Despite the constant drumbeat of news about the alarming frequency of school shootings around the country, many communities still view their schools as safe havens, and quite a few schools double as shelters from natural disasters.
In Texas, E-class buildings must include a tornado shelter, according to Jon Moreau, Balfour Beatty Construction Services’ VP of Operations, in Houston. “Some schools use underground parking garages, others use gyms or music halls. All of these shelters have hardened structures, restrooms, backup power, and air circulation systems,” says Moreau.
To keep its classrooms above the area’s seismic line, Seaside (Ore.) School District bought out nearby forestland and developed its own water reservoir for a new middle and high school campus, says David Chesley, PE, a Principal and Senior Electrical Engineer with Interface Engineering, which worked on that school’s mechanical/electrical design. BRIC Architecture designed the facility.
“Frankly, there’s funding available for this kind of thing,” says Gary Benson, Director of Project Planning and Development for Kraus-Anderson. One of his firm’s recent K-12 projects—a replacement school in Edina, Minn., that includes a tornado safe room—received some of its financing from FEMA. Another project—an elementary school for 100 students in North Dakota—was funded, in part, by a federal Emergency Impact Aid Grant (Kraus-Anderson helped that school district write its grant proposal).
See Also: Is STEM running out of steam?
But natural disasters might be the least that schools need to worry about, at a time when security is now a topic of intense national debate, and with good reason. In the first 21 weeks of 2018 alone, there were 23 school shootings where someone was killed or injured, according to CNN.
Community demand and support for securing schools are strong. But this problem is not new: Stantec has included secured vestibules in its school designs for at least 15 years, says Laura Flannery Sachtleben, a Principal in that firm’s Houston office. She and other AEC executives are the first to concede that design and construction can only do so much to help keep students safe.
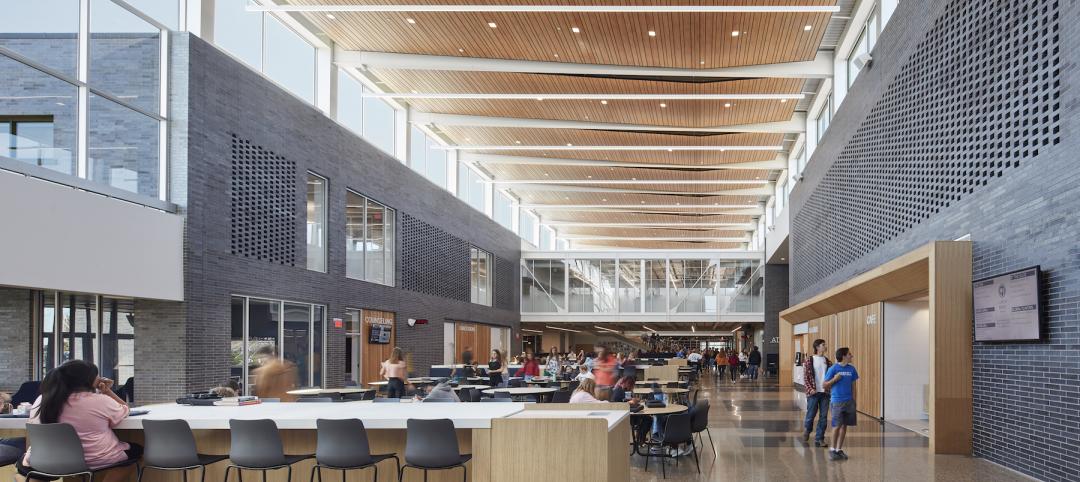
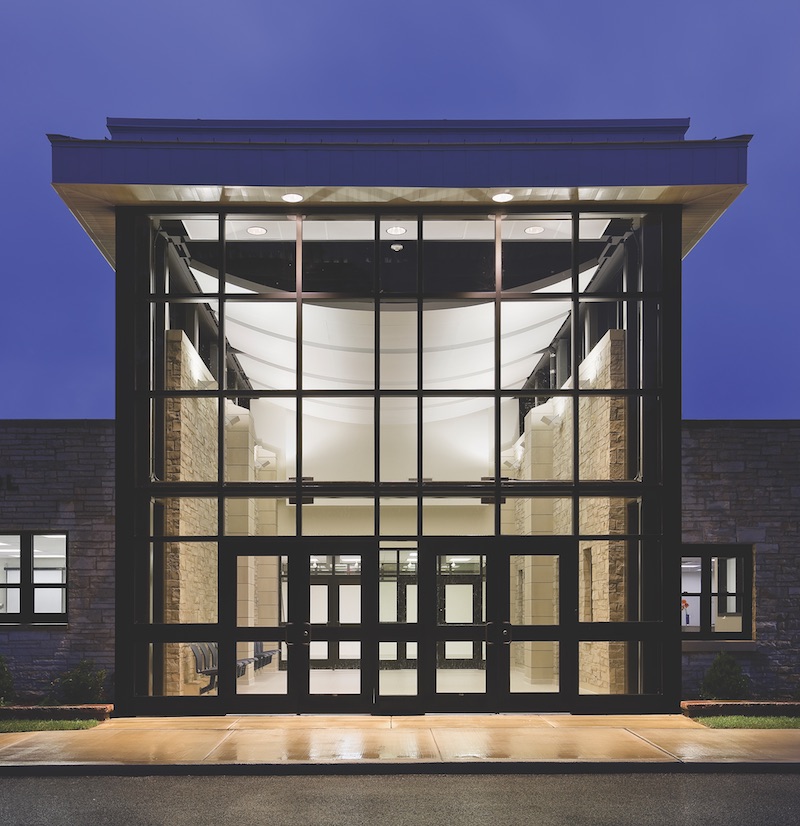 A safety audit of Parker Junior High School in Flossmoor, Ill., School District 161 identified changes to improve the facility’s overall security. One was to modify the main entrance to limit access to the building. The New Entry Pavilion separates visitor seating in the vestibule from the student seating in the office area. Craig Dugan Photography.
A safety audit of Parker Junior High School in Flossmoor, Ill., School District 161 identified changes to improve the facility’s overall security. One was to modify the main entrance to limit access to the building. The New Entry Pavilion separates visitor seating in the vestibule from the student seating in the office area. Craig Dugan Photography.
“There’s still no consensus about what works,” admits Andrew Grote, Associate Principal and Technical Director with Perkins+Will, especially when security counters transparency, another equally palpable trend in the K-12 sector.
Nevertheless, in Texas, schools are being built with bulletproof glass and drywall, and tight access controls, says Moreau. California “isn’t at the bulletproof stage yet,” says Gill Fullen, VP of Education with Balfour Beatty’s office in Orange County. “School districts are trying to evaluate what security systems make sense, like cameras and entry control points, to minimize loss of life.”
Stantec has created a firmwide internal task force that’s been vetting a series of different technologies for school security that, says Sachtleben, are less intrusive and easier
to conceal.
Any strategy for securing schools needs to start at “saving as many seconds and minutes as possible,” asserts Stephen Raskin, AIA, NCARB, a Principal with FGM Architects in St. Louis. He notes that the shooting at Virginia Tech University in 2007 lasted 17 minutes, and 11 minutes at Sandy Hook Elementary in Newtown, Conn., in 2012. The average time it takes first responders to arrive on the scene of an active shooting is 10 minutes, says Raskin.
FGM’s design strategies for school security stem from FEMA’s 428 guidelines and the Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design Association. Raskin says his firm’s solutions rely heavily on “human observation.” That means putting people at the school’s front door who can spot patterns in who’s coming and going. FGM’s school designs regularly advance the benefits of more and larger windows.
Security doesn’t have to be expensive. Raskin says ballistics-resistant window film costs about $15-$20 per sf. On the other hand, he’s dubious about whether security cameras, regardless of their ubiquity, actually deter shooters.
Other security and safety measures that FGM recommends to school districts include making corridors wider, moving the youngest students farther back in the building, allowing classrooms to be locked down individually from the inside, and making alerts as simple and clear as possible.
FGM recently worked with the NW R1 school district in Jefferson County, Mo., on a comprehensive assessment of its buildings to develop a long-range plan to establish safety priorities. The district identified 10-12 projects, and then held “listening sessions” with the public. The plan it came up with, claims Raskin, influenced the vote for a $14.5 million school bond that passed in April.
Related Stories
K-12 Schools | Dec 10, 2021
Trends in K-12 school design, with Dan Boggio and Melissa Turnbaugh of PBK
Dan Boggio and Melissa Turnbaugh of PBK, the largest K-12 design firm in the U.S., discuss the favorable market conditions and the latest trends in K-12 school design with BD+C's Rob Cassidy.
Giants 400 | Nov 18, 2021
2021 K-12 School Sector Giants: Top architecture, engineering, and construction firms in the U.S. K-12 school facilities sector
PBK, Gilbane, AECOM, and DLR Group head BD+C's rankings of the nation's largest K-12 school facilities sector architecture, engineering, and construction firms, as reported in the 2021 Giants 400 Report.
2021 Building Team Awards | Nov 17, 2021
Caltech's new neuroscience building unites scientists, engineers to master the human brain
The Tianqiao and Chrissy Chen Institute for Neuroscience at the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena wins a Gold Award in BD+C's 2021 Building Team Awards.
Designers / Specifiers / Landscape Architects | Nov 16, 2021
‘Desire paths’ and college campus design
If a campus is not as efficient as it could be, end users will use their feet to let designers know about it.
K-12 Schools | Nov 14, 2021
New Blackwater Community School completed for Gila River Indian Community, in Arizona
Construction on the new Blackwater Community School, a two-story structure on the Gila River Indian Community, located southeast of Phoenix, Arizona, was completed on August 31, 2021.
K-12 Schools | Nov 10, 2021
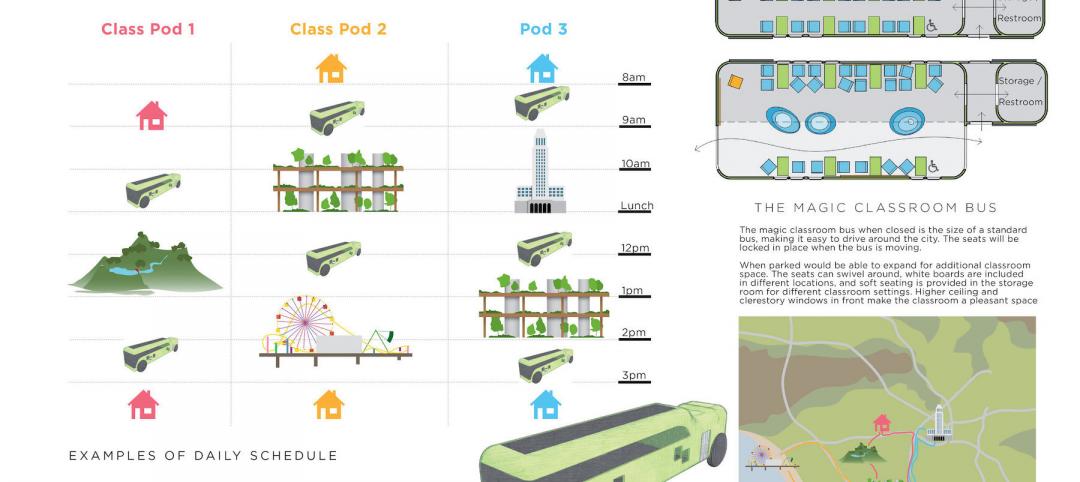
K-12 school design innovation: 'Learning Everywhere' and the mobile classroom
Last September, AIA San Francisco awarded the Professional Category in its 2021 Future Classroom Competition to a five-person team from Culver City, Calif.-based Berliner Architects. The firm was selected for its “Learning Everywhere” idea that features a mobile strategy for education at school, home, on field trips, and in transit. BD+C's John Caulfield discuss that concept with Richard Berliner, AIA, Principal, Berliner Architects.
Cladding and Facade Systems | Oct 26, 2021
14 projects recognized by DOE for high-performance building envelope design
The inaugural class of DOE’s Better Buildings Building Envelope Campaign includes a medical office building that uses hybrid vacuum-insulated glass and a net-zero concrete-and-timber community center.
Education Facilities | Oct 20, 2021
Kenneth K.T. Yen Humanities Building completes for The Pennington School
Voith & Mactavish Architects designed the project.
| Oct 14, 2021
The future of mass timber construction, with Swinerton's Timberlab
In this exclusive for HorizonTV, BD+C's John Caulfield sat down with three Timberlab leaders to discuss the launch of the firm and what factors will lead to greater mass timber demand.
University Buildings | Sep 28, 2021
Designing for health sciences education: Specialty instruction and human anatomy labs
It is a careful balance within any educational facility to provide both multidisciplinary, multiuse spaces and special-use spaces that serve particular functions.