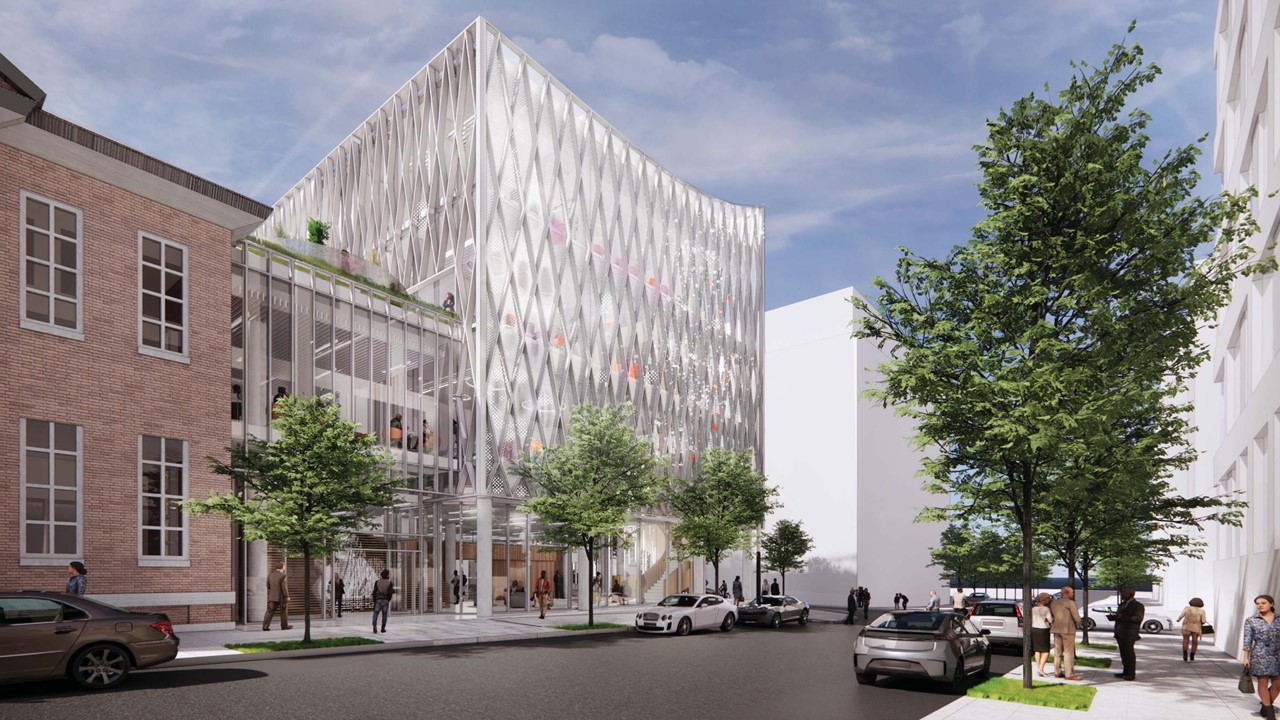
In November, Johns Hopkins University and Johns Hopkins Medicine shared the initial design plans for a campus building project named in honor of Henrietta Lacks, the Baltimore County woman whose cells have advanced medicine around the world. Diagnosed with cervical cancer, Lacks, an African-American mother of five, sought treatment at the Johns Hopkins Hospital in the early 1950s. Named HeLa cells, the cell line that began with Lacks has contributed to numerous medical breakthroughs.
In East Baltimore, the roughly 34,000-sf building will adjoin Deering Hall, which houses the Berman Institute of Bioethics. The new building will support multidisciplinary and complementary programs of the Berman Institute and the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, as well as other university divisions. It will provide flexible program and classroom space for education and research, as well as meeting space for community use.
The building is meant to inspire efforts to address inequities in biomedical research and healthcare, according to Jeffrey Kahn of the Berman Institute of Bioethics.
The project aims to direct 30% of addressable spend to minority-owned and women-owned businesses and disadvantaged business enterprises, and 20% to local business enterprises. The building is designed and managed by local and/or minority-owned businesses. Vines Architecture, an African American-owned firm based in Raleigh, N.C., completed a yearlong feasibility study for the new building and has been selected as the project’s design architect of record. Turner Construction and Baltimore construction firm Mahogany lead the pre-construction services and provide construction management.
“The design reflects not only [my grandmother’s] strong and beautiful spirit but the important role she plays in the history, and future, of East Baltimore,” Jeri Lacks Whye, granddaughter of Henrietta Lacks and member of the Henrietta Lacks Building Advisory Committee, said in a statement.
Construction is scheduled to start in early 2023, with completion planned for 2025.
Here is the office statement from Johns Hopkins Medicine:
Johns Hopkins University and Johns Hopkins Medicine today presented the initial design plans for the on-campus building project named in honor of Henrietta Lacks, the Baltimore County woman whose cells have advanced medicine around the world, during an Urban Design and Architecture Advisory Panel meeting for Baltimore City Planning. This marks an important milestone in the building project, for which design work will continue through the end of the year.
“The architectural design of the building to be named for Henrietta Lacks reflects Johns Hopkins’ commitment to proudly honor and celebrate Mrs. Lacks’ extraordinary legacy on our campus,” says Ronald Daniels, president of Johns Hopkins University. “We are excited to share these plans with the city’s design and architecture advisory panel, and we look forward to continuing to work closely with the Baltimore community and the family of Henrietta Lacks as this important project moves forward.”
The new, approximately 34,000 square foot building in East Baltimore will adjoin Deering Hall, a historic structure that is home to the Berman Institute of Bioethics. Located at the corner of Ashland and Rutland avenues, in the heart of Baltimore’s Eager Park community, the building will support multidisciplinary and complementary programs of the Berman Institute and the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, and other university divisions, and will include flexible program and classroom space to support education and research. Meeting space will also be made available for community use.
"It is exciting to know what the building named in honor of my grandmother, Henrietta Lacks, will look like from the outside, captivating her legacy. I’m happy to see it presented to the Baltimore community,” says Jeri Lacks Whye, granddaughter of Henrietta Lacks and member of the Henrietta Lacks Building Advisory Committee. “The design reflects not only her strong and beautiful spirit but her important role she plays in the history, and future, of East Baltimore.”
“This important building will significantly expand our capacity for teaching, scholarship and community-building, inspiring efforts to address inequities in biomedical research and health care that are an additional tribute to its remarkable namesake,” says Jeffrey Kahn, Ph.D., M.P.H., Andreas C. Dracopoulos director of the Berman Institute of Bioethics.
Construction is planned to start next year. Johns Hopkins also announced that the building will be completed in 2025, with an opening celebration to be planned.
“The expression of this building is unique to its surroundings, as Henrietta Lacks was a unique African American human being in this world. Our team has worked to design a building that fits within the urban context but has a special identity that we hope people believe warrants carrying the name of Henrietta Lacks,” says Victor Vines, president and Robert Thomas, director of design of Vines Architecture. “As we continue progress on the design, we believe that this building will remain a critical way to share the story of Henrietta Lacks for generations to come.”
For more information about the project, visit hopkinsmedicine.org/henriettalacks/updates.html.
About Henrietta Lacks and the HeLa Cells
Henrietta Lacks was a 31-year-old African American mother of five from Baltimore County who sought treatment at The Johns Hopkins Hospital in the early 1950s. Doctors diagnosed Mrs. Lacks with cervical cancer, and as medical records show, she received care that included the best medical treatment available at the time for this terrible disease. Unfortunately, treatment was unsuccessful, and Mrs. Lacks passed away in October 1951.
A sample of Mrs. Lacks’ cancer cells was retrieved during a biopsy and sent to cancer researcher Dr. George Gey's nearby tissue lab, where he had been collecting cells from patients who came to Johns Hopkins Hospital with cervical cancer. He discovered these cells were unlike any of the others he had seen: Where other cells would die, Mrs. Lacks' cells survived, and the number of cells would double every 20 to 24 hours. Soon after that, he began sharing the cells, at no cost, with researchers around the world. Deemed “HeLa” cells, the cell line that began from the biopsy from Mrs. Lacks proved to be remarkably durable and prolific, and while many additional cell lines are in use today, HeLa cells have had a unique contribution to untold medical breakthroughs over the decades since their discovery.
In 2013, Johns Hopkins worked with members of the Lacks family and the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to help craft an agreement that requires scientists to receive permission to use Henrietta Lacks’ genetic blueprint in NIH-funded research.
The NIH committee tasked with overseeing the use of HeLa cells now includes two members of the Lacks family. The biomedical research community has also made significant strides in updating research practices for the donation and use of tissue from patients, in part thanks to the lessons learned from Henrietta Lacks’ story.
To learn more about Henrietta Lacks and the wide-ranging impact of HeLa cells on medical research, please visit hopkinsmedicine.org/henriettalacks.
Related Stories
Giants 400 | Nov 18, 2021
2021 K-12 School Sector Giants: Top architecture, engineering, and construction firms in the U.S. K-12 school facilities sector
PBK, Gilbane, AECOM, and DLR Group head BD+C's rankings of the nation's largest K-12 school facilities sector architecture, engineering, and construction firms, as reported in the 2021 Giants 400 Report.
2021 Building Team Awards | Nov 17, 2021
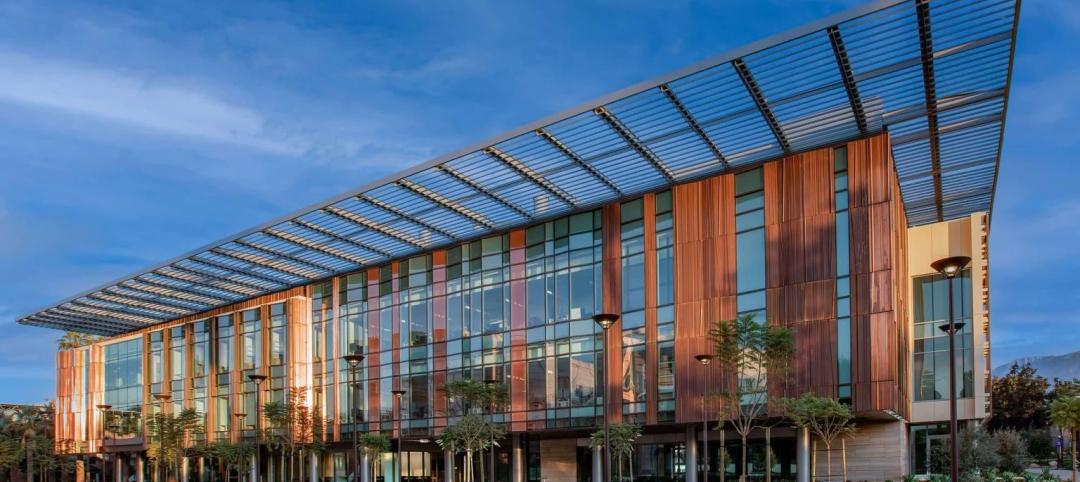
Caltech's new neuroscience building unites scientists, engineers to master the human brain
The Tianqiao and Chrissy Chen Institute for Neuroscience at the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena wins a Gold Award in BD+C's 2021 Building Team Awards.
Designers / Specifiers / Landscape Architects | Nov 16, 2021
‘Desire paths’ and college campus design
If a campus is not as efficient as it could be, end users will use their feet to let designers know about it.
K-12 Schools | Nov 14, 2021
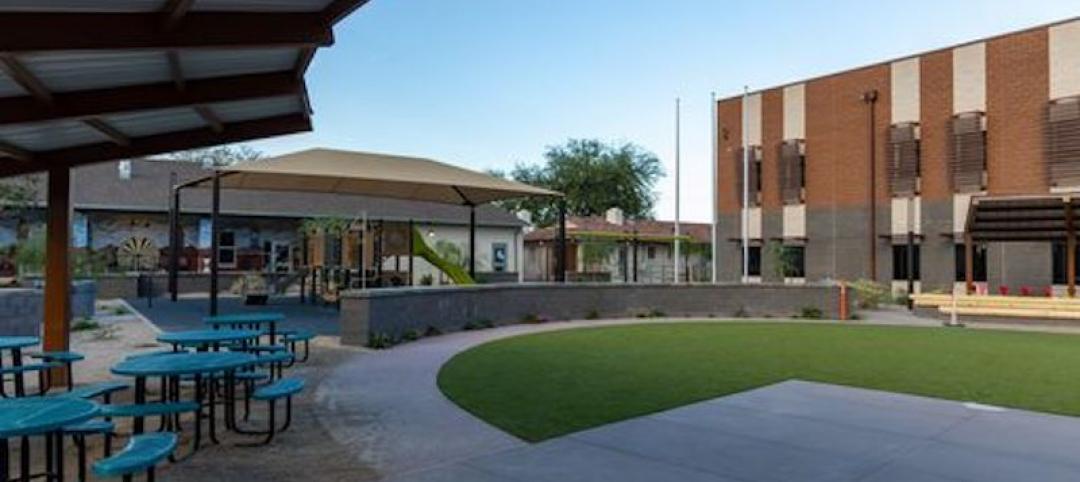
New Blackwater Community School completed for Gila River Indian Community, in Arizona
Construction on the new Blackwater Community School, a two-story structure on the Gila River Indian Community, located southeast of Phoenix, Arizona, was completed on August 31, 2021.
K-12 Schools | Nov 10, 2021
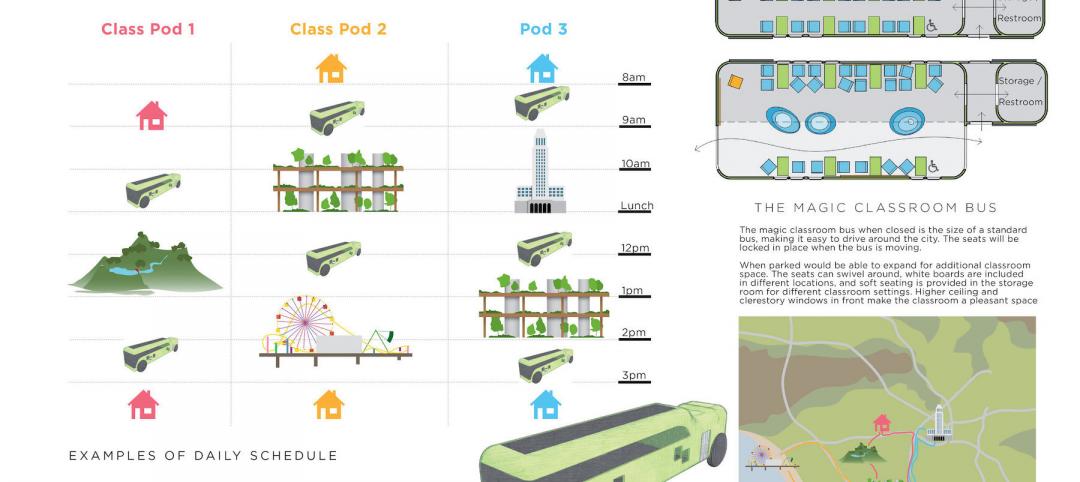
K-12 school design innovation: 'Learning Everywhere' and the mobile classroom
Last September, AIA San Francisco awarded the Professional Category in its 2021 Future Classroom Competition to a five-person team from Culver City, Calif.-based Berliner Architects. The firm was selected for its “Learning Everywhere” idea that features a mobile strategy for education at school, home, on field trips, and in transit. BD+C's John Caulfield discuss that concept with Richard Berliner, AIA, Principal, Berliner Architects.
Cladding and Facade Systems | Oct 26, 2021
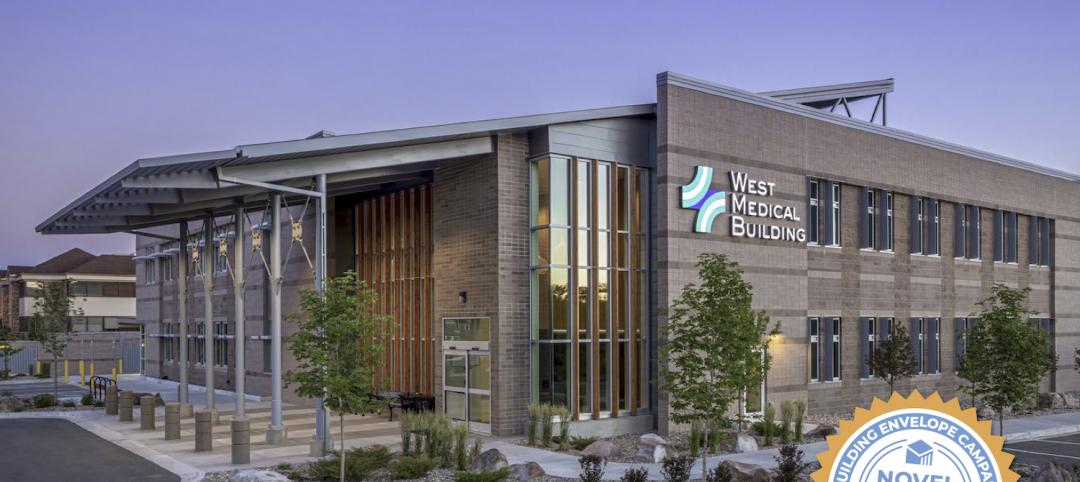
14 projects recognized by DOE for high-performance building envelope design
The inaugural class of DOE’s Better Buildings Building Envelope Campaign includes a medical office building that uses hybrid vacuum-insulated glass and a net-zero concrete-and-timber community center.
Education Facilities | Oct 20, 2021
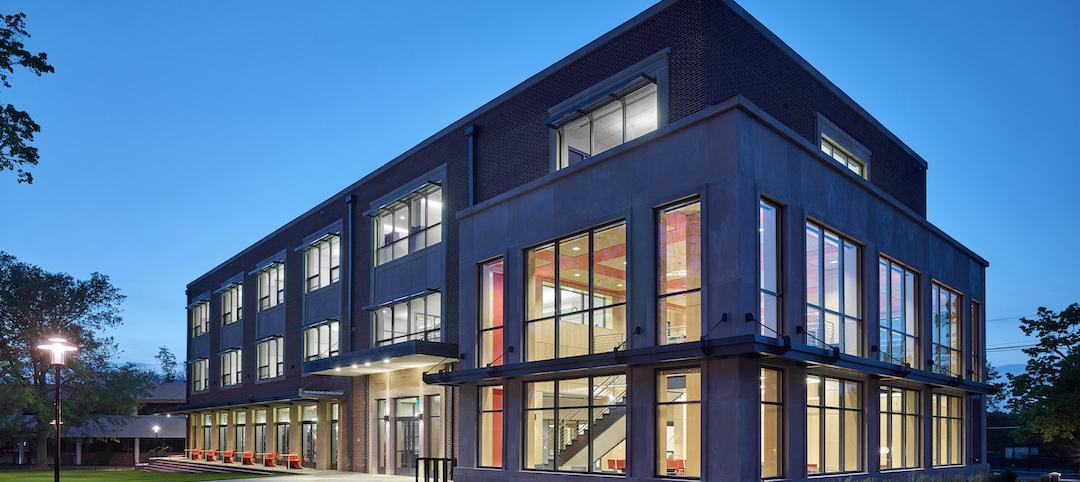
Kenneth K.T. Yen Humanities Building completes for The Pennington School
Voith & Mactavish Architects designed the project.
| Oct 14, 2021
The future of mass timber construction, with Swinerton's Timberlab
In this exclusive for HorizonTV, BD+C's John Caulfield sat down with three Timberlab leaders to discuss the launch of the firm and what factors will lead to greater mass timber demand.
University Buildings | Sep 28, 2021
Designing for health sciences education: Specialty instruction and human anatomy labs
It is a careful balance within any educational facility to provide both multidisciplinary, multiuse spaces and special-use spaces that serve particular functions.
| Sep 20, 2021
K-12 school design trends for 2021, with Wold's Vaughn Dierks
K-12 school design exert Vaughn Dierks discusses the latest K-12 school design trends and needs.