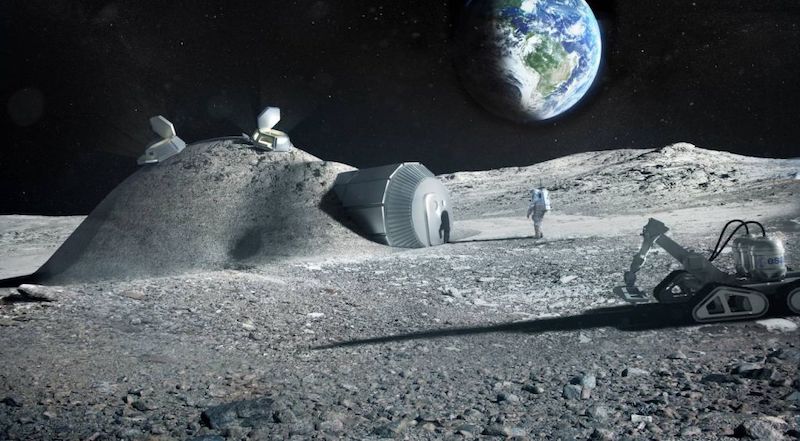
When it comes to building architecture in space, researchers, scientists, and architects have been offering up possible solutions for years. Concrete made from soil, ice shelters, and those grown from fungus have all been offered up as possible building materials. But a new possible building method may just use the most unique component of them all: urine.
Norwegian, Spanish, Italian, and Dutch scientists, together with the Advanced Concepts Team (ACT) of the European Space Agency (ESA), have conducted experiments using urea from urine as a superplasticizer for lunar geopolymer mixtures that can then be used to 3D print structures. The scientists presented their findings in the Journal of Cleaner Production.
In their paper titled "Utilization of urea as an accessible superplasticizer on the moon for lunar geopolymer mixters," the scientists say urea can break hydrogen bonds and therefore reduces the viscosities of many aqueous mixtures. And since urea is the second most abundant component of urine (water being the first), it would be readily available, even in a location as barren and distant as the moon.
See Also: Designing for the final frontier: Space architecture
"Addition of urea has been compared with polycarboxylate and naphthalene based superplasticizers, and with a control mixture without superplasticizer. When curing the sample containing urea at 80 °C, the initial setting time became longer. The samples containing urea or naphthalene-based superplasticizers could bear heavy weights shortly after mixing, while keeping an almost stable shape. Samples without superplasticizer or containing the polycarboxylate-based admixture were too stiff for mold-shaped formation after casting. Samples containing urea and naphthalene-based admixtures could be used to build up a structure without any noticeable deformation," according to the paper.
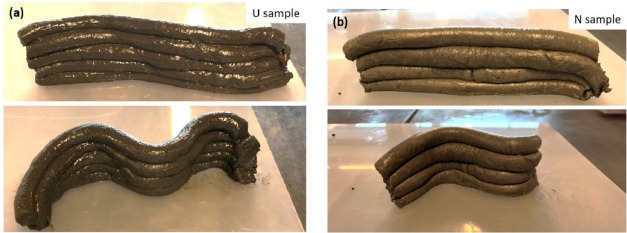
Additionally, the samples with urea also had higher compressive strength than the other two specimens containing superplasticizers, "and it continued to rise even after 8 freeze-thaw cycles."
The scientists conclude the paper by explaining further studies are needed to assess how the lunar regolith geopolymers will behave under the severe lunar conditions, which include a vacuum that can cause the volatile components to evaporate and large temperature fluctuations that can cause the structure to crack.
But if all goes according to plan, Moon Base Number 1 may have a more literal meaning than anyone ever anticipated.
Related Stories
| Apr 17, 2012
Princeton Review releases “Guide to 322 Green Colleges”
The guide profiles 322 institutions of higher education in the U.S. and Canada that demonstrate notable commitments to sustainability in their academic offerings, campus infrastructure, activities and career preparation.
| Apr 17, 2012
FMI report examines federal construction trends
Given the rapid transformations occurring in the federal construction sector, FMI examines the key forces accelerating these changes, as well as their effect on the industry.
| Apr 17, 2012
Alberici receives 2012 ASA General Contractor of the Year award
Alberici has been honored by the ASA eight times in the award’s nineteen-year history--more than any other general contractor in its class.
| Apr 16, 2012
Freeland promoted to vice president at Heery International
Recently named to Building Design+Construction’s 40 Under 40 Class of 2012.
| Apr 16, 2012
University of Michigan study seeks to create efficient building design
The result, the researchers say, could be technologies capable of cutting the carbon footprint created by the huge power demands buildings place on the nation’s electrical grid.
| Apr 16, 2012
UNT lab designed to study green energy technologies completed
Lab to test energy technologies and systems in order to achieve a net-zero consumption of energy.
| Apr 16, 2012
$80 million in export financing for solar project in India
The project, “Rajasthan Sun Technique Energy Private Limited,” is a subsidiary of Reliance Power and is being co-financed by the Asian Development Bank and FMO, the Dutch development bank.
| Apr 13, 2012
Goettsch Partners designs new music building for Northwestern
The showcase facility is the recital hall, an intimate, two-level space with undulating walls of wood that provide optimal acoustics and lead to the stage, as well as a 50-foot-high wall of cable-supported, double-skin glass
| Apr 12, 2012
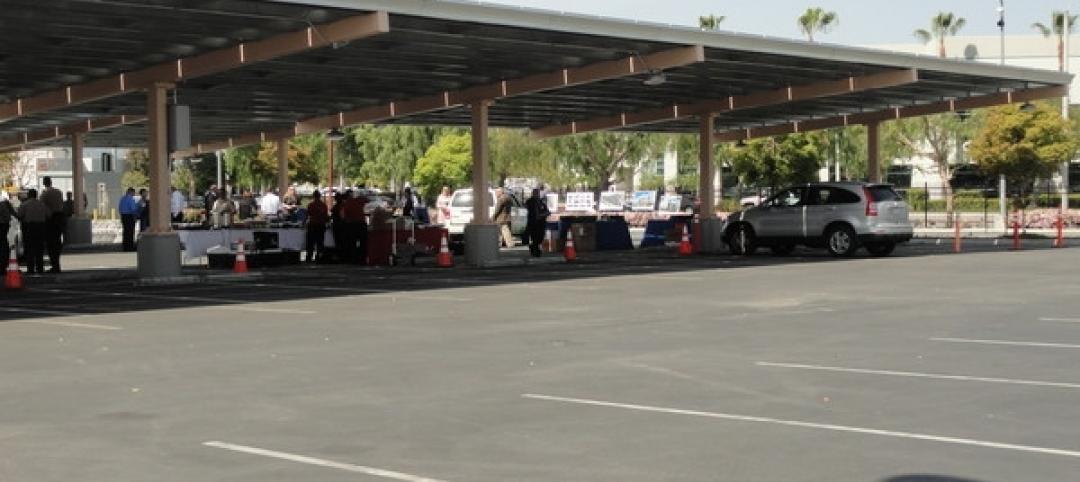
Solar PV carport, electrical charging stations unveiled in California
Project contractor Oltman Construction noted that the carport provides shaded area for 940 car stalls and generates 2 MW DC of electric power.
| Apr 10, 2012
JE Dunn completes two medical office buildings at St. Anthony’s Lakewood, Colo. campus
Designed by Davis Partnership Architects, P.C., Medical Plaza 1 and 2 are four-story structures totaling 96,804-sf and 101,581-sf respectively.















