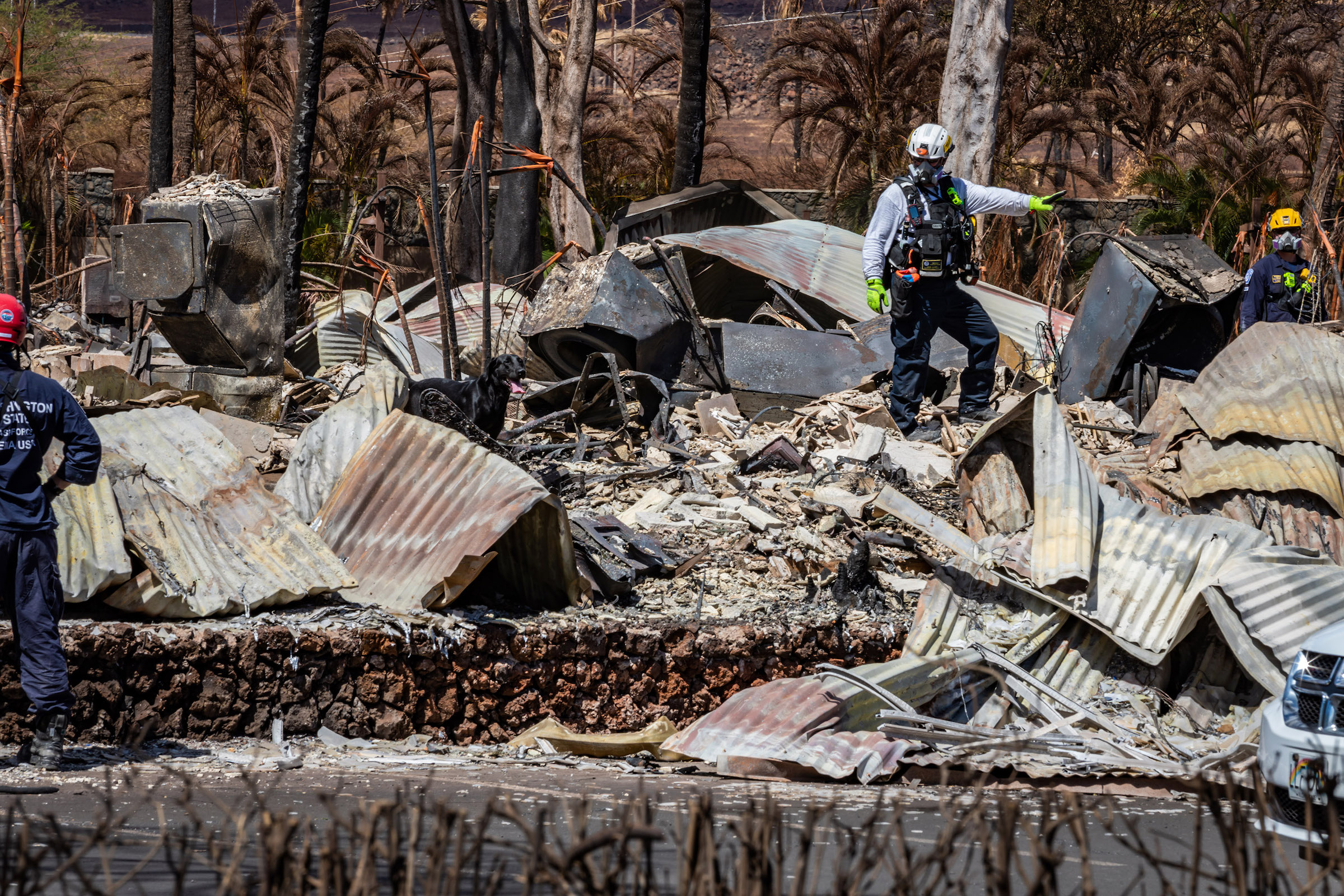
Modern building codes and construction techniques were effective in saving buildings from the devastating Maui wildfire on August 9th, according to a recent report, IBHS Early Insights Lahaina Fire—2023, from the Insurance Institute for Business and Home Safety’s research division.
The report cited a residential development, consisting of a mix of single-family homes and a cluster of multifamily units built between 2019 and 2020, that escaped destruction. The structures survived the conflagration at least partly due to fire retardant construction and modern building codes, the report says.
The exteriors of several of these buildings did ignite, but they were not consumed by flames. “Hawaii’s modern building code has high-wind requirements that introduced elements that helped newer construction resist wildfire conditions,” the report says.
Despite the buildings being located close together, the development was spared in part because of:
- Class A roof covers—specifically asphalt shingles and metal
- Non-combustible exterior wall materials
- High wind-rated attic vents that prevented embers from entering the attic space
Notably, the report adds that landscape vegetation did not cover as much ground as it did in other locations that were destroyed by the fire. This provided less fuel for the flames to jump from one structure to another.
Related Stories
| Nov 14, 2014
Army net-zero initiative moving past pilot stage
The U.S Army's ambitious net-zero initiative has had several successful pilot trials, and planners are prepared to expand the nine-part demonstration field to scores of other Army facilities.
| Nov 14, 2014
Former U.S. Treasury Secretary Paulson works to upgrade China’s building codes
Former U.S. Treasury Secretary Hank Paulson is today focused on making new construction in China more energy efficient by working with leaders to upgrade building codes.
| Nov 14, 2014
California aims for 20% reduction in water consumption by 2020
California’s comprehensive new water use plan makes conservation a priority, reinforcing a 2009 plan to reduce statewide per capita water consumption by 20% by 2020.
| Nov 6, 2014
Demountable structural steel could up the ante on sustainability
Demountable structural steel assemblies would be a greener way to make use of steel in the construction industry than recycling.
K-12 Schools | Nov 6, 2014
New Sandy Hook school features could influence security standards
The design of the new Sandy Hook Elementary School on the site of the 2012 Newtown, Conn., school shooting features enhanced security measures—some subtle and others more prominent.
| Nov 6, 2014
OSHA seeking input on electrical standards
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) is reviewing electrical standards for the construction industry to make sure proper safeguards are in place as electrical wiring is being installed and maintained.
Smart Buildings | Oct 30, 2014
Energy Department pledges $9 million for energy efficiency improvements on commercial buildings
The U.S. Dept. of Energy will spend $9 million to encourage investments in energy-saving technologies that can be tested and deployed in offices, shops, restaurants, hospitals, hotels and other types of commercial buildings.
| Oct 30, 2014
Steel Framing Industry Association’s certification program aims to ensure connector quality
The Steel Framing Industry Association has launched a certification program to ensure that cold-formed steel connectors meet quality guidelines, building codes, and ASTM standards.
| Oct 30, 2014
American Concrete Institute releases reorganized structural concrete code requirements
The reorganized document is organized from an engineer’s perspective. The requirements flow more intuitively and have fewer cross-references for improved logic and flow of information.
| Oct 30, 2014
USGBC pushes back LEED v4 deadline
Extending the deadline gives LEED users additional time to prepare for LEED v4, the latest version of LEED, which features increased rigor and multiple updates.