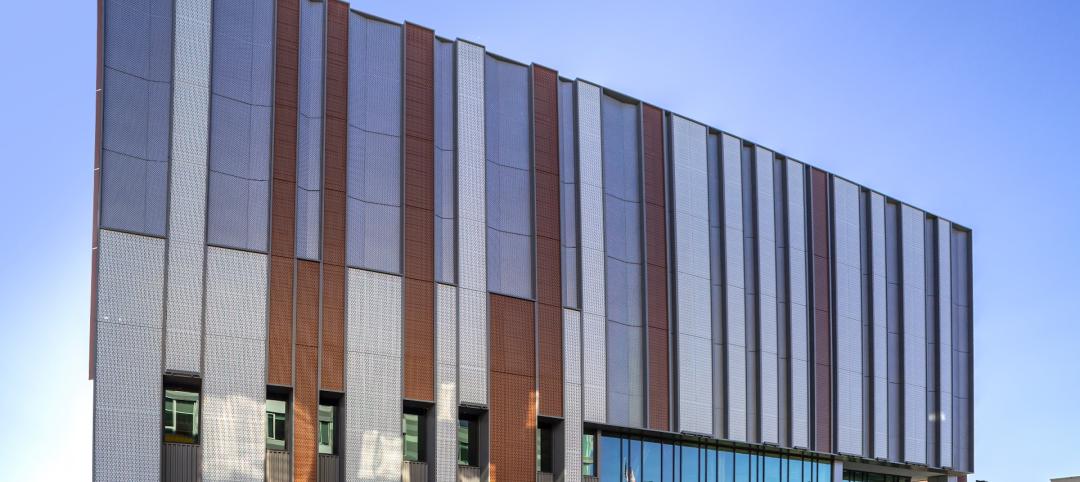
The Center for Medical Education Innovation (CMEI) at Kansas City University was designed to adapt to changes in medical curriculum and pedagogy. The project program supported the mission of training leaders in osteopathic medicine with a state-of-the-art facility that leverages active-learning and simulation-based training.
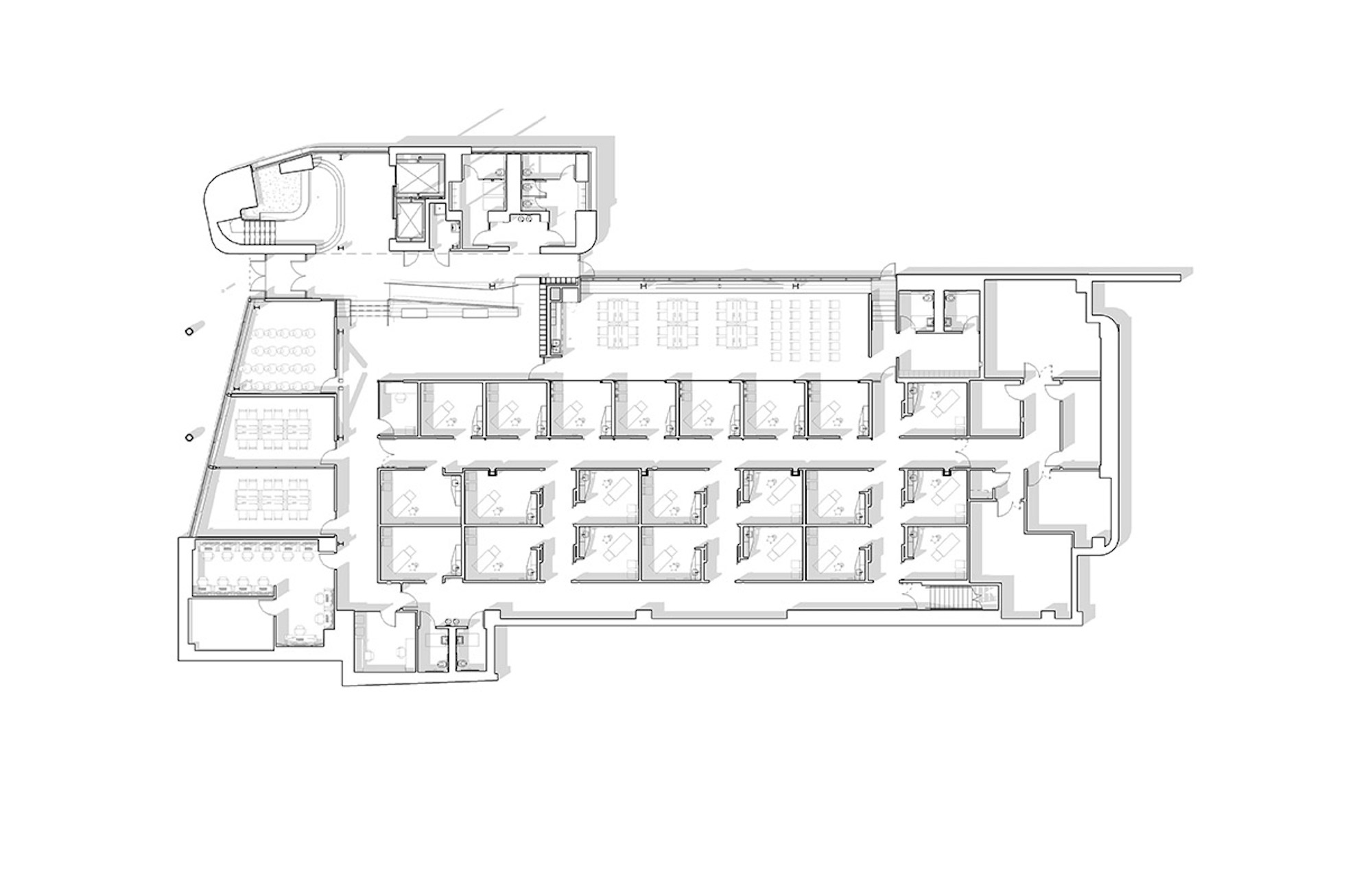
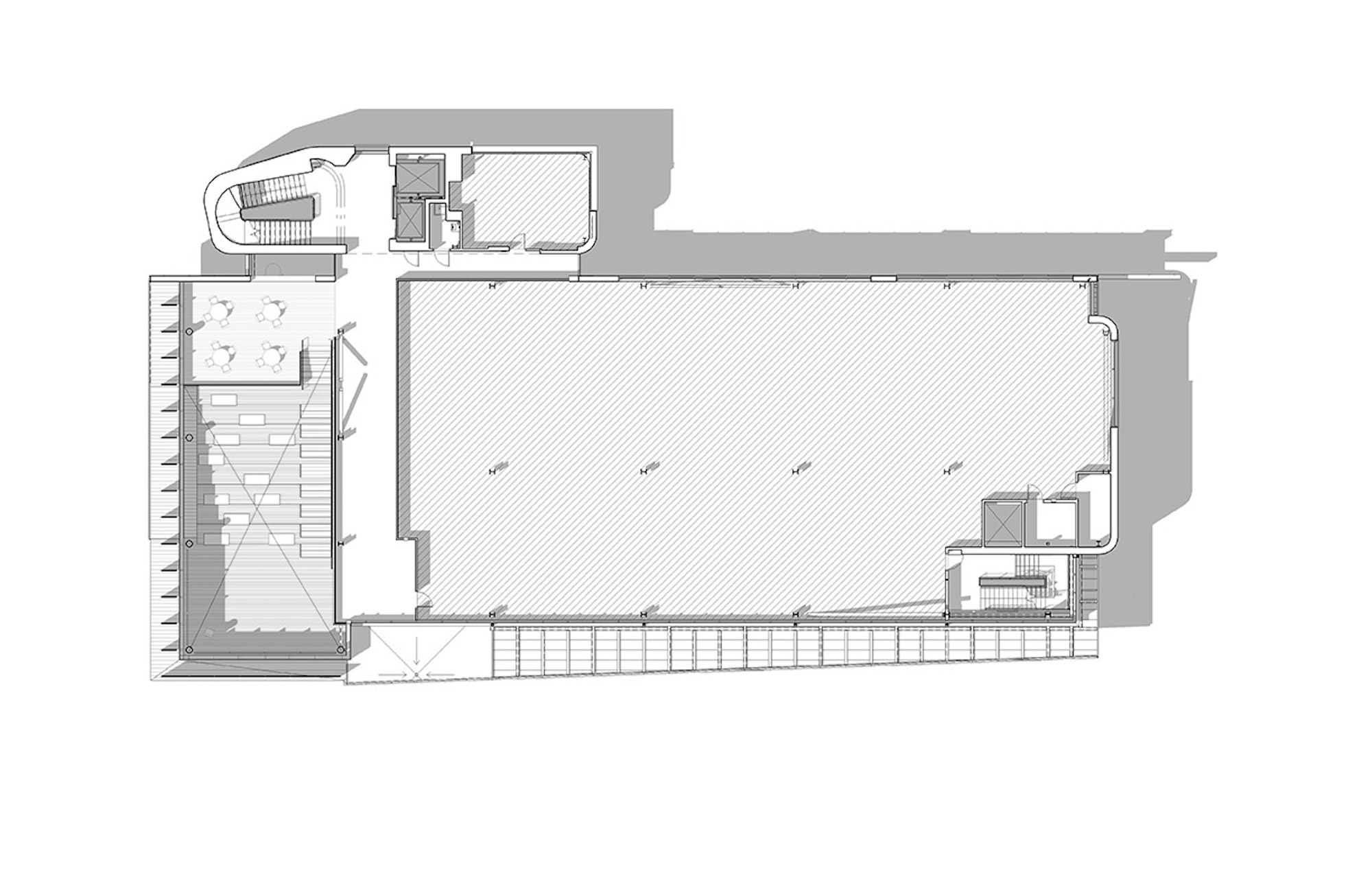
The four-story, 56,000-sf medical education facility and an adjacent two-level free-standing parking structure were designed with key themes of transparency and multi functionality. The building consists of about 26,000 sf of assignable medical education space and an additional 9,500 sf of shelled classroom space.
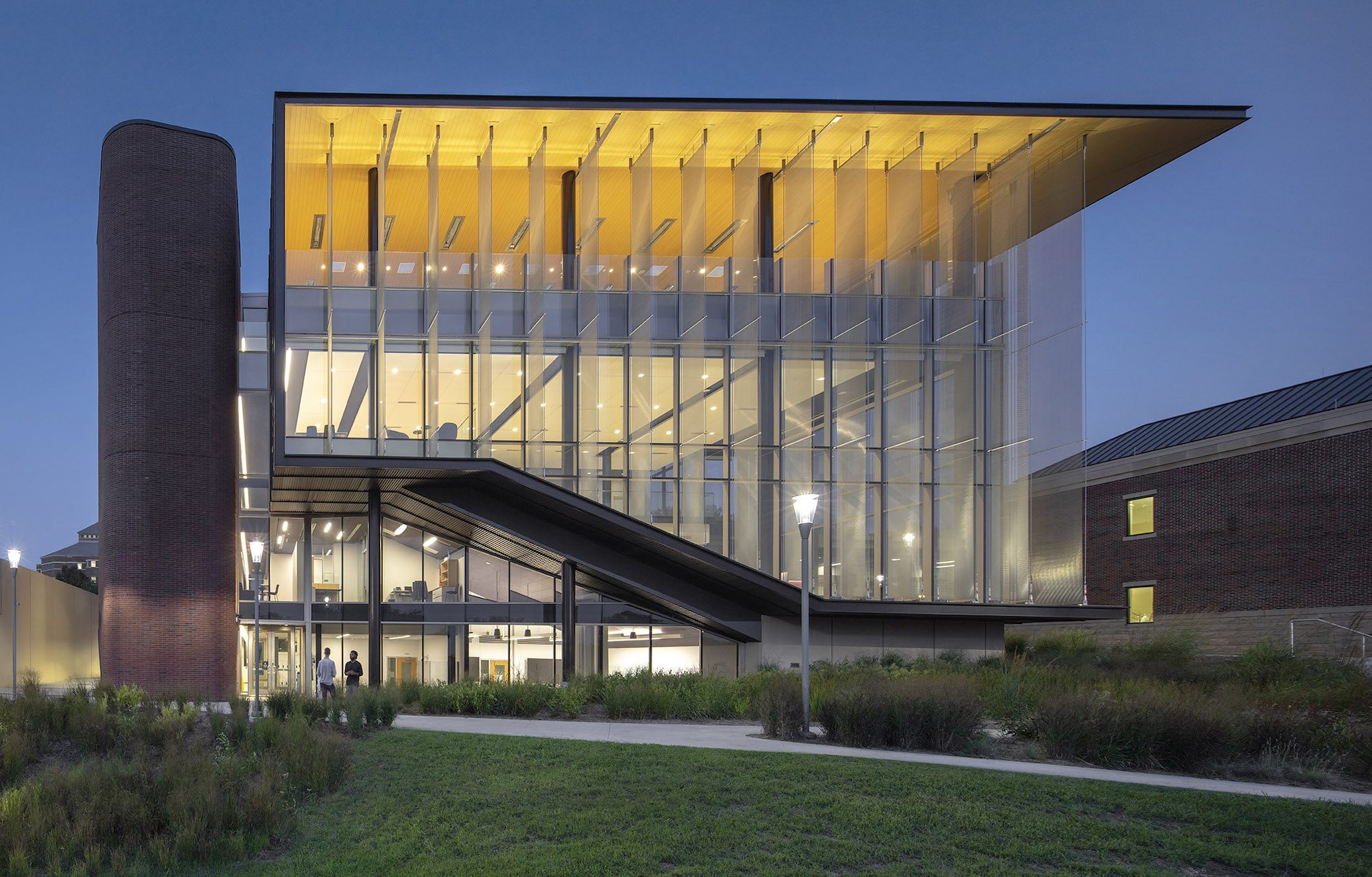
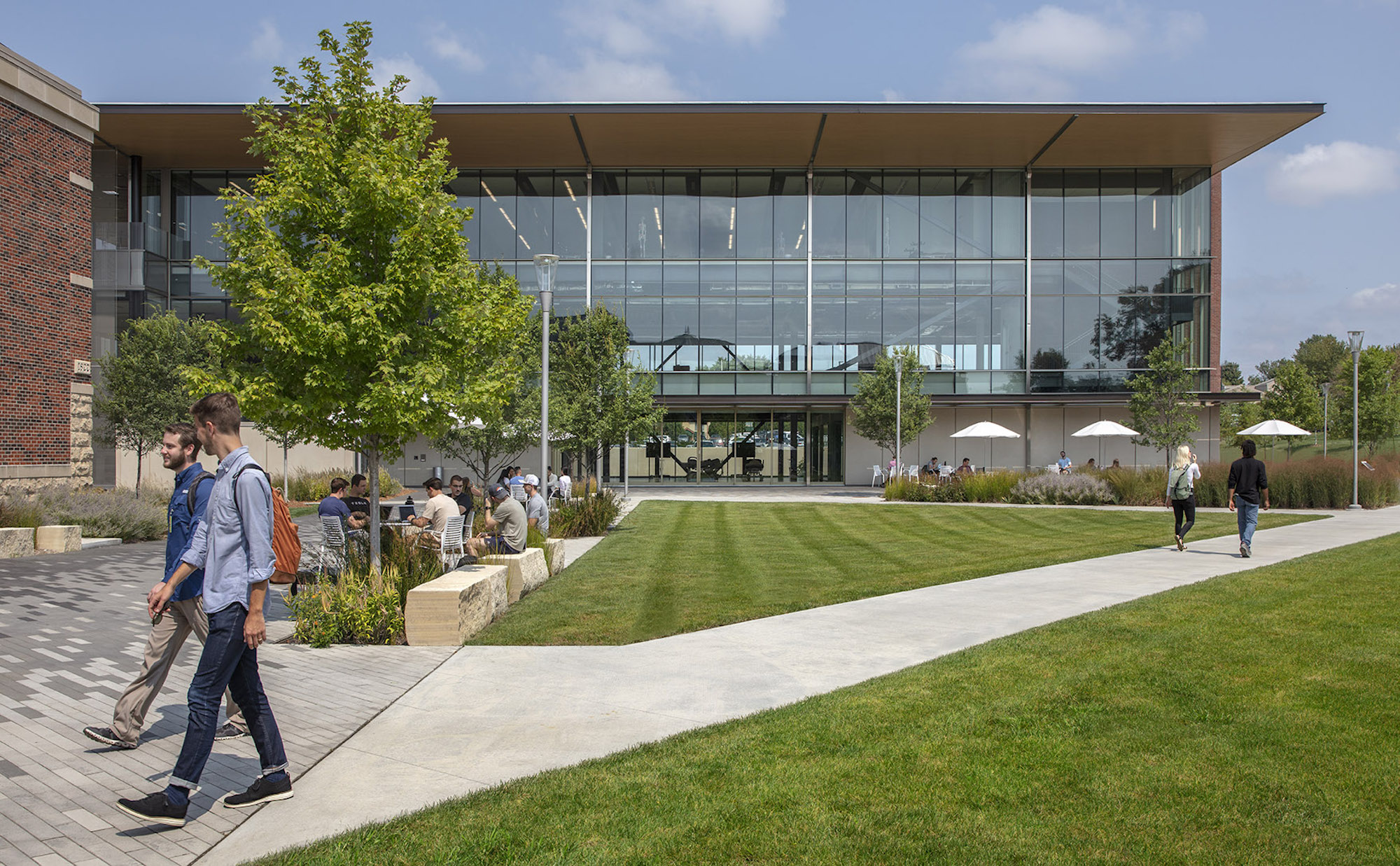
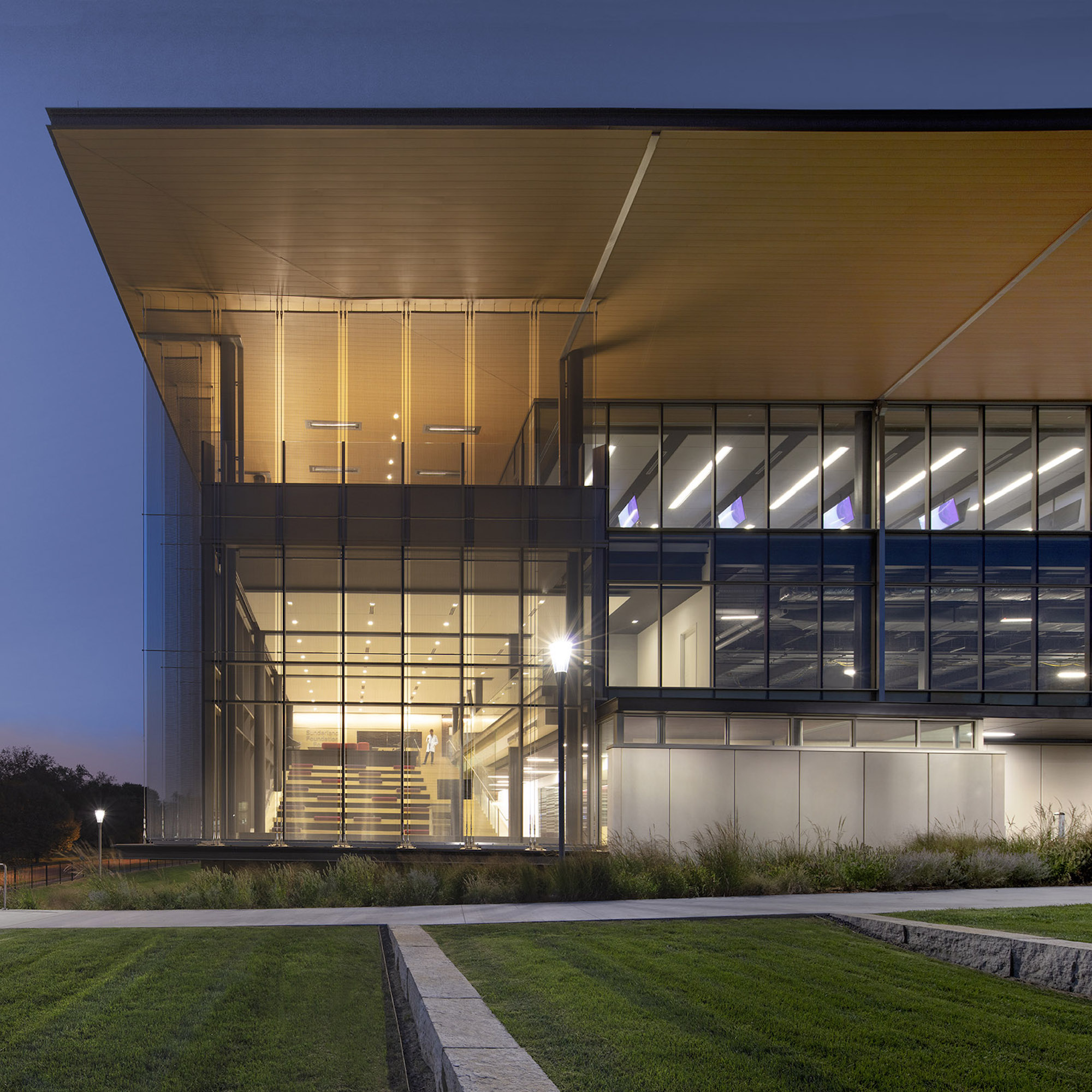
The CMEI helps define a new campus entry and lower quad. The pavilion-like four-story building takes advantage of the site’s sloping topography while maintaining the scale of the existing campus by lowering one floor into the sloping site. This approach creates the illusion of a three-story structure on the campus quad.
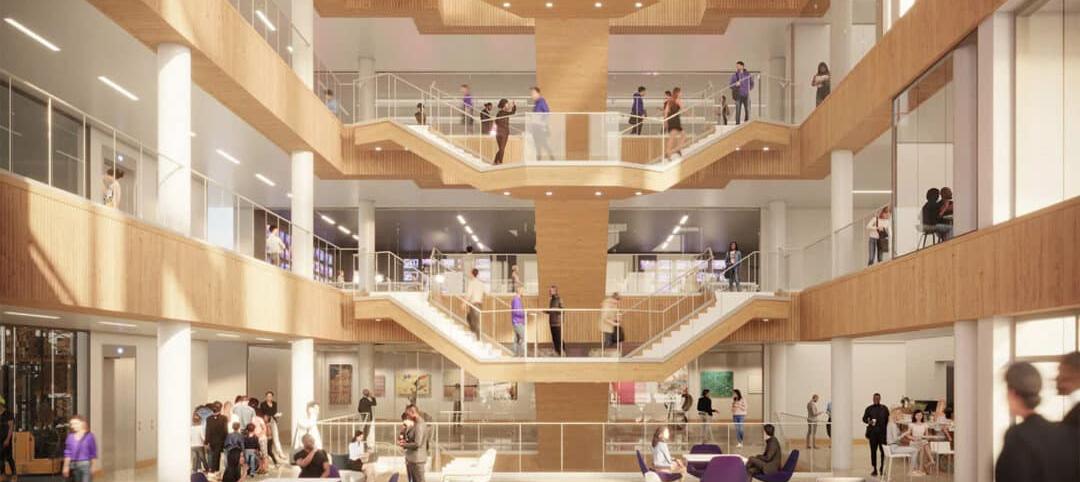
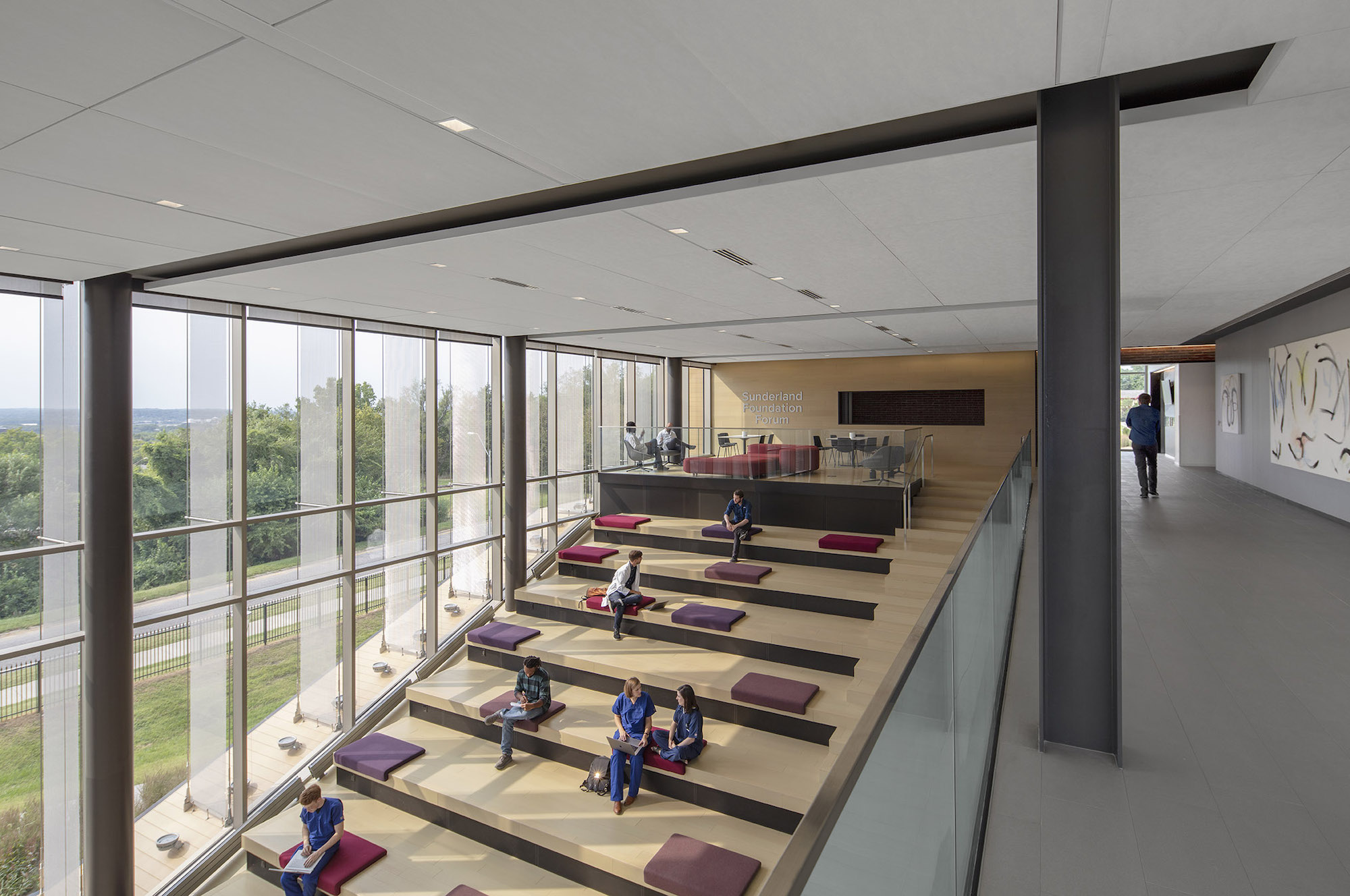
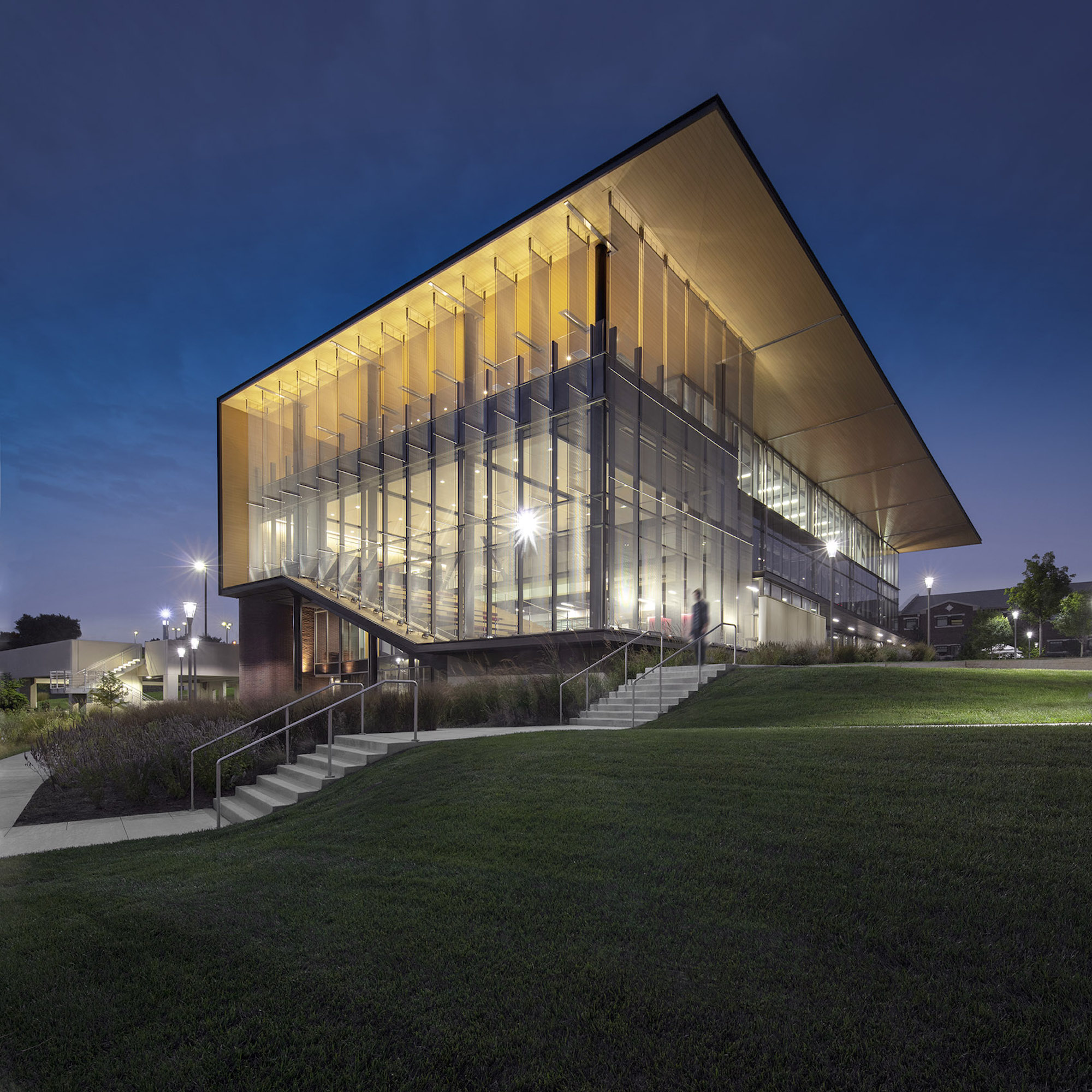
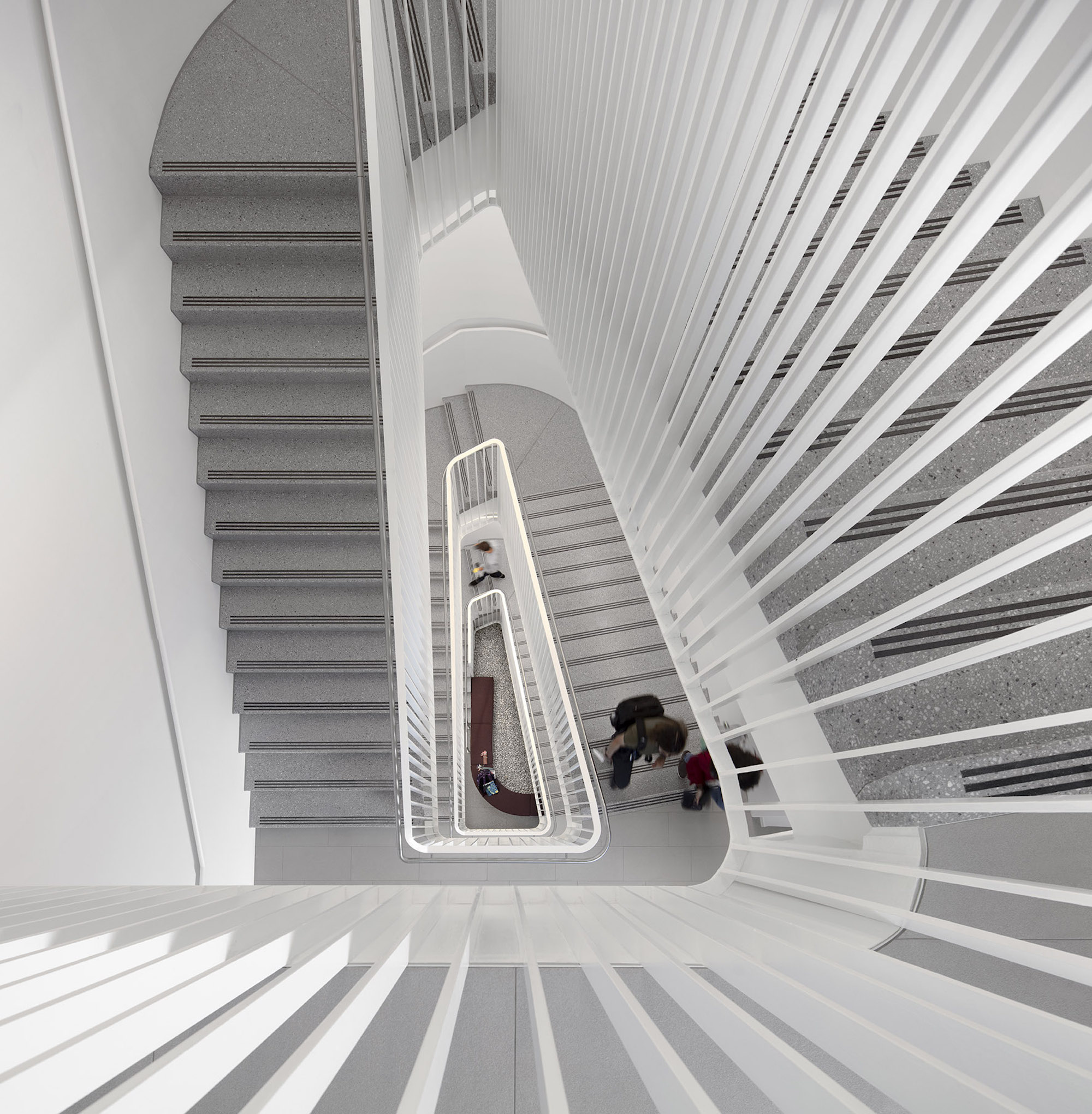
Users are introduced to the building through the connective, multi-level, 3,000 sf lobby that doubles as a public forum to provide waiting, colloquia, study, and briefing functions. The raked, glazed two-story lobby and third-floor terrace appear to hover over the ground plane to offer a panoramic view of downtown Kansas City. The pavilion is wrapped with a single folding-plane gesture, which begins at the articulated lobby floor, bends upward to form the north wall, and crests to create a dramatically extended roof to help shade the south-facing glass elevation.
Transparency guided the articulation of the glass curtain wall to showcase the next-generation medical education environments within. The glazing defines the visually open facility, highlighting its learning activities during the day, and transforming into a subtle, illuminated beacon on campus at night. Evoking the heritage of the campus’ brick-clad buildings, the materials palette is rounded out with low-maintenance brick, metal panel, and precast concrete.
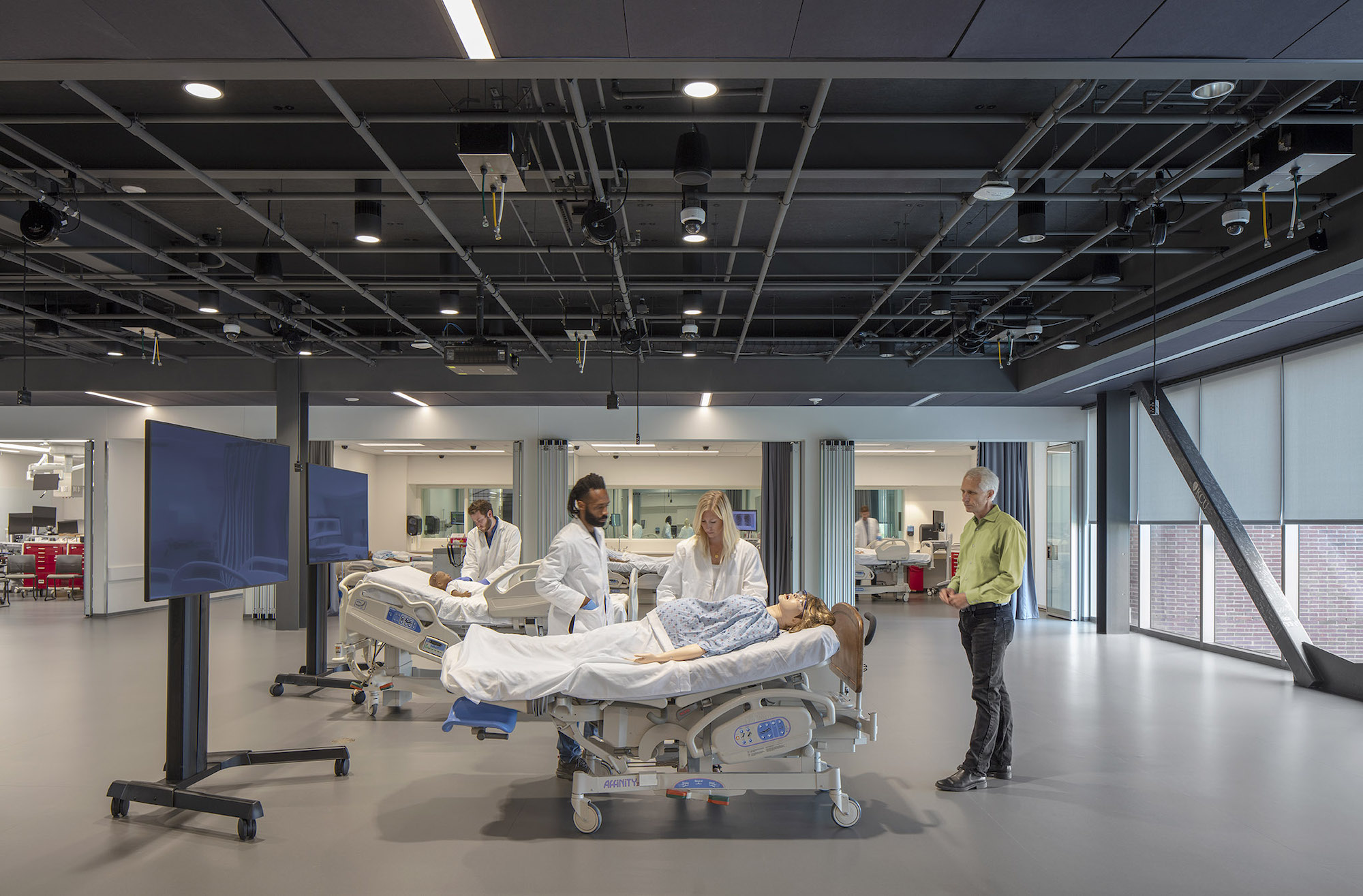
The building can adapt to changes in medical curriculum and pedagogy with a 2,800 sf simulation deck, clinical skills suite with 22 mock exam rooms, a 6,500 sf osteopathic manipulative medicine lab, and multi‐use forum that support multiple functions. The simulation suite houses an innovative and adaptable “black box” stage that can accommodate small-scale scenarios as well as large trauma events. The open ceiling utilizes a theater grid of steel tubes to supply air, vacuum, electricity, and data for simulation use, as well as hanging lights and simulation equipment that can be freely arranged throughout the space.
Situating the simulation suite at grade with its 40-foot opening to the exterior enables the space to expand onto the adjacent campus quad. Operable walls along exam rooms allow the standardized patient lounge to flex as a health assessment lab or serve as an after-hours student study space.
On the project team:
Owner and/or developer: Kansas City University of Medicine and Biosciences
Design architect: CO Architects
Architect of record: Helix Architecture + Design
MEP engineer (and lighting): Henderson Engineers
Structural (and civil) engineer: Walter P Moore
Acoustical, AV/IT Design: The Sextant Group (now NV5)
Landscape: Confluence
General contractor/construction manager: JE Dunn Construction
KCUMB Video from CO Architects on Vimeo.
A vision of the future of medical education buildings
Here is the design statement from architect CO Architects:
The Center for Medical Education Innovation (CMEI) project for Kansas City University of Medicine and Biosciences (KCU) in Kansas City, MO, is the first of a new generation of buildings at KCU aimed at fostering growth within the ever-evolving field of osteopathic medical education. Designed by CO Architects in collaboration with Helix Architecture + Design, the $33-million CMEI has an iconic design that bridges KCU’s history and traditions with its forward-looking role as a leader in osteopathic medicine.
Sited on approximately 4.5 acres of previously undeveloped green space on the west edge of campus, the CMEI helps define a new campus entry and Lower Quad. The pavilion-like four-story building takes advantage of the site’s sloping topography while maintaining the scale of the existing campus by lowering one floor into the sloping site, creating the illusion of a three-story structure on the campus quad.
Users are introduced to the building through the connective, multi-level, multi-functional, 3,000-square-foot lobby that doubles as a public forum to provide waiting, colloquia, study, and briefing functions. The raked, glazed two-story lobby and third-floor terrace appear to hover over the ground plane to offer a panoramic view of downtown Kansas City, thereby visually connecting the university with the city to emphasize KCU’s mission of improving the well-being of the larger community. The pavilion is wrapped with a single folding-plane gesture, which begins at the articulated lobby floor, bends upward to form the north wall, and then crests to create a dramatically extended roof to help shade the south-facing glass elevation.
Transparency is a key element of the design of the CMEI, guiding the articulation of the glass curtain wall to showcase the next-generation medical education environments within. The glazing defines the visually open facility, highlighting its learning activities during the day, and transforming into a subtle, illuminated beacon on campus at night. The building is a dramatic anchor to a future new campus entry. Evoking the heritage of the campus’ brick-clad buildings, the materials palette is rounded out with low-maintenance brick, metal panel, and precast concrete.

Paramount to the success of the project is the building’s ability to adapt to changes in medical curriculum and pedagogy, and for the programed spaces—a 2,800-square-foot simulation deck, clinical skills suite with 22 mock exam rooms, 6,500-square-foot osteopathic manipulative medicine lab, and multi‐use forum—to support multiple functions. The simulation suite houses an innovative and adaptable “black box” stage that can accommodate small-scale scenarios as well as large trauma events.
The open ceiling above utilizes a theater grid of steel tubes to supply air, vacuum, electricity, and data for simulation use, as well as hanging lights and simulation equipment that can be freely arranged throughout the space. Situating the simulation suite at grade with its 40-foot opening to the exterior enables the space to expand onto the adjacent campus quad. Operable walls along exam rooms allow the standardized patient lounge to flex as a health assessment lab, or serve as an after-hours student study space.
The design of the CMEI, which is LEED certified, addresses sustainability from multiple fronts. The building form was conceived to strengthen performance: It is oriented lengthwise in the east/west direction, so solar heat gain is easier to control on the longer north and south façades. The broad, 24-foot-deep cantilevered roof fully shades the south façade during the summer. Brick construction on the east façade blocks harsh early morning sunlight, and semi-transparent metal-mesh fins on the west side shade the glazing while maintaining the impressive views of the Kansas City skyline. The metal-mesh system, which features a horizontal pattern at 50% opacity, attaches to the building via ultra-thin cable rail, which allowed the design team to meet challenging wind-load requirements.
CMEI supports the University’s educational mission to train compassionate and competent leaders in osteopathic medicine by creating a state-of-the-art facility that leverages active-learning and simulation-based training. Through its sensitive yet bold architectural design—with the key themes of transparency and multi functionality—the building reflects both the University’s heritage and tradition as well as its vision for the future of medical education and community engagement.




Related Stories
Architects | Apr 6, 2023
Design for belonging: An introduction to inclusive design
The foundation of modern, formalized inclusive design can be traced back to the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) in 1990. The movement has developed beyond the simple rules outlined by ADA regulations resulting in features like mothers’ rooms, prayer rooms, and inclusive restrooms.
Sports and Recreational Facilities | Mar 30, 2023
New University of St. Thomas sports arena will support school's move to Division I athletics
The University of St. Thomas in Saint Paul, Minn., last year became the first Division III institution in the modern NCAA to transition directly to Division I. Plans for a new multipurpose sports arena on campus will support that move.
Designers | Mar 28, 2023
Inclusive design requires relearning how we read space
Pulling from his experience during a campus design workshop, David Johnson, AIA, LEED AP, encourages architects to better understand how to design spaces that are inclusive for everyone.
Healthcare Facilities | Mar 26, 2023
UC Davis Health opens new eye institute building for eye care, research, and training
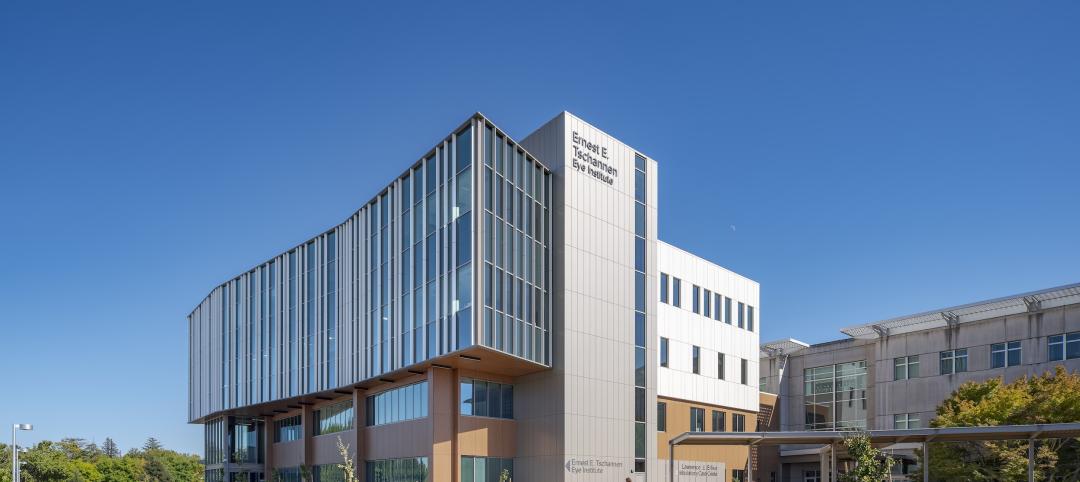
UC Davis Health recently marked the opening of the new Ernest E. Tschannen Eye Institute Building and the expansion of the Ambulatory Care Center (ACC). Located in Sacramento, Calif., the Eye Center provides eye care, vision research, and training for specialists and investigators. With the new building, the Eye Center’s vision scientists can increase capacity for clinical trials by 50%.
Sports and Recreational Facilities | Mar 15, 2023
Georgia State University Convocation Center revitalizes long-neglected Atlanta neighborhood
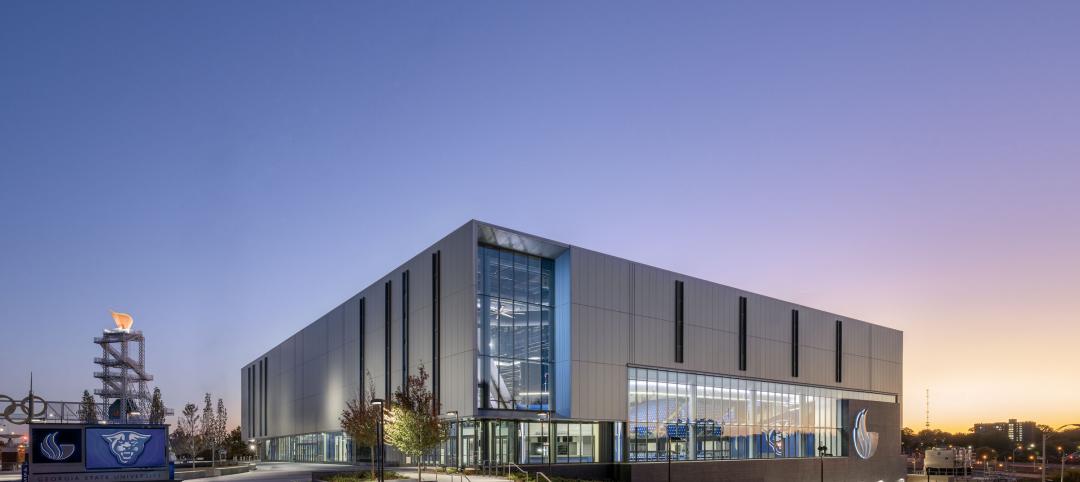
Georgia State University’s new Convocation Center doubles the arena it replaces and is expected to give a shot in the arm to a long-neglected Atlanta neighborhood. The new 200,000 sf multi-use venue in the Summerhill area of Atlanta is the new home for the university’s men’s and women’s basketball teams and will also be used for large-scale academic and community events.
Sponsored | Cladding and Facade Systems | Mar 15, 2023
Metal cladding trends and innovations
Metal cladding is on a growth trajectory globally. This is reflected in rising demand for rainscreen cladding and architectural metal coatings. This course covers the latest trends and innovations in the metal cladding market.
Student Housing | Mar 13, 2023
University of Oklahoma, Missouri S&T add storm-safe spaces in student housing buildings for tornado protection
More universities are incorporating reinforced rooms in student housing designs to provide an extra layer of protection for students. Storm shelters have been included in recent KWK Architects-designed university projects in the Great Plains where there is a high incidence of tornadoes. Projects include Headington and Dunham Residential Colleges at the University of Oklahoma and the University Commons residential complex at Missouri S&T.
Virtual Reality | Feb 27, 2023
Surfing the Metaversity: The future of online learning?
SmithGroup's tour of the Metaversity gives us insight on bringing together physical and virtual campuses to create a cohesive institution.
University Buildings | Feb 23, 2023
Johns Hopkins shares design for new medical campus building named in honor of Henrietta Lacks
In November, Johns Hopkins University and Johns Hopkins Medicine shared the initial design plans for a campus building project named in honor of Henrietta Lacks, the Baltimore County woman whose cells have advanced medicine around the world. Diagnosed with cervical cancer, Lacks, an African-American mother of five, sought treatment at the Johns Hopkins Hospital in the early 1950s. Named HeLa cells, the cell line that began with Lacks has contributed to numerous medical breakthroughs.
Sustainability | Feb 9, 2023
University of Southern California's sustainability guidelines emphasize embodied carbon
A Buro Happold-led team recently completed work on the USC Sustainable Design & Construction Guidelines for the University of Southern California. The document sets out sustainable strategies for the design and construction of new buildings, renovations, and asset renewal projects.

















