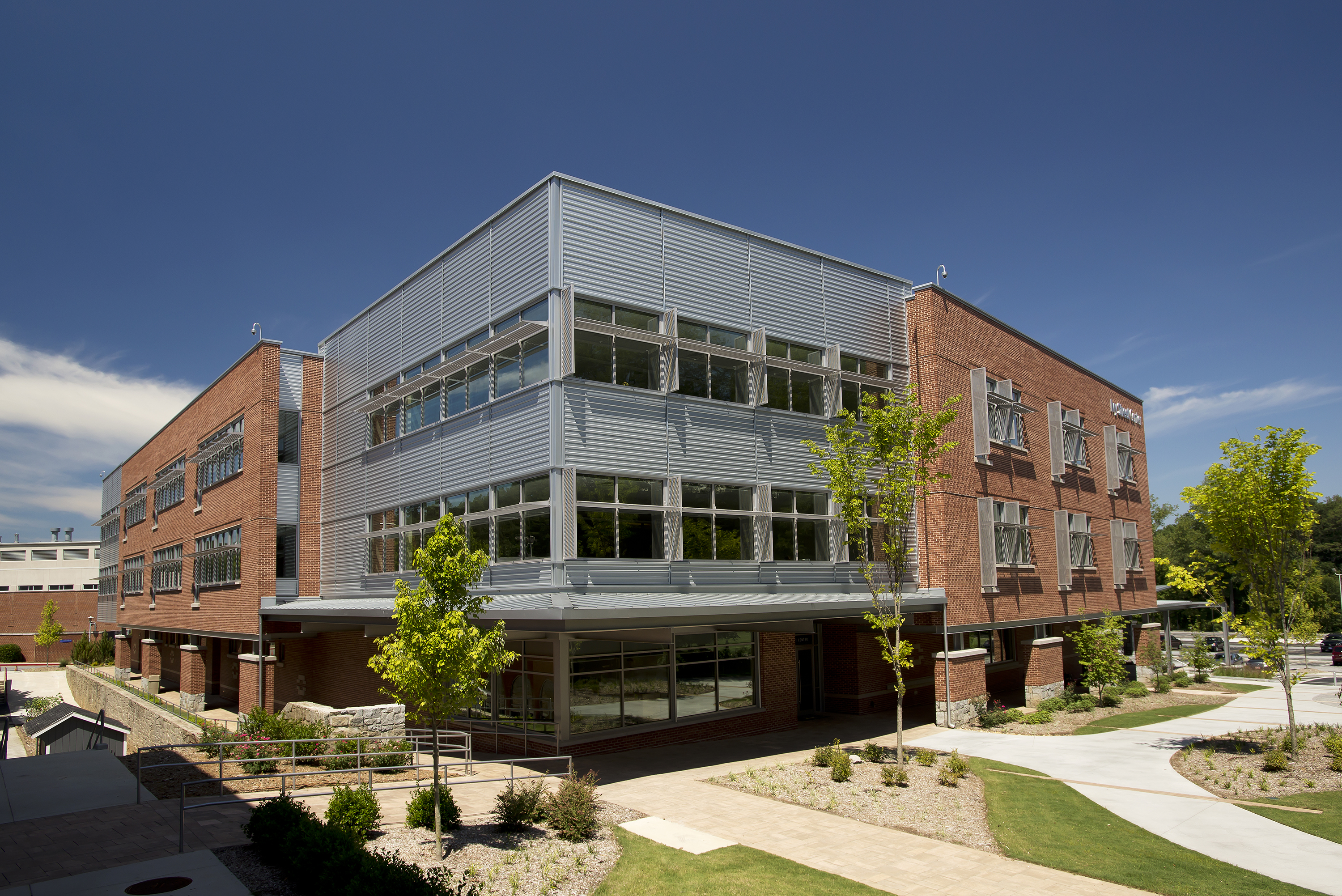
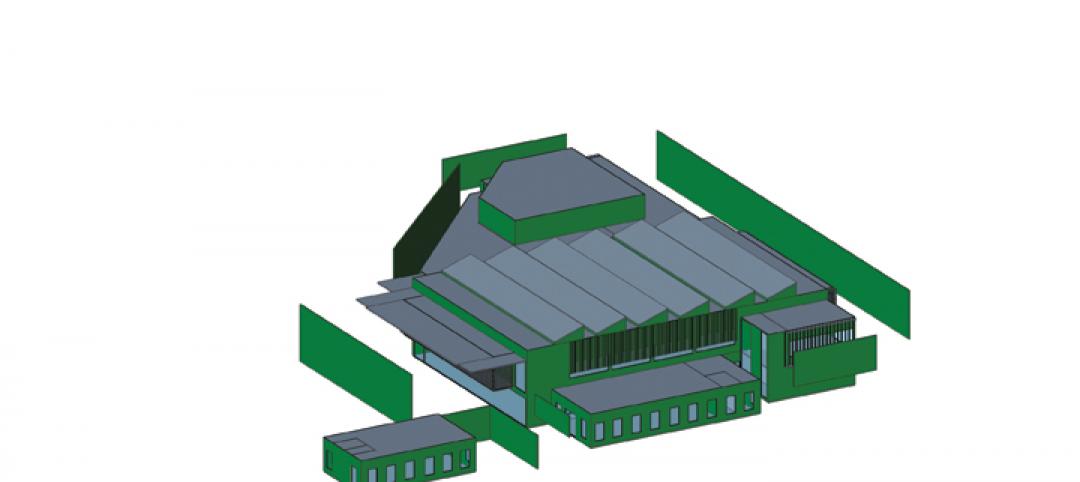
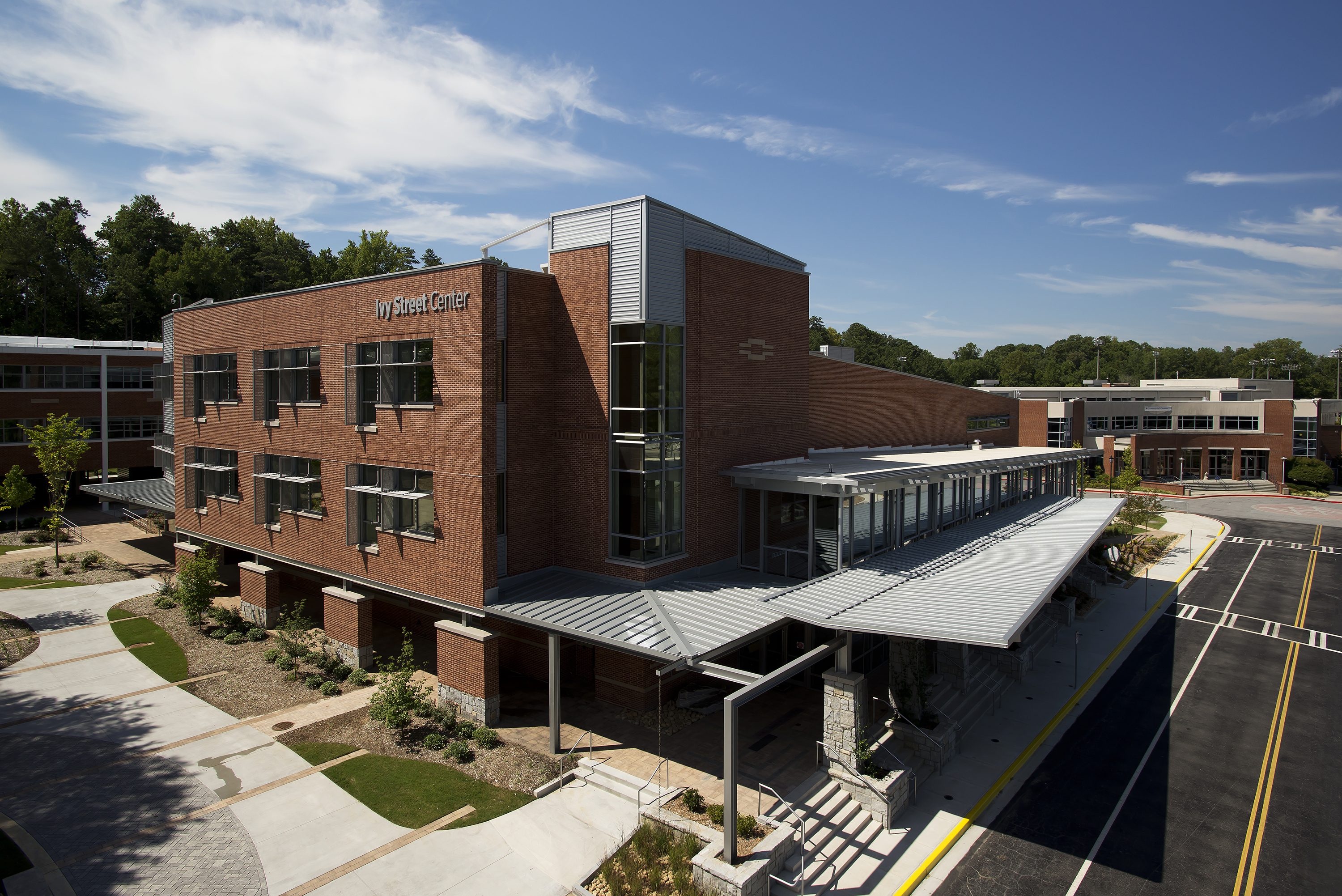
Ivy Street Center is the first new academic building on the Marist School campus in Brookhaven, Ga., in more than 20 years, and is the signature project in Phase 1 of the Campus Master Plan. Marist School is a private Roman Catholic college preparatory school serving 1,100 students in grades 7-12. The new 55,000 sq. ft. Ivy Street Center serves as home for the mathematics and English departments. The building’s name pays homage to Marist’s original three-story schoolhouse located on Ivy Street (now Peachtree Center Avenue) in downtown Atlanta.
Architectural design was created by S/L/A/M Collaborative, Atlanta. Will Stelten, design architect and a 1985 graduate of Marist, said the school community chose carefully to design a building that will serve students for years. “Marist gets full credit for embracing this. They took this farther than any other client has,” Stelten said.
The structure was built on the footprint of the razed Kuhrt Gym, a 50-year-old building. “The charge was to design a combination classroom building that wrapped around a new gymnasium,” Stelten said. The new building now offers 16 classroom spaces, a tiered lecture hall, a 275 seat gymnasium plus collaborative areas and a campus store.
Two PAC-CLAD profiles were specified for roofing and wall applications on the three-story, highly-sustainable structure. Approximately 6,000 sq. ft. of Petersen Aluminum’s M-36 wall panels were used to clad a major portion of the façade. An additional 6,000 sq. ft. of Tite-Loc Plus roof panels were used on large canopies and overhangs at prominent locations on the building.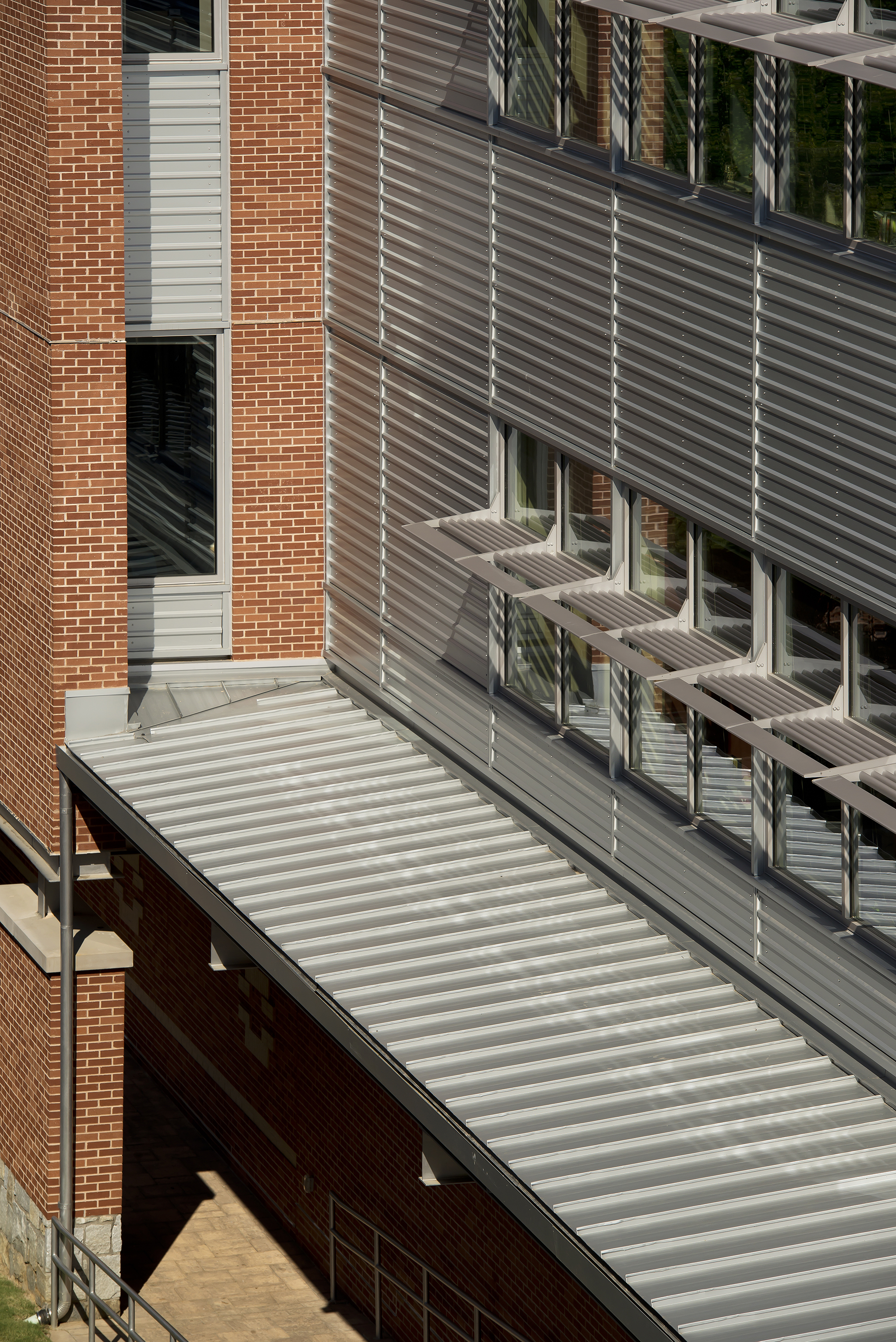
All panels were finished with Valspar Fluropon Silver and manufactured at Petersen Aluminum’s Acworth, Ga., plant. The Tite-Loc Plus panels were distributed by Commercial Roofing Specialties in College Park, Ga.
The building is larger than most on the campus, Stelten notes. “We felt that introducing the metal panels helped lighten the building and break up the massing in a way that made it more interesting,” he said. “The M-36 panel is an interesting profile to use on a building like this. It has deep shadow lines that help add lightness and a horizontal feel.”
The PAC-CLAD M-36 wall panels were installed by SECO Architectural Systems, Snellville, Ga. “Exposed fastener panels are often thought of as an industrial or utilitarian type of system,” said Joe Creighton, president of SECO. “But when they are installed horizontally, the panels suddenly create a nice architectural effect. The flashings become much more important and the folded corners add interest.”
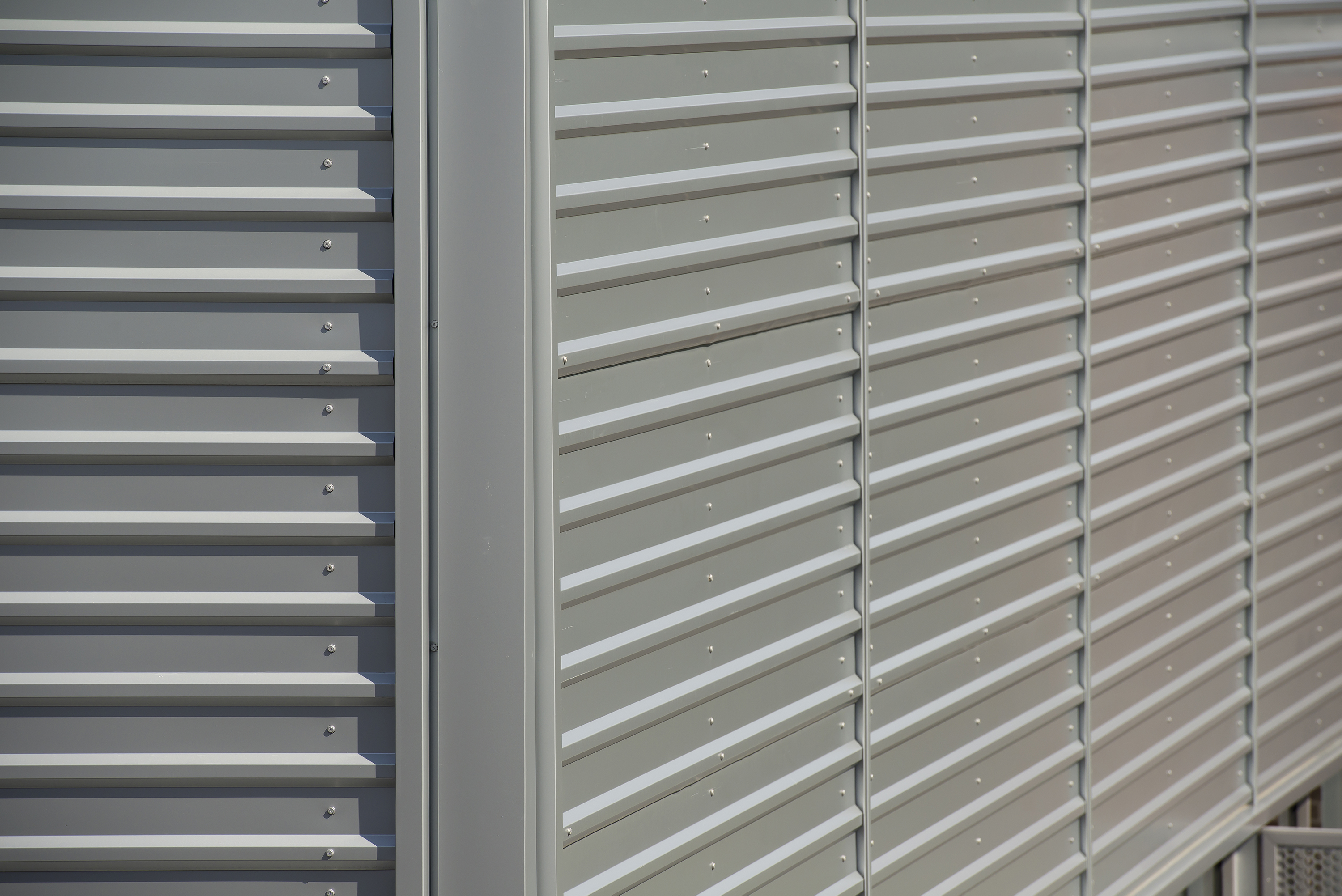 The original design called for aluminum composite material to be used for the siding, but that proved to be too expensive. SECO worked closely with the general contractor, Brasfield & Gorrie, to arrive at an affordable solution that met the architectural design criteria. “One of the options I gave the GC was the Petersen M-36 system. It was quite a departure from the original plan but it was aluminum, it was silver and I knew it would make a nice statement with the right detailing. After quite a bit of discussion, we got to the point where the architect liked the look and the owner could afford it,” Creighton said.
The original design called for aluminum composite material to be used for the siding, but that proved to be too expensive. SECO worked closely with the general contractor, Brasfield & Gorrie, to arrive at an affordable solution that met the architectural design criteria. “One of the options I gave the GC was the Petersen M-36 system. It was quite a departure from the original plan but it was aluminum, it was silver and I knew it would make a nice statement with the right detailing. After quite a bit of discussion, we got to the point where the architect liked the look and the owner could afford it,” Creighton said.
The key to the job was pre-planning and attention to detail, Creighton added. “There was a high degree of both and that’s what led to success. The M-36 panel really makes for a nice architectural look and not for a lot of money.”
The second PAC-CLAD system used on the job was Petersen Aluminum’s Tite-Loc Plus roofing panels. Installation of the Tite-Loc Plus panels was done by Saco Systems, Suwanee, Ga. John Salo, vice president, said the double-lock, mechanically seamed panels “are about as structurally sound as you can get. They are highly engineered panels that satisfy the most stringent design criteria.” Saco Systems has considerable experience in working with Petersen Aluminum profiles. “There were no real challenges on the project other than the normal coordination with other trades,” Salo said. “The panels went down easily and the job came out great—that’s the way we like it!”
Marist School made a commitment to environmental stewardship as it built the new facility. “Sustainability has been a big feature on the campus. It fits in with the overall philosophy of the school,” said Marist Father John Harhager, school president.
Sustainability features of the building include a three-part daylight harvesting system of exterior sunshades, interior light shelves and sloped ceilings. Glare inside classrooms is minimized, and daylight reaches deeply into rooms, allowing classroom lights to remain off the majority of the time. Rain water is saved to a 3,400-gal. cistern filled from two sources: the sloped gym roof and condensate from the HVAC system. The water in the cistern is used for irrigation of the planted rain garden. The building also features water bottle refill stations to reduce disposable water bottle waste. Sustainable materials include colorful sound-absorbing panels made of machine pressed, recycled plastic bottles in the gymnasium, reclaimed elm wood panels in the lobby, and locally sourced materials.

Long-recognized as an industry leader in metal standing seam roofing products, Petersen also offers exposed fastener panels, flush panels, composite wall panels and column covers. All provide the well-known Petersen quality and are available in PAC-CLAD® Kynar 500® finish in 38 standard colors on steel and 37 aluminum. Most colors meet LEED, ENERGY STAR and cool roof certification requirements.
For more information on the complete line of Petersen metal products, call 800-PAC-CLAD or visit www.pac-clad.com.
Related Stories
| Nov 2, 2010
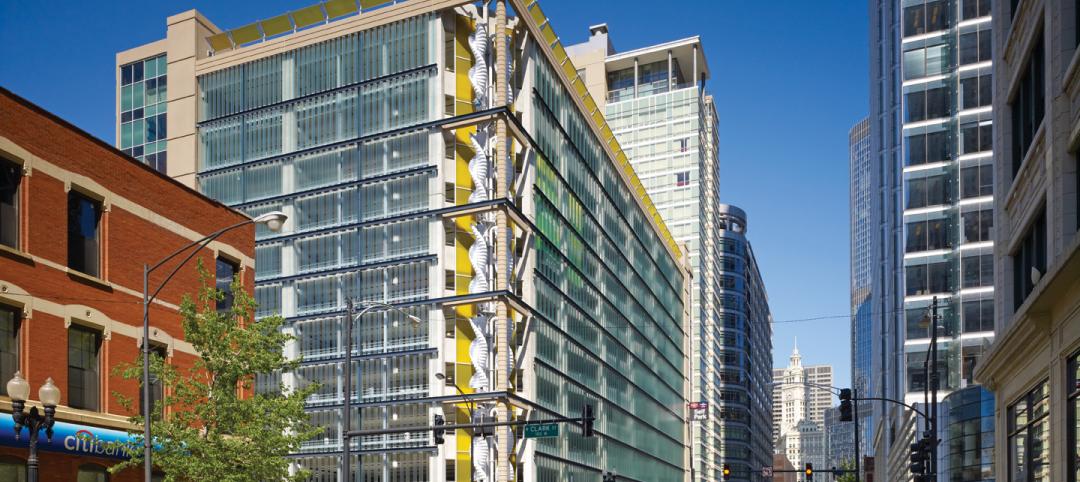
Wind Power, Windy City-style
Building-integrated wind turbines lend a futuristic look to a parking structure in Chicago’s trendy River North neighborhood. Only time will tell how much power the wind devices will generate.
| Nov 2, 2010
Energy Analysis No Longer a Luxury
Back in the halcyon days of 2006, energy analysis of building design and performance was a luxury. Sure, many forward-thinking AEC firms ran their designs through services such as Autodesk’s Green Building Studio and IES’s Virtual Environment, and some facility managers used Honeywell’s Energy Manager and other monitoring software. Today, however, knowing exactly how much energy your building will produce and use is survival of the fittest as energy costs and green design requirements demand precision.
| Nov 2, 2010
Yudelson: ‘If It Doesn’t Perform, It Can’t Be Green’
Jerry Yudelson, prolific author and veteran green building expert, challenges Building Teams to think big when it comes to controlling energy use and reducing carbon emissions in buildings.
| Nov 2, 2010
Historic changes to commercial building energy codes drive energy efficiency, emissions reductions
Revisions to the commercial section of the 2012 International Energy Conservation Code (IECC) represent the largest single-step efficiency increase in the history of the national, model energy. The changes mean that new and renovated buildings constructed in jurisdictions that follow the 2012 IECC will use 30% less energy than those built to current standards.
| Nov 1, 2010
Sustainable, mixed-income housing to revitalize community
The $41 million Arlington Grove mixed-use development in St. Louis is viewed as a major step in revitalizing the community. Developed by McCormack Baron Salazar with KAI Design & Build (architect, MEP, GC), the project will add 112 new and renovated mixed-income rental units (market rate, low-income, and public housing) totaling 162,000 sf, plus 5,000 sf of commercial/retail space.
| Nov 1, 2010
Vancouver’s former Olympic Village shoots for Gold
The first tenants of the Millennium Water development in Vancouver, B.C., were Olympic athletes competing in the 2010 Winter Games. Now the former Olympic Village, located on a 17-acre brownfield site, is being transformed into a residential neighborhood targeting LEED ND Gold. The buildings are expected to consume 30-70% less energy than comparable structures.
| Oct 27, 2010
Grid-neutral education complex to serve students, community
MVE Institutional designed the Downtown Educational Complex in Oakland, Calif., to serve as an educational facility, community center, and grid-neutral green building. The 123,000-sf complex, now under construction on a 5.5-acre site in the city’s Lake Merritt neighborhood, will be built in two phases, the first expected to be completed in spring 2012 and the second in fall 2014.
| Oct 21, 2010
GSA confirms new LEED Gold requirement
The General Services Administration has increased its sustainability requirements and now mandates LEED Gold for its projects.
| Oct 18, 2010
World’s first zero-carbon city on track in Abu Dhabi
Masdar City, the world’s only zero-carbon city, is on track to be built in Abu Dhabi, with completion expected as early as 2020. Foster + Partners developed the $22 billion city’s master plan, with Adrian Smith + Gordon Gill Architecture, Aedas, and Lava Architects designing buildings for the project’s first phase, which is on track to be ready for occupancy by 2015.
| Oct 13, 2010
Editorial
The AEC industry shares a widespread obsession with the new. New is fresh. New is youthful. New is cool. But “old” or “slightly used” can be financially profitable and professionally rewarding, too.