Estate Investor and Developer Survey conducted by CBRE’s U.S. Healthcare Capital Markets Group. The results of the 27-question survey are based on a total of 91 respondents.
Sixty three of those firms say they’ve allocated an aggregate of $14.9 billion in equity for healthcare real estate investment and development this year. That total represents about a 3% increase over what respondents said they allocated in 2016.
However, the survey notes that this sector’s supply-demand imbalance would continue this year, “as the total allocation of funds to purchase medical office buildings is far greater than the available supply.” Respondents expect that demand and supply for every healthcare real estate asset type would remain relatively the same in 2017. (At the time of the survey, 57% of respondents said the occupancy rates in their healthcare portfolios were about level with a year ago.)
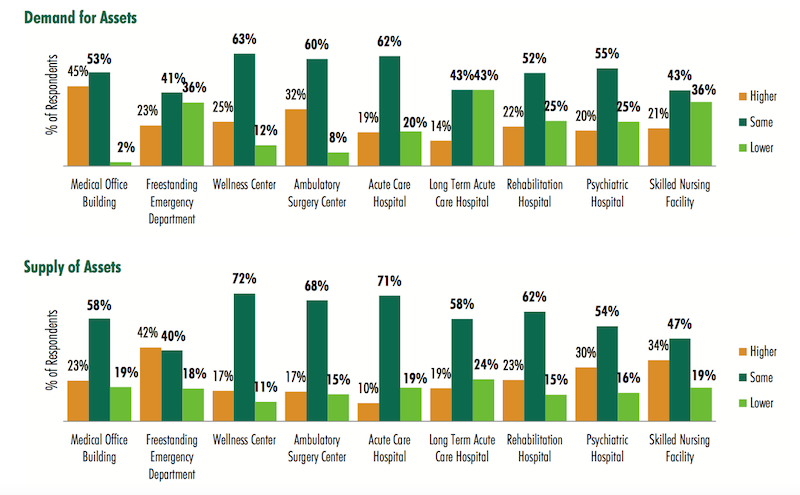 Investors and developers surveyed by CBRE expect supply of quality healthcare facilities for purchase will continue to fall short of the capital available for purchases in 2017. Image: CBRE 2017 Healthcare Real Estate Investor and Developer Survey
Investors and developers surveyed by CBRE expect supply of quality healthcare facilities for purchase will continue to fall short of the capital available for purchases in 2017. Image: CBRE 2017 Healthcare Real Estate Investor and Developer Survey
The preferred transaction size for a sizable majority of respondents—72%—falls somewhere between $10 million and $50 million. Nearly all of the respondents indicated they were most interested in MOBs, followed by Ambulatory Surgery Centers (80%), Wellness Centers (36%), and Freestanding Emergency Departments (35%).
More than three-quarters of respondents rely on bank debt to finance their transactions, although nearly two fifths (39%) said they’d pay for purchases with cash exclusively.
Retention plans vary markedly, as 29% said they expected to hold onto their healthcare purchases for 5-7 years, whereas 28% would retain the asset for more than 10 years (that percentage goes up to 60% among healthcare REITs that responded to the survey).
The survey takes investors’ and developers’ pulses on their Internal Rate of Return requirements by product type. (For example, 42% indicated their target all-cash IRR this year ranges from 7% to 9.49%.)
Value for core product—namely, Class “A” on-campus medical office buildings—continues to be high, with 49% of the survey respondents projecting cap rates below 6%.
Single-tenant medical office buildings are being priced the most aggressively again this year, with the largest group of survey respondents (39%) indicating a cap rate range of between 6% and 6.49%. Ambulatory Surgery Centers followed medical office buildings, but respondents expressed a wide variety of expectations, with 26% projecting a cap rate between 6% and 6.49%, 26% of respondents projecting a cap rate in the range of 6.5% to 6.99%, and 28% of respondents projecting a cap rate between 7% and 7.49%.
More than two-fifths of respondents expect MOB lease rates to increase 1-2% this year, compared to 26% that predicted that rate level in 2016. There was also a drop—to 55% from 60%—of respondents to this year’s survey from last year’s that thought lease rates would increase 2-3%
Nearly 90% of respondents said the minimum lease term they would accept for a sale-leaseback by a healthcare system would be at least 10 years (it’s 10-14 years for 70%). More than two-fifths of respondents—42%—said the minimum annual rental rate hike they’d consider for a sale-leaseback would be 2-2.49%
The highest percentage of respondents said the minimum hospital credit rating they’d consider investing in would be BBB- to BBB+. Sixteen percent, though, said they wouldn’t go below A- to A+.
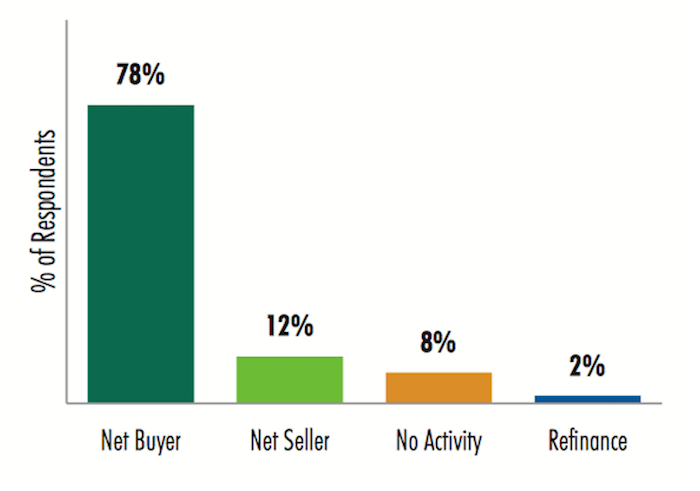 The vast majority of investors and developers polled will be buyers of healthcare-related assets this year. Image: CBRE
The vast majority of investors and developers polled will be buyers of healthcare-related assets this year. Image: CBRE
Twenty-seven percent said that 60-69 years was the minimum ground lease they would consider for investment, compared to a 50-59 year threshold that 35% responding to the 2016 survey would accept. When structuring a ground lease with a hospital for an MOB, 48% of respondents said a fair land value to use in the calculation to determine rent is 5-6%.
CBRE conducted this survey before Republicans pulled their bill to repeal and replace the Affordable Care Act. But developers and investors were asked to predict what they thought would happen, and majorities expected a repeal of the individual mandate for insurance coverage, a repeal of state and federal insurance marketplace exchanges, and a rollback of Medicaid funding.
They also predicted that health insurers would be allowed to sell policies across state borders; that the Trump administration would favor the expansion of Health Savings Accounts; and that insurers would funnel their most expensive patients into subsidized high-risk pools.
Related Stories
Design Innovation Report | Apr 27, 2023
BD+C's 2023 Design Innovation Report
Building Design+Construction’s Design Innovation Report presents projects, spaces, and initiatives—and the AEC professionals behind them—that push the boundaries of building design. This year, we feature four novel projects and one building science innovation.
Sustainability | Apr 20, 2023
13 trends, technologies, and strategies to expect in 2023
Biophilic design, microgrids, and decarbonization—these are three of the trends, technologies, and strategies IMEG’s market and service leaders believe are poised to have a growing impact on the built environment.
Design Innovation Report | Apr 19, 2023
HDR uses artificial intelligence tools to help design a vital health clinic in India
Architects from HDR worked pro bono with iKure, a technology-centric healthcare provider, to build a healthcare clinic in rural India.
Healthcare Facilities | Apr 17, 2023
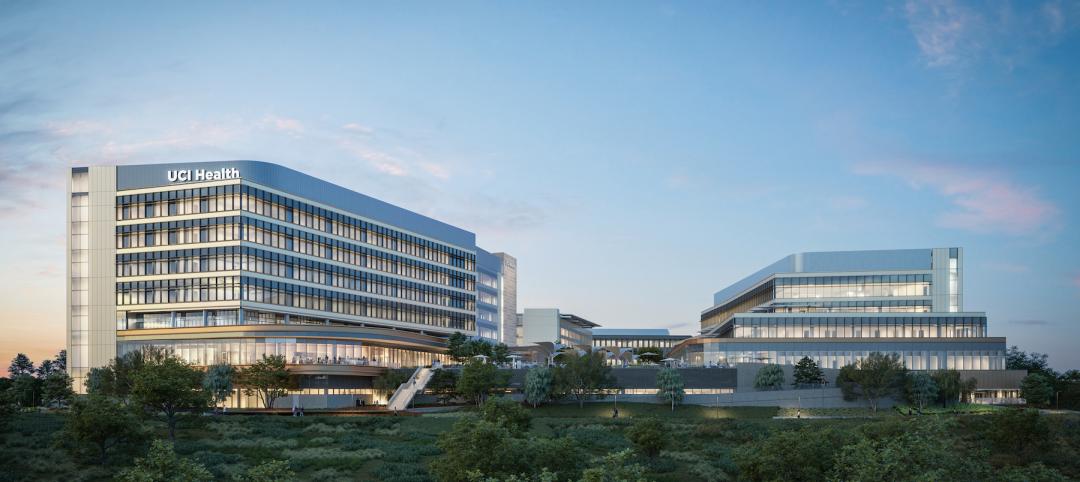
UC Irvine takes sustainability to new level with all-electric medical center
The University of California at Irvine (UCI) has a track record for sustainability. Its under-construction UCI Medical Center is designed, positioned, and built to preserve the nearby San Joaquin Marsh Reserve, to reduce the facility’s solar gain by 85%, and to be the first medical center in the country to operate on an all-electric central plant.
Healthcare Facilities | Apr 13, 2023
Healthcare construction costs for 2023
Data from Gordian breaks down the average cost per square foot for a three-story hospital across 10 U.S. cities.
Healthcare Facilities | Apr 13, 2023
Urgent care facilities: Intentional design for mental and behavioral healthcare
The emergency department (ED) is the de-facto front door for behavior health crises, and yet these departments are understaffed, overwhelmed, and ill-equipped to navigate the layered complexities of highly demanding physical and behavioral health needs.
Urban Planning | Apr 12, 2023
Watch: Trends in urban design for 2023, with James Corner Field Operations
Isabel Castilla, a Principal Designer with the landscape architecture firm James Corner Field Operations, discusses recent changes in clients' priorities about urban design, with a focus on her firm's recent projects.
Market Data | Apr 11, 2023
Construction crane count reaches all-time high in Q1 2023
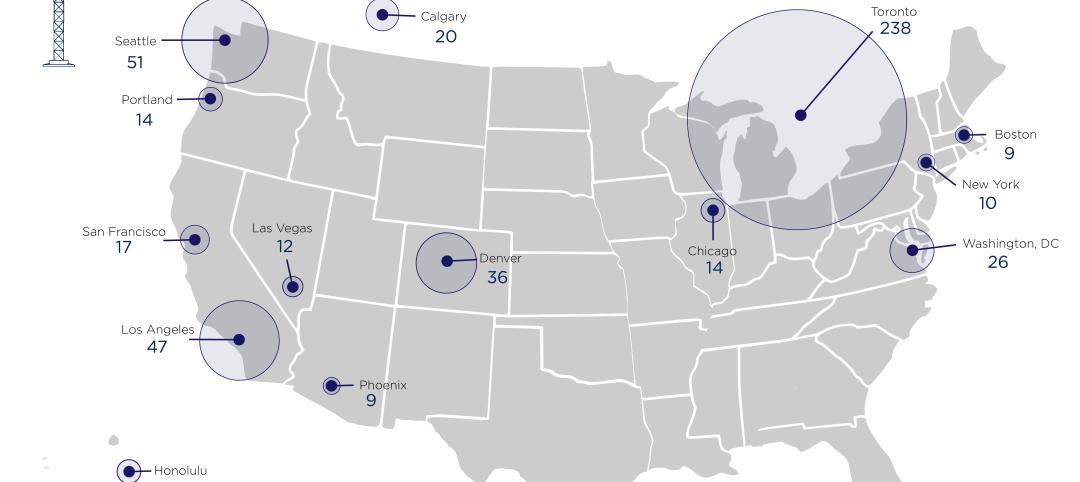
Toronto, Seattle, Los Angeles, and Denver top the list of U.S/Canadian cities with the greatest number of fixed cranes on construction sites, according to Rider Levett Bucknall's RLB Crane Index for North America for Q1 2023.
Contractors | Apr 10, 2023
What makes prefabrication work? Factors every construction project should consider
There are many factors requiring careful consideration when determining whether a project is a good fit for prefabrication. JE Dunn’s Brian Burkett breaks down the most important considerations.
Architects | Apr 6, 2023
New tool from Perkins&Will will make public health data more accessible to designers and architects
Called PRECEDE, the dashboard is an open-source tool developed by Perkins&Will that draws on federal data to identify and assess community health priorities within the U.S. by location. The firm was recently awarded a $30,000 ASID Foundation Grant to enhance the tool.