Last month, I wrote about how automation and AI are dramatically changing all four fundamental relationships between buildings and machines. For example, nanotechnology, which manipulates individual atoms and molecules to assemble things, could make the modernist metaphor of a “machine for living in” into reality, since the building would actually be composed of many tiny machines.
In fact, that’s not quite accurate. The definition of “machine” is “an apparatus using or applying mechanical power and having several parts, each with a definite function and together performing a particular task.”
So machines are made of distinct parts, cobbled together to fulfill a function. They are characterized by their composition, as assemblages of singular bits and pieces in which the whole is greater than the sum.
SEE ALSO: Assessing AI's impact on the AEC profession and the built environment
But nanotech will completely change this. When entire buildings can be shaped from microscopic components, the visible distinction between the individual parts will evaporate. A structure built from invisible machines will not appear to be a machine at all, since it no longer will be perceived as an assembly of parts. An edifice made of congealed cybernetic butter will look to be all whole, no parts. The very concept of a “building” could become meaningless, since it will no longer be “built” in any traditional way.
Remember “Terminator 2”? Arnold Schwarzenegger’s T-800 is a machine: steel and servos wrapped in human skin. Robert Patrick’s T-1000 is made of liquid metal (“mimetic polyalloy”). He’s like sentient mercury, morphing into any shape he needs. A nanotech building (“nanotecture”?) would make conventional structures seem like Robby the Robot (of “Forbidden Planet” fame).
Buttery buildings could change everything we think and know about architecture. Frank Lloyd Wright felt that architectural form should stem from the inherent “nature” of its materials: “Each material speaks a language of its own.” In his mind, the proportions, heft, and texture of brick logically translated into structures such as the Robie House, which extends horizontally and hugs the land. But when the constituent parts of a building are too small to be seen with the naked eye, the relationships between form and materials will change. What is the “language” of a nanobot?
Because the character of a building could vary upon command—hard and opaque one minute, soft and transparent the next—the fabric of buildings could become fluid, fluctuating states from solid to liquid to gas and back. The notion of truth in materials will become irrelevant. In fact, the word material could go away. When the basic building blocks of architecture have no strict definition, structure and substance could separate. Matter may not matter.
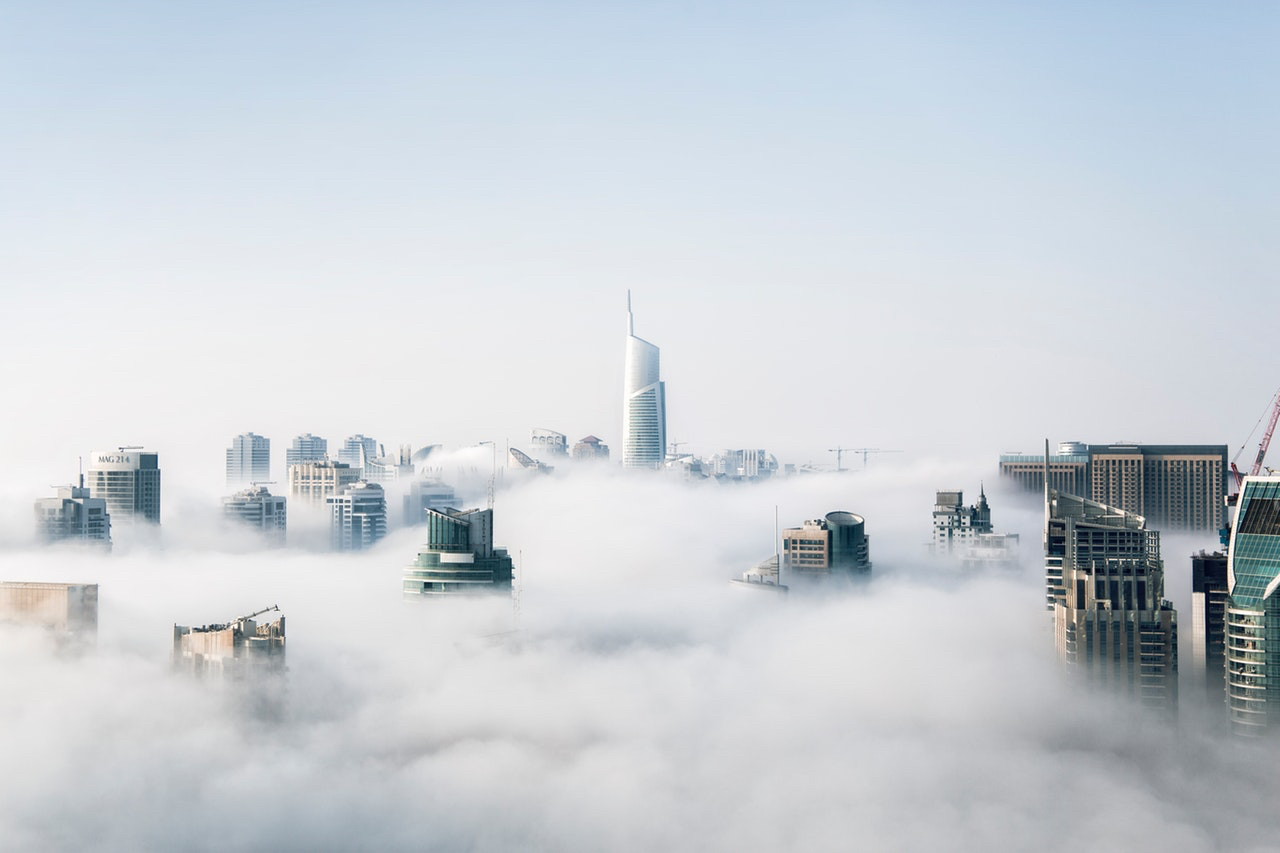
Could there come a time when buildings will become less about bricks and mortar and feel more like mists or fogs, vaguely enveloping space in ways we can barely picture now? What will it be like to live in a cloud?
Lance Hosey, FAIA, LEED Fellow, is a Design Director with Gensler. His book, The Shape of Green: Aesthetics, Ecology, and Design, has been an Amazon #1 bestseller in the Sustainability & Green Design category.
Related Stories
AEC Tech | Mar 26, 2019
Embracing collaboration tools from outside the AEC industry
Let's take a look at the available technologies from outside AEC that are seeing greater adoption within the industry.
AEC Tech | Mar 24, 2019
5 ways designers and builders can use business intelligence with data they already have
Tricky construction budgets, large project teams, and unique designs needing extensive coordination are all problems increasingly being handled with new software tools and data.
AEC Tech | Feb 8, 2019
BI(m): BIM data without models
A new breed of data tools creates a valuable opportunity for the next wave of BIM and facilities management, one where “pure data” is at the center, writes John Tobin of SMRT Architects.
AEC Tech | Jan 9, 2019
Our robotic future: Assessing AI's impact on the AEC profession and the built environment
This is the first in a series by Lance Hosey, FAIA, on how automation is disrupting design and construction.
3D Printing | Dec 7, 2018
Additive manufacturing heads to the jobsite
Prototype mobile 3D printing shop aims to identify additive manufacturing applications for construction jobsites.
AEC Tech | Sep 27, 2018
BD+C editors want your input on AEC technology
Please help us improve our editorial coverage by taking this brief survey.
Sponsored | AEC Tech | Sep 14, 2018
Sponsored webinar: Benefits of traceable construction
In this free 60-minute webinar, Keith Alcorn of FARO Technologies will talk about the concept of traceable construction and how 3D reality capture solutions provide portable, efficient, secure, and forward-looking solutions for data collection, pre-processing, and evaluation in the design, build and operating phase. September 18, 2:00 EST.
AEC Tech | Jul 24, 2018
Weidt Group’s Net Energy Optimizer now available as software as a service
The proprietary energy analysis tool is open for use by the public.
Accelerate Live! | Jul 17, 2018
Call for speakers: Accelerate AEC! innovation conference, May 2019
This high-energy forum will deliver 20 game-changing business and technology innovations from the Giants of the AEC market.
Accelerate Live! | Jun 24, 2018
Watch all 19 Accelerate Live! talks on demand
BD+C’s second annual Accelerate Live! AEC innovation conference (May 10, 2018, Chicago) featured talks on AI for construction scheduling, regenerative design, the micro-buildings movement, post-occupancy evaluation, predictive visual data analytics, digital fabrication, and more. Take in all 19 talks on demand.