Technology has always played a role in our work as architects and designers, but its effect has been more exponential the past few years.
We now have BIM modeling, data-driven design, iterative design tools along with cloud-based collaboration software that help us create more robust, meticulous buildings and components. For the past two years, many of us have worked from our homes, but these programs, virtual meeting software, and the cloud have kept us connected to our work and each other.
As we continue to lean into learning and mastering the latest technologies—as we should—we must not forget the foundational, fundamental skills that are still expected from us by our clients. These low-tech—and even no-tech—hallmarks, when used in conjunction with the latest tech, can help us design better projects and better communicate them with the outside world.
No Tech, No Matter
There are different demands on us as designers from our communities and the public realm down to architecture review boards. The public realm requires the ability to express yourself in a setting other than the office, sometimes a charged public environment, which can be challenging especially when not everyone wants to hear what you have to say.
We have an obligation to say the things that need to be said to benefit society. Oftentimes, finding that courage can be difficult. We’re not trained to participate in such an environment, but there are ways we can step into those conversations—with respect and dignity—and then own that moment.
The projects we work on are often complicated and may have a lot of stakeholders at the table. Many of these stakeholders may not see the whole purpose, best use or the full nature of what a building owes the end user and community around it. When their decisions start to turn in a tragic direction based on their rationale, sometimes we only have a few seconds of a gap in between to step in and communicate that full picture to get a project back on track.
For instance, when it comes to sustainability, we can talk about energy savings but some struggle to talk about the social responsibility we have. Those conversations need to happen as often as we talk about savings. Those conversations can change where investments are made in the building and remind people of their obligations.
After all, we have an obligation ourselves to speak on the behalf of the 98 percent of people who don’t work with architects but are subject to our decisions in the built environment.
That obligation carries into our design workshops and charrettes. These environments present a melee of activity, and oftentimes the most knowledgeable people in the room can be the quietest. We have to lift these voices up. By the same token, sometimes the loudest voices are the least knowledgeable, so they have to be managed.
We must pursue a just-in-time delivery of intellectual content. There is a perfect time for that interjection in these complicated projects. If you are directing the conversation, you may as well be a conductor of an orchestra. You must know when to bring these voices in and amplify them. You have to be able to harmonize the group. That harmonic convergence of these different voices is when miracles occur.
When the project enters the construction phase, we must continue to be vigilant. While construction can be difficult and lead to overwhelming situations, we have to return to the documents, remain open to what the situation is and have those difficult conversations with contractors and designers and owners—again, doing so with respect and dignity.
How are these interpersonal skills developed? It goes back to training.
When new designers join our group at RS&H, I start with them in a safe environment to get their ideas across—just them and me. From there, we can bring their voice into our internal meetings in a group environment, which is not as safe as a one-on-one environment.
I make sure they are knowledgeable about the subject matter and that they are expected to deliver, knowing I will call on them. They prepare and prepare over and over and over again, and I get to watch them rise up in our meetings. At that point, they are ready to have a meaningful role in our client meetings. I let them know what’s expected and what the design workflow is and when they will be expected to engage the team.
Time and time again, these new voices hit their marks and deliver. They rise to the occasion.
Low-tech, high-minded design techniques
There are low-tech skills our clients and the public at large still expect from us. They expect us to be able to draw—even right in front of them—to communicate a project. They think of architects and their drafting abilities, which are still honorable skills, but so are low-tech skills like drawing and painting, using chalk and oils. These skills release a creativity that is different depending on the medium.
When you paint a watercolor, it’s unforgiving. Anything that goes down on the paper can’t be erased. It requires flawless delivery—of course, if you think about it like that, you’re bound to make a mistake. On the other hand, using oil pastels over a photograph creates a gooey blending that matures in different ways. The same goes for Gouache or graphite and turpentine on mylar.
Look at some of the old masters and their half-painted pieces, and you’ll see something like a profile of angel’s wings shifting down until they finally get into that perfect state. What is intriguing to me are all the states before that built up to the perfect state. All these lines are going to be painted over, which means all these drafts will be lost, but for a moment you can see the movement of it.
You don’t get that experience with some of the new technologies. The big advantage of computer programs is in their definitive properties. There are thousands of options for doors, windows, flooring and everything else you need to create the most specific of building projects. But sometimes you’re just not ready for that. Access to so many options can cause you to lose track of your big idea.
The pencil process is different. If you draw a line wrong, it’s OK to get it wrong and get it wrong and get it wrong again. These imperfect lines can ultimately settle themselves into the perfect place.
Sketching, drawing and painting can release the mind in different ways. You may get hints of a big idea in your mind, but these moments can be fleeting – and often disappear before you can fire up your computer. That’s why it’s important to keep that sketchbook close by. Once you draw something, you capture an idea that you can now develop.
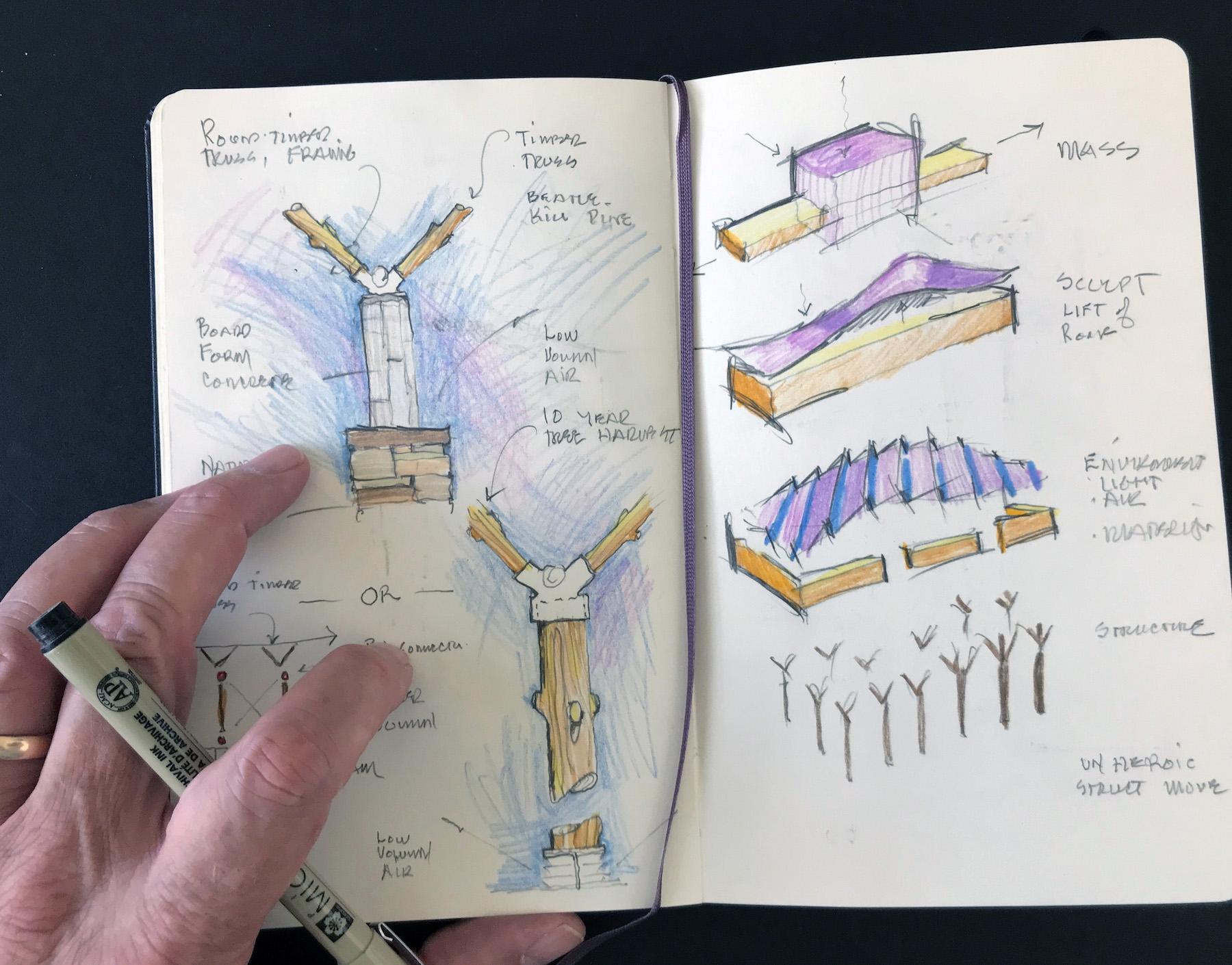
Put another way, when we wake up in the morning from a dream, the dream slowly begins to slip away. By the end of the day, it’s gone. The reverse of that is true for the creative process. It’s elusive and undefined, and as the day goes on, it gains clarity. As time goes on, it becomes real. You just have to let that creative state go from an unbridled suggestion to concrete form.
As I sit in my studio there is a marker board behind me. Even in zoom meetings, when I illustrate the non-physical aspects of a building, it is captured most clearly with diagrams that can be non-form generating. Clients get it when you say it and diagram it, and the idea gets embedded with them. Our thoughts, words and simple sketches have power.
Another way to embed the project idea with them? Build a physical model. When I build one, I know every piece of it, the back, side, top and bottom along with proportions. Having something in your hand and moving it around is different than spinning a computer model.
I can walk into a room and hand the model to a client. We’ve used models not only to win work, but to mature different aspects of a project. When a client holds a model or looks at a sketch right in front of them, they understand their project in a new way.
High Tech Expands Our Capabilities
What does an architect’s office look like now? In mine, I have three monitors, a camera and light for virtual meetings, VR goggles next to a drafting elbow, a markerboard and a curtain to sit in front of for conversations.
The modern architect’s office should support the high-tech, low-tech and no-tech tactics we must use. Moving effortlessly between these three levels of technology is the talent of the modern designer.
As design charrettes have gone digital, there are new tools we use that we could never have brought to a physical charrette.
We can provide environmental modeling through open-source software like Ladybug, Honeybee and Dragonfly along with Insight and Safaira. Iterative design is achieved through the dynamic scripting in Grasshopper, which allows us to on the fly explore the many possibilities. Real time, anonymous surveys and polls allow us to rapidly advance the design and get accurate data on consensus. Cloud based collaboration tools like Mural become digital sketchbooks capturing everybody's contributions.
This allows for a dynamic design process, where we can watch our project morph and change.
We can even bring watercolors into digital models with programs like Enscape, do real-time flythroughs and then share with a client via a QR code that they can view on their phone. As we focus more and more on sustainability in every project, we use the concepts of biophilia and biomimicry to develop a more meaningful connection with the world around us.
I’m a firm believer in all these tools. Time and time again, the best designers I have been around can model on multiple platforms, and they can draw.
By having access to all of these tools we must, through practice and learning, know when to sketch and when to go to our computers. With a balanced toolkit, we can create beautiful, insightful projects and buildings that reflect our emerging face of humanity.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
Philip Robbie, AIA OAA, is the National Design Director for RS&H. He has more than 30 years of international experience in all areas of architectural practice, including master planning, programming, space planning, interior design and architectural design. He has specialized in the collaborative process and is a graphics facilitator. He can be reached at philip.robbie@rsandh.com.






