With increasing demand to reduce the cost of operation, healthcare leadership is challenging their facility engineers to increase efficiency of the buildings they manage. Healthcare owners are struggling with the need to improve the bottom line with limited capital to spend on projects even with the best rate of return. The return on investment is typically much more attractive and more visible when related to the addition of clinical services as opposed to an investment in infrastructure.
However, studies have shown that when looking at the total lifecycle cost for a healthcare facility, 87 percent of the total cost is spent once healthcare owners start operating the new facility, with almost half of that cost allocated to utilities. The right approach during the planning, design and construction of a new facility can yield a positive return on investment and lower the overall cost basis for ongoing operations.
Form Follows Function
As with any new endeavor, the challenge is to have the right strategy, process and tools and then utilize the latest technology and systems to achieve maximum efficiencies. To have effective facility management, healthcare owners must invest the time to determine how to best manage and operate their facilities. With little to no additional premium in construction, systems can be incorporated into the design of a new facility project that will meet the technical capabilities of existing staff. If additional capabilities are required to meet the new systems goals, identification should be made early to allow for proper training and implementation. Additionally, a clear understanding of the volume of operations that will be outsourced will have an impact on the type of systems that will be built. In architecture, the phrase form follows function is often used. This is highly applicable to systems development as well.
Vital to success is the creation of an infrastructure plan concept. Healthcare leadership can implement this critical step in conjunction with a facility master plan. Development of the plan should begin with a review of the following:
1. Hospital leadership’s vision as it relates to focus on “non-core” services
2. Existing staff capabilities and their readiness to maintain complex systems
3. Number of full-time employees and level of staffing
4. Cost of purchasing utilities
5. Level of outsourcing as it relates to preventive maintenance and service contracts
6. Availability of skilled workforce in the market
7. Hospital’s financial strength to absorb the skilled workforce
8. Structure - single entity or part of a larger system
9. Level of sharing workforce within the hospital system
10. Centralization options within the system
11. Standardization within the hospital system (inventory and purchasing strength)
12. Method of acquiring and purchasing service contracts
13. Number and location of off-site facilities — owned verses leased
14. Energy baseline for the existing facilities
15. Level of modernization and implementation of the right technology
Reviewing, evaluating and developing strategies to close the gaps in the data discussed above forms the basis of an infrastructure plan concept.
As more hospitals are becoming part of larger systems, opportunities exist to capitalize on the economies of scale. Healthcare leaders are experiencing increased responsibility for managing multiple locations, many of which are off-site. Centralizing operations, negotiating and bundling service contracts for the entire system, implementing the right technology to network all facilities, eliminating duplications with staffing and “right staffing” are all areas in which savings can be realized.
To reduce the utility costs, many are negotiating new purchasing agreements utilizing large purchasing groups. However, the demand side of business requires additional investments to also reduce the cost of consumption. With limited resources and capital available, creative measures that require minimal investment need to be implemented to reduce the demand.
Streamlining Operations
● Utilize the latest in technology to reduce the energy cost and improve staffing efficiencies by standardizations, centralizations and sharing resources. Examples of these initiatives include ensuring all systems are commissioned during any new installation and identifying the utility baseline and Energy Star rating and comparing to industry standards.
● Conduct retro-commissioning of the existing systems at locations where there are opportunities to reduce cost. Identify any deficiencies and shortcomings. Opportunities to reduce cost may be as important as reducing liabilities by ensuring systems are operating optimally, per code and can provide patient comfort and safety.
● Ensure that existing service contractors and staff make necessary corrections to systems. Typically most are processed through the existing maintenance work order system. Experience has shown that the majority of such corrections require minimum investments.
● Provide continuous commissioning via a remote monitoring program to identify “bad habits” and modify the way the systems are maintained and operated in order to reduce costs.
● Make adjustments and correct bad habits to optimize performance and reduce energy consumption. These adjustments typically require limited expenditure.
● Utilize technology to share information between facilities and improve staff efficiencies. Examples are dispatching more trained staff from a central location or reduce the staffing on remote locations by reporting alarms to a central location.
It should be noted that the latter steps cannot be implemented unless more advanced energy management and remote monitoring capabilities are in place. The implementation of such technologies will be cost prohibitive unless implemented while a major capital project takes place. This re-emphasizes the importance of planning and having the right process in place during project launch and delivery.
Conclusion
Ultimately, the direction taken to create a more efficient building and systems must be strategic. If an organization is planning a capital expansion there will be more tools and options with which to work. However, if there is no immediate capital plan to be the catalyst for this effort, then retrofit tactics could be employed. By following a structured plan through the capital delivery process a more efficient building can be achieved. The simplistic formula begins with the right concept that is an extension of the strategic vision.
Related Stories
Giants 400 | Jan 15, 2024
Top 130 Hospital Facility Architecture Firms for 2023
HKS, HDR, Stantec, CannonDesign, and Page Southerland Page top BD+C's ranking of the nation's largest hospital facility architecture and architecture engineering (AE) firms for 2023, as reported in the 2023 Giants 400 Report.
Healthcare Facilities | Jan 7, 2024
Two new projects could be economic catalysts for a central New Jersey city
A Cancer Center and Innovation district are under construction and expected to start opening in 2025 in New Brunswick.
Designers | Jan 3, 2024
Designing better built environments for a neurodiverse world
For most of human history, design has mostly considered “typical users” who are fully able-bodied without clinical or emotional disabilities. The problem with this approach is that it offers a limited perspective on how space can positively or negatively influence someone based on their physical, mental, and sensory abilities.
Healthcare Facilities | Dec 19, 2023
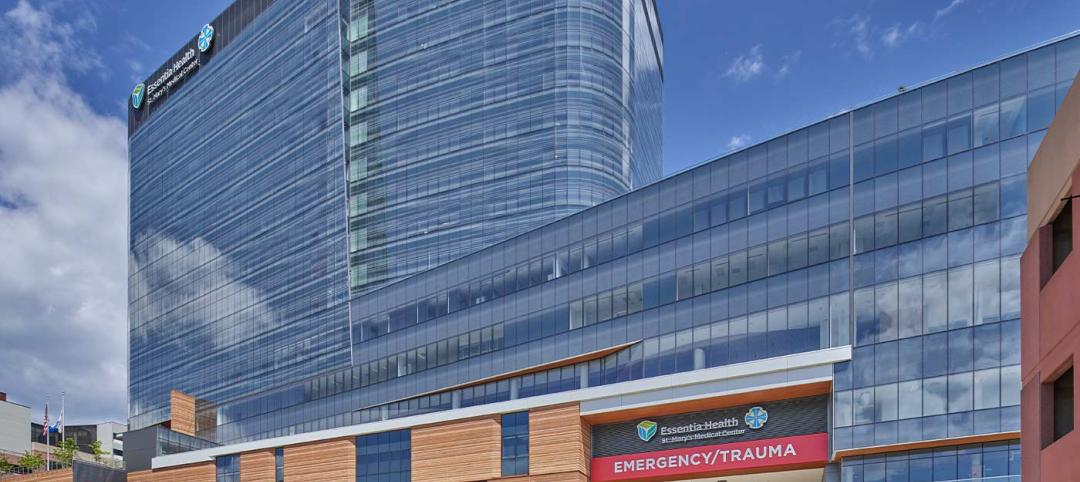
A new hospital in Duluth, Minn., is now the region’s largest healthcare facility
In Duluth, Minn., the new St. Mary’s Medical Center, designed by EwingCole, is now the largest healthcare facility in the region. The hospital consolidates Essentia Health’s healthcare services under one roof. At about 1 million sf spanning two city blocks, St. Mary’s overlooks Lake Superior, providing views on almost every floor of the world’s largest freshwater lake.
Healthcare Facilities | Dec 7, 2023
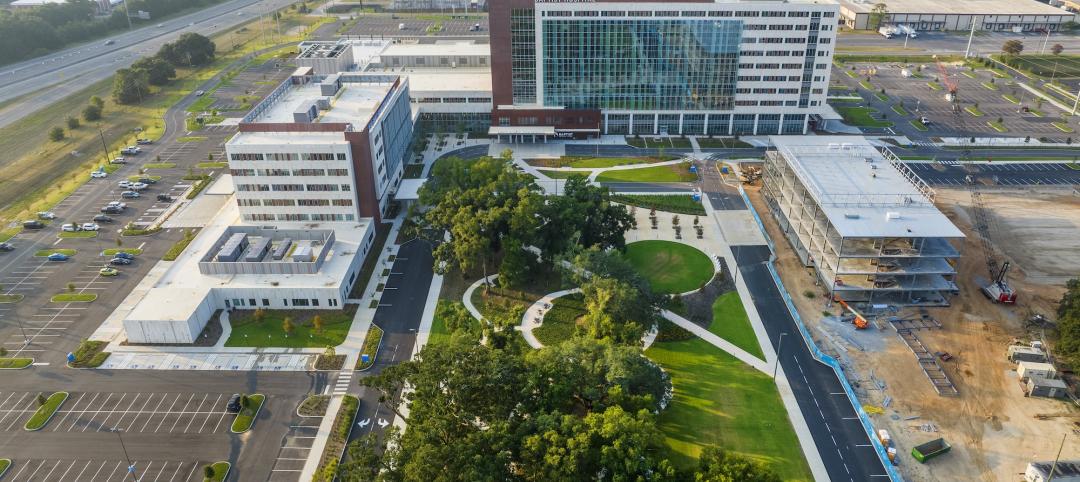
New $650 million Baptist Health Care complex opens in Pensacola
Baptist Health Care’s new $650 million healthcare complex opened recently in Pensacola, Fla. Featuring a 10-story, 268-bed hospital, the project “represents the single-largest investment in the healthcare history of northwest Florida,” said Gresham Smith project executive Robert “Skip” Yauger, AIA, LEED AP. The 602,000 sf Baptist Hospital is equipped with a Level II trauma center that provides 61 exam rooms and three triage areas.
Engineers | Nov 27, 2023
Kimley-Horn eliminates the guesswork of electric vehicle charger site selection
Private businesses and governments can now choose their new electric vehicle (EV) charger locations with data-driven precision. Kimley-Horn, the national engineering, planning, and design consulting firm, today launched TREDLite EV, a cloud-based tool that helps organizations develop and optimize their EV charger deployment strategies based on the organization’s unique priorities.
Healthcare Facilities | Nov 3, 2023
The University of Chicago Medicine is building its city’s first freestanding cancer center with inpatient and outpatient services
The University of Chicago Medicine (UChicago Medicine) is building Chicago’s first freestanding cancer center with inpatient and outpatient services. Aiming to bridge longstanding health disparities on Chicago’s South Side, the $815 million project will consolidate care and about 200 team members currently spread across at least five buildings. The new facility, which broke ground in September, is expected to open to patients in spring 2027.
Sponsored | | Oct 17, 2023
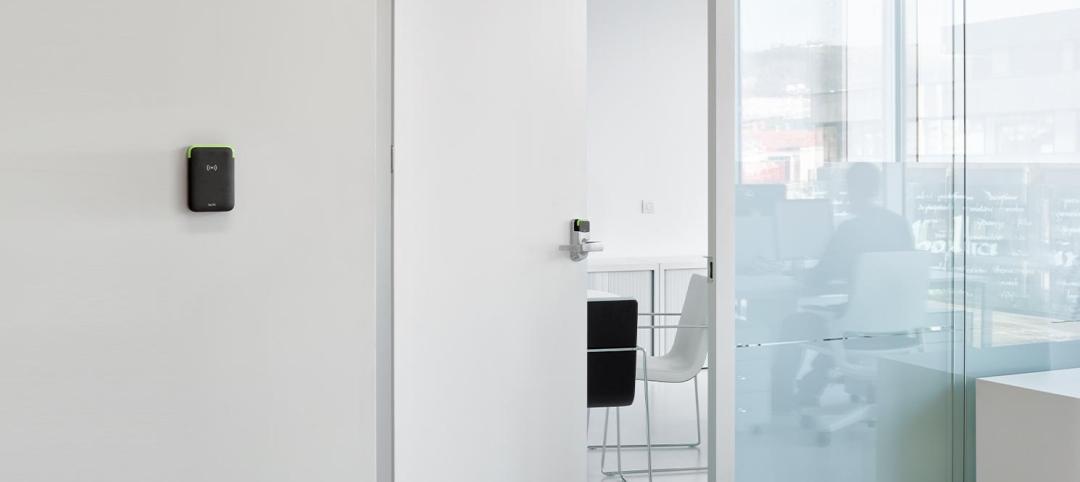
The Evolution of Medical Facility Security
As the healthcare system grows, securing these facilities becomes ever more challenging. Increasingly, medical providers have multiple facilities within their networks, making traditional keying systems and credentialing impractical.
Healthcare Facilities | Oct 11, 2023
Leveraging land and light to enhance patient care
GBBN interior designer Kristin Greeley shares insights from the firm's latest project: a cancer center in Santa Fe, N.M.
Healthcare Facilities | Oct 9, 2023
Design solutions for mental health as a secondary diagnosis
Rachel Vedder, RA, LEED AP, Senior Architect, Design Collaborative, shares two design solutions for hospitals treating behavioral health patients.