LEED for Healthcare debuted in spring 2011, and certifications are now beginning to roll in. The first LEED-HC certified project, Group Health Cooperative’s new Puyallup (Wash.) Medical Center, is an outpatient site designed by CollinsWoerman, which opened at the end of 2012. The 53,000-sf project incorporates Lean design principles and the increasingly popular “medical home” concept; it was certified Gold this past April.
LEED-HC is the first of the LEED rating systems to institutionalize a prerequisite for Integrated Project Planning and Design, as well as an available credit for advanced coordination. These factors helped the Puyallup team—including GLY Construction and design-build MEP partners UMC, Prime Electric, and Patriot Fire Protection—rack up six Innovation points. In addition, the building earned credits in the new categories Connection to the Natural World, Water Use Reduction (medical equipment cooling), Community Contaminant Prevention/Airborne Releases, and PBT (persistent bioaccumulative toxins) Source Reduction.
Hot on the heels of Group Health’s win came the first LEED-HC Platinum certification: The W.H. and Elaine McCarty South Tower at Dell Children’s Medical Center of Central Texas, in Austin. The main Dell building became the world’s first LEED-NC Platinum-certified hospital in 2008, and the McCarty project, a 72-bed tower offering special services in epilepsy management and pediatric rehab, builds on the green track record established by owner Seton Healthcare Family.
Greenbuild coverage of Healthcare Firms brought to you by:
Important aspects of the certification included waste reduction and diversion, sustainable sourcing of materials, water efficiency, and avoidance of materials with known negative health effects. An advanced thermal envelope, high-efficiency glazing, reduced interior lighting power density (aided by copious use of LEDs), an enthalpy wheel, and photovoltaic systems augmented an important built-in benefit of the site: a district energy heating and cooling system with a co-generation plant.
The Building Team, led by contractor The Beck Group, also scored six Innovation points, including two LEED-HC pilot credits involving reduction of PBTs and phthalates. To earn these credits, the team had to be particularly careful to spec materials, furniture, and equipment that do not contain mercury, lead, cadmium, copper, and other suspect chemicals.
Methodist Olive Branch (Miss.) Hospital is also enrolled in LEED-HC and is targeting Gold certification. The 100-bed, 210,000-sf project opened in August and is the first hospital in the nation to use dynamic photoelectric glazing, which is manufactured by View Inc. in a nearby factory. The product was installed in the two-story lobby to reduce energy needs for heating and cooling.
The hospital also has a geothermal heat pump system encompassing 206 units, including one in each patient room. “Our designers created special soundproof closets to house the pumps, allowing patients to enjoy individualized climate control and a consistently quiet, calming atmosphere,” says Greg Gore, AIA, NCARB, Principal at Gresham, Smith and Partners. Using IPD, Gresham, Smith and its Building Team partners Smith Seckman Reed and Turner Construction designed and built the project in 23 months.
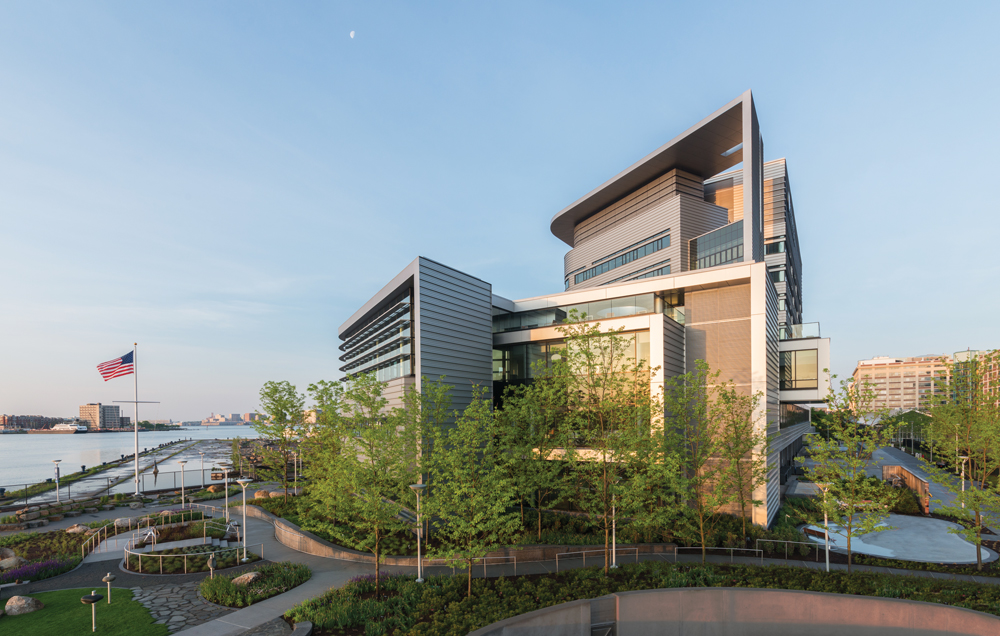
The 132-bed Spaulding Rehabilitation Hospital was built on a brownfield parcel in the Charlestown (Mass.) Navy Yard, opening just in time to serve victims of the Boston Marathon bombing. Resiliency planning included placement of HVAC infrastructure on the roof rather than underground or at ground level. Vegetated roofs mitigate stormwater runoff and reduce cooling loads and the heat island effect. On the third and fourth floors, therapeutic terraces help patients and their families stay connected with the natural environment. On the Building Team: Perkins+Will (architect), Thompson Consultants and Buro Happold Consulting Engineers (MEP), McNamara/Salvia (SE), Vanasse Hangen Brustlin (CE), Copley Wolff Design Group (landscape architect), Haley & Aldrich (environmental/geotechnical), and Walsh Brothers (CM). PHOTO: © JAMES STEINKAMP PHOTOGRAPHY
Among the first large government projects enrolled in LEED-HC is a VA Healthcare Center under way in Kernersville, N.C., anticipating Gold certification. Lend Lease Healthcare is designing, building, and managing the $150 million, 280,000-nsf facility in collaboration with architect Perkins Eastman. The center will support area veterans with primary care, plus mental health, dental, diagnostic, laboratory, pathology, radiology, and ancillary services.
A few unusual sustainable strategies will be thrown into the mix, along with standards such as daylighting, high-efficiency HVAC, and a green roof. A stormwater retention pond will be landscaped with native species and will use a windmill for aeration, eliminating the need for electrically powered pumps. The windmill is planned as a distinctive centerpiece for a rehabilitation activity pathway that will circle the pond, fitting LEED-HC’s emphasis on patients’ connection to the outdoors.
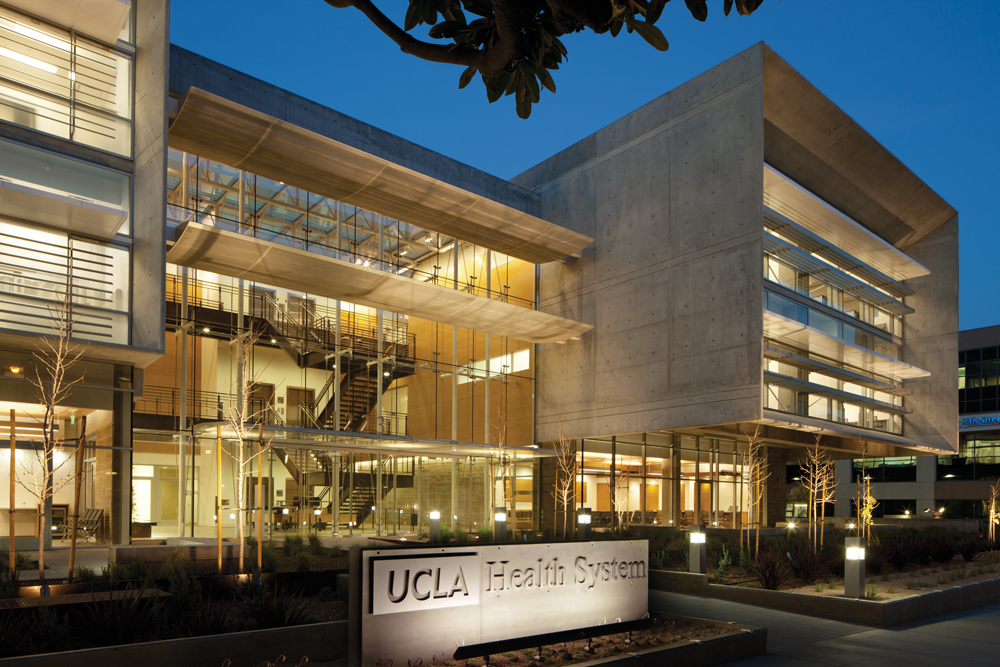
On the opposite coast, the UCLA Outpatient Surgery and Medical Building, in Santa Monica, is slated for Gold under LEED-NC. Winner of a 2013 National Healthcare Design Award from the AIA Academy of Architecture for Health in the Built category, the facility was designed to facilitate linkages between the community and UCLA’s medical students and faculty.
The building provides eight operating rooms for outpatient surgery, oncology treatment facilities (including two linear accelerators), a pharmacy, and academic and medical offices. The generous number of ORs was intended to help relieve strain on inpatient facilities at the nearby UCLA Medical Center.
Michael W. Folonis Architects created the 50,000-sf building to interface with an automated underground parking lot, which uses cranes to stage up to 250 vehicles in and out of a parking lobby. The equipment greatly reduces the need for lighting and HVAC that would normally be required for a parking garage, as well as the environmental impact of idling vehicles. Additional green features include passive solar design plus extensive PV arrays, recycled and sustainable materials (notably, a large amount of bamboo flooring and walls), and water-conserving fixtures and landscaping.
Methodist Olive Branch Hospital is on track for LEED-HC Gold. The Mississippi hospital includes two sustainable technologies that are unusual for inpatient facilities: photochromic glass, which is manufactured in a local factory, and geothermal heat pumps, with each patient room served by its own unit. “Our team was committed to providing a new hospital that would play a vital role in the community and that would also reflect our organization’s commitment to building innovative, sustainable facilities,” says David Rosenbaum, VP/Facility Management, Methodist Le Bonheur Healthcare. PHOTO: JEFFREY JACOBS
With high-profile stories of healthcare facilities strained by extreme weather events such as Superstorm Sandy and the Joplin, Mo., tornado, resiliency is also becoming a priority for the sector. Green thinking incorporates life cycle considerations, since deterioration, destruction, and reconstruction always entail some negative environmental impacts.
Spaulding Rehabilitation Hospital in Charlestown, Mass., exemplifies the resiliency trend. The 262,000-sf LEED Gold building, designed by Perkins+Will, was built on a remdiated brownfield parcel in the Charlestown Navy Yard. To protect infrastructure from any future rises in sea level, the main floor was raised a foot above ground level, and all HVAC equipment was located on the roof. Automatic operable windows were provided to the three-story wing that houses the therapeutic gym and pool, which has systems separate from those in the bed tower. The windows will provide ventilation even in times of power outages.
Patient room windows can also be operated on an emergency basis, and owner Partners HealthCare is measuring the effects of opening windows in some controlled zones to determine possible effects on air quality, with an eye toward future projects.
The LEED-NC Gold Benjamin Russell Hospital for Children at Children’s of Alabama, Birmingham, is the nation’s third-largest pediatric hospital, encompassing 772,000 sf, 248 beds, and 48 NICU bassinets. Green strategies include daylighting, a rooftop healing garden, and use of air-conditioning condensate for landscape irrigation and equipment cooling. Salvaged materials from the demolition of two existing buildings were incorporated. The Building Team: KLMK Group (project manager), HKS Inc. in partnership with Giattina Aycock Studio (architects), HKS Inc. (interiors, SE, programming), ccrd (MEP), Walter Schoel Engineering Co. (CE), Macknally Land Design (landscape architect), and Hoar Construction in partnership with BE&K (CM). PHOTO: HKS
Related Stories
| Dec 29, 2014
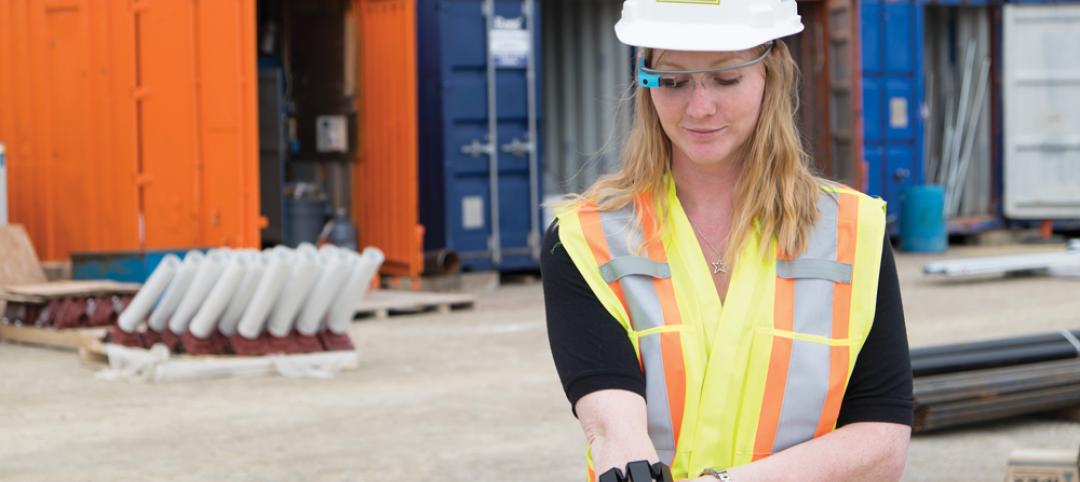
Wearable job site management system allows contractors to handle deficiencies with subtle hand and finger gestures [BD+C's 2014 Great Solutions Report]
Technology combines a smartglass visual device with a motion-sensing armband to simplify field management work. The innovation was named a 2014 Great Solution by the editors of Building Design+Construction.
| Dec 29, 2014
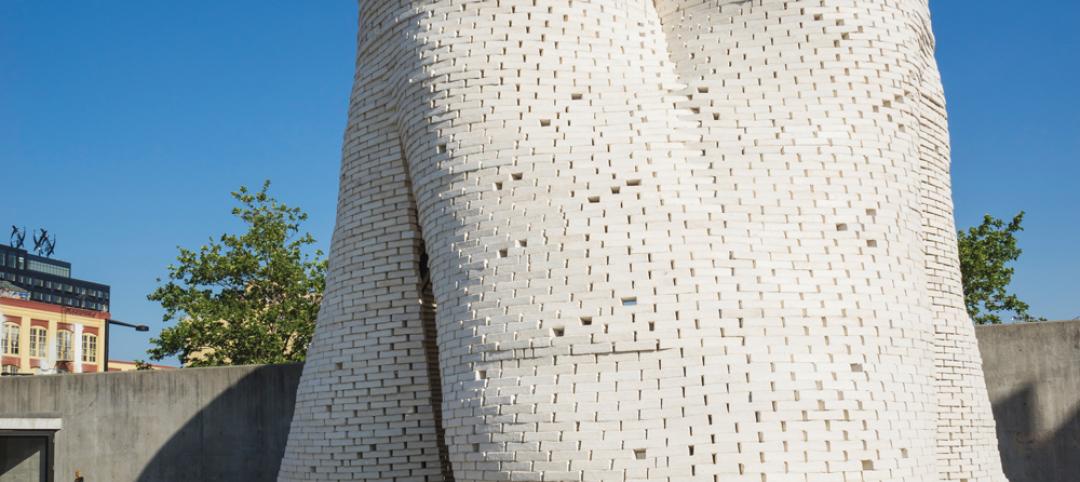
From Ag waste to organic brick: Corn stalks reused to make construction materials [BD+C's 2014 Great Solutions Report]
Ecovative Design applies its cradle-to-cradle process to produce 10,000 organic bricks used to build a three-tower structure in Long Island City, N.Y. The demonstration project was named a 2014 Great Solution by the editors of Building Design+Construction.
| Dec 29, 2014
14 great solutions for the commercial construction market
Ideas are cheap. Solutions are what count. The latest installment in BD+C's Great Solutions series presents 14 ways AEC professionals, entrepreneurs, and other clever folk have overcome what seemed to be insoluble problems—from how to make bricks out of agricultural waste, to a new way to keep hospitals running clean during construction.
| Dec 29, 2014
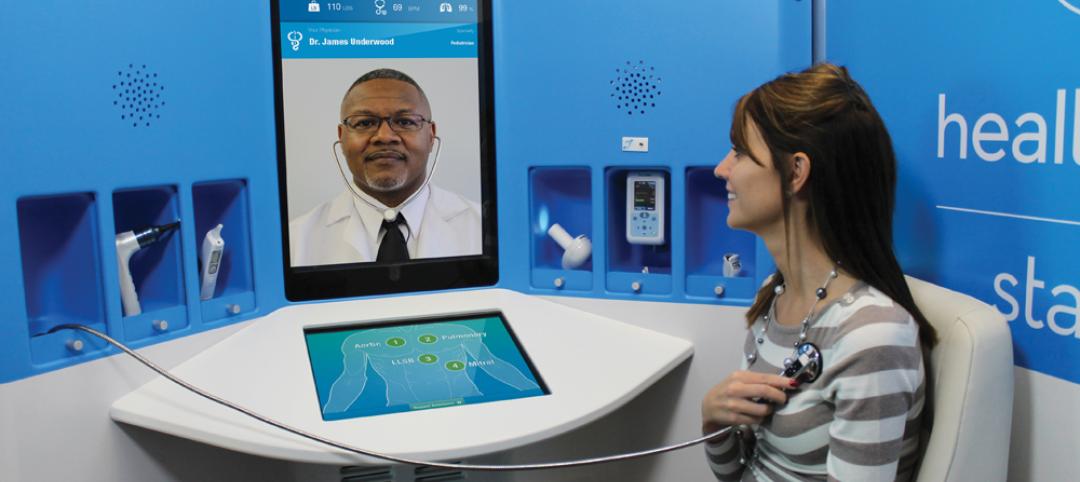
HealthSpot station merges personalized healthcare with videoconferencing [BD+C's 2014 Great Solutions Report]
The HealthSpot station is an 8x5-foot, ADA-compliant mobile kiosk that lets patients access a network of board-certified physicians through interactive videoconferencing and medical devices. It was named a 2014 Great Solution by the editors of Building Design+Construction.
| Dec 28, 2014
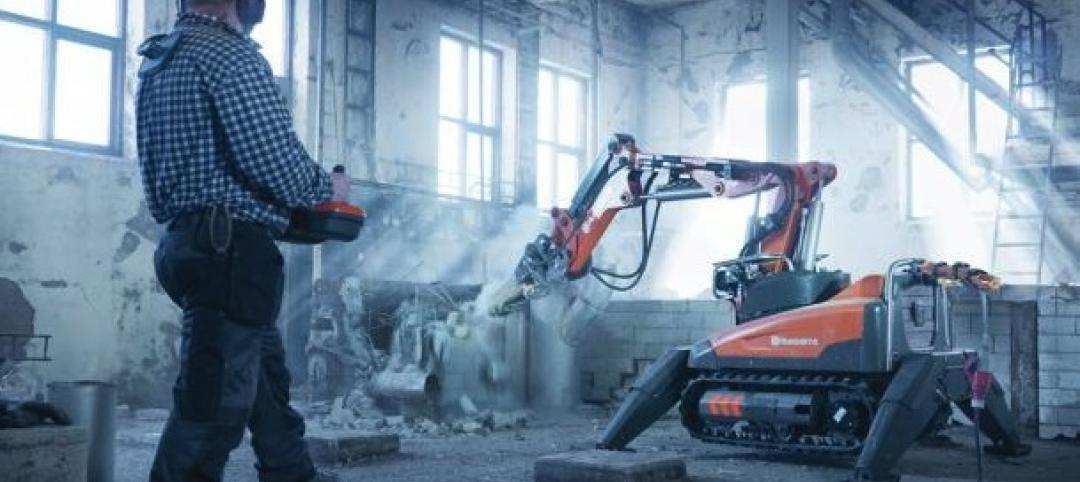
Robots, drones, and printed buildings: The promise of automated construction
Building Teams across the globe are employing advanced robotics to simplify what is inherently a complex, messy process—construction.
BIM and Information Technology | Dec 28, 2014
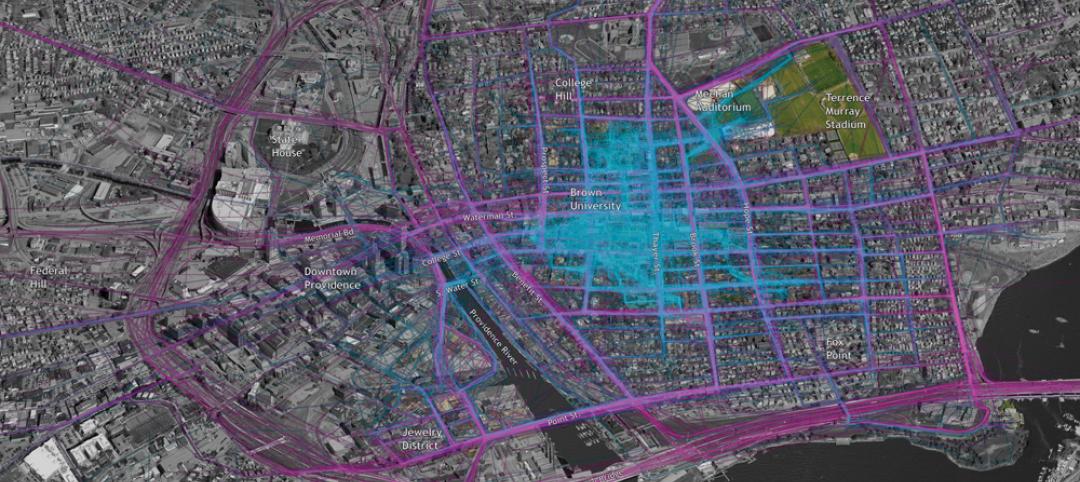
The Big Data revolution: How data-driven design is transforming project planning
There are literally hundreds of applications for deep analytics in planning and design projects, not to mention the many benefits for construction teams, building owners, and facility managers. We profile some early successful applications.
| Dec 28, 2014
AIA course: Enhancing interior comfort while improving overall building efficacy
Providing more comfortable conditions to building occupants has become a top priority in today’s interior designs. This course is worth 1.0 AIA LU/HSW.
| Dec 28, 2014
6 trends steering today's college residence halls
University students want more in a residence hall than just a place to sleep. They want a space that reflects their style of living and learning.
| Dec 28, 2014
Using energy modeling to increase project value [AIA course]
This course, worth 1.0 AIA LU/HSW, explores how to increase project value through energy modeling, as well as how to conduct quick payback and net present value studies to identify which energy strategies are most viable for the project.
| Dec 28, 2014
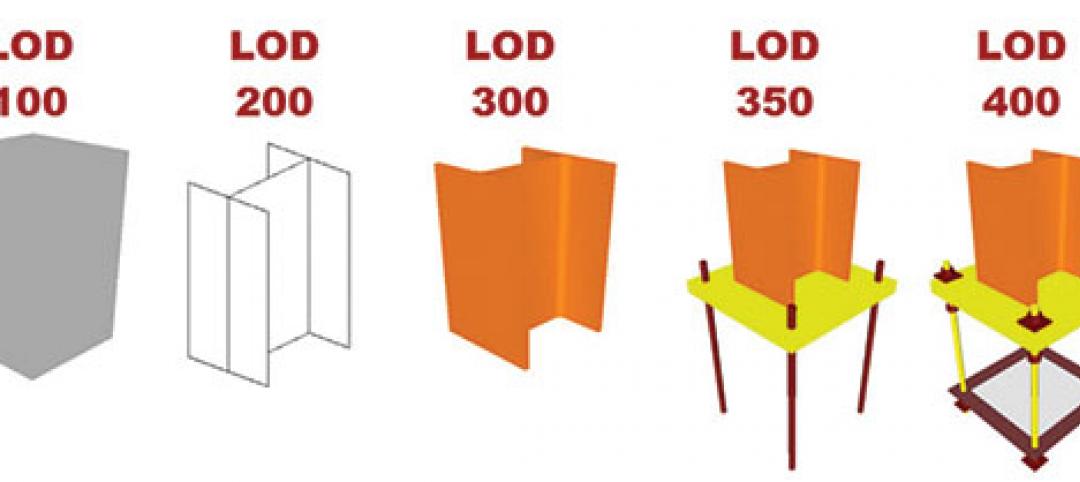
The lowdown on LODs: Bringing clarity to BIM
These days, BIM is par for the course across most facets of design. But a lot of the conversation surrounding BIM still lacks clarity due to ambiguous terminology, a lack of clear-cut guiding illustrations, and widely varying implementation, writes GS&P's John Scannell.