In its 20th year, Studio Gang is enjoying its moment in the sun.
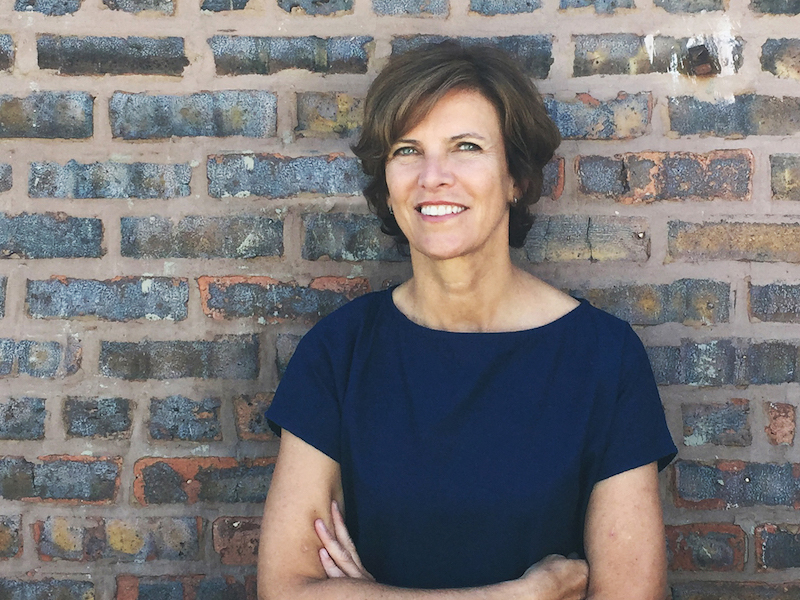
Jeanne Gang, the firm’s 53-year-old Founding Principal, who has garnered a MacArthur Fellowship and a passel of design accolades, is among a small handful of architects—and even more rarefied band of female architects—whom the press tags with the adjective “star.”
Studio Gang’s design work is much in vogue these days. Its offices in Chicago and New York are currently juggling 14 projects in various stages of design or construction (see box, page 38). To keep up with rising demand, it has steadily increased its workforce to 91 people, from 19 a decade ago.
The firm’s impact on the built environment stems from Jeanne Gang’s ecologically tinted design
aesthetic that views buildings as “social connectors” for people and their surrounding environments. And her firm’s approach to arrive at a design solution is through rigorous and detailed investigations of its clients’ project goals.
Internally, Studio Gang, despite its growth, still operates like a “collective,” where associates are encouraged to chime in freely on projects. As such, the company seems less cultish than some other high-profile design firms. And the firm’s leadership is making sure that the projects it takes on don’t overload its staff’s capacity.
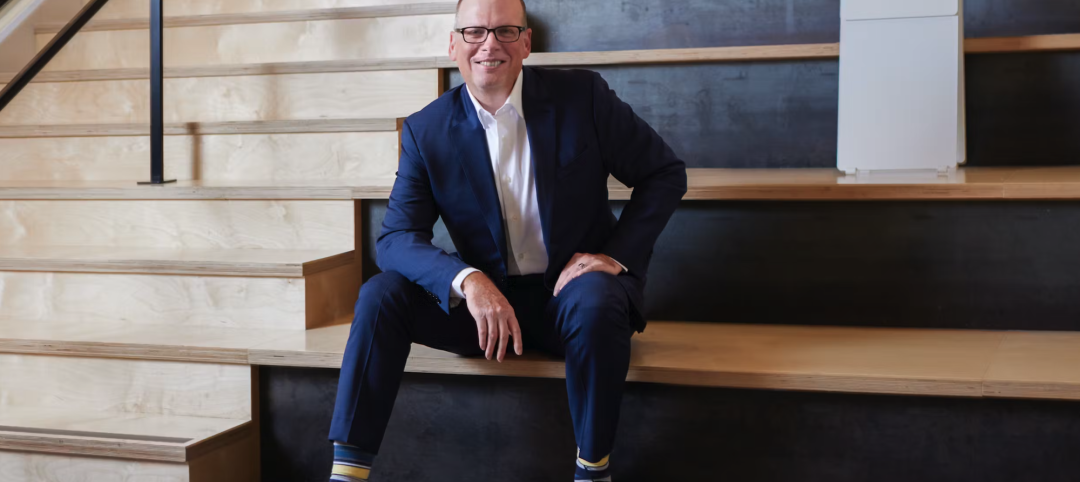
“We could have gotten larger quicker, but we pace ourselves,” says Design Principal Juliane Wolf, who started working for Studio Gang while she was a student and has been with the firm full time since 2001.
 A large, open “living room” with a fireplace, kitchen, and lots of daylight stimulates encounters and discussions at The Arcus Center for Social Justice Leadership at Kalamazoo (Mich.) College. Photo: Steve Hall/Hedrich Blessing.
A large, open “living room” with a fireplace, kitchen, and lots of daylight stimulates encounters and discussions at The Arcus Center for Social Justice Leadership at Kalamazoo (Mich.) College. Photo: Steve Hall/Hedrich Blessing.
Making contact
At a TED Talk in San Francisco last October, Gang explained that, in a world whose urban habitat is “out of balance,” her firm strives to design buildings as “relationships, where people can come together.”
Studio Gang has applied this concept to a wide range of structures: firehouses, civic buildings, theaters, offices, and residential projects. Case in point: The three-building, 394,000-sf Campus North Residence Commons it designed for the University of Chicago is probably best known for its “house hub,” which over three floors creates a home-like environment with communal spaces for cooking, studying, and relaxing that allow students to interact and collaborate.
Wolf says Studio Gang’s design philosophy has remained consistent through her years there. She points to two cultural projects she’s worked on—the Bengt Sjostrom Starlight Theatre, built in 2003, and the Writers Theatre, built last year—that had similar design goals of becoming community and regional destinations with an emphasis on facilitating audience interaction and enjoyment.
Studio Gang doesn’t have a recognizable style, per se. Boldness often jockeys for position with common sense. “Sometimes, just tweaking slightly can make something special happen,” says Wolf. But the firm’s design intent never strays too far from connecting a building with its surrounding environs. For example, Studio Gang’s designs for two boathouses in Chicago are distinguished by “V” and “M” roof shapes that are meant to “reflect the movement and rhythm of rowing,” says Gang.
Deep Research
The starting point for each of Studio Gang’s projects, says Wolf, is an extensive “research and discovery phase, and a thorough investigation of the client and the project.”
Take one of Gang’s favorite recent projects: Arcus Center for Social Justice Leadership at Kalamazoo (Mich.) College, built in 2014. Prior to putting Sharpie to paper, her firm assembled a book-size compendium of documents and notes that included details about a nearby 100-year-old farmhouse made from “log brick”—a mixture of two-foot-long logs and cementitious material. That became the architectural model for Arcus’s cordwood masonry exterior walls, whose construction, says Gang, is “super low tech—anyone can do it, and the act of making it is a social activity.”
Gang the environmentalist also likes the fact that the wood’s carbon is “trapped” within the wall.
The 10,000-sf Arcus Center is designed to “break down traditional barriers” among its occupants and visitors, says Wolf. The open “living room” at its center, activated by daylight, features a kitchen and fireplace. This space creates the potential for “informal meetings and casual encounters,” says Gang.
Wolf notes that since the Arcus Center opened, its applications have increased tenfold.
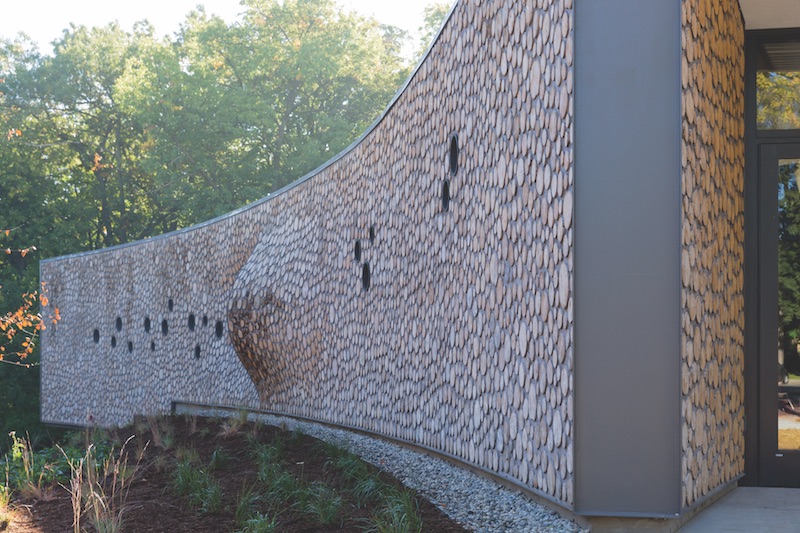 Cordwood masonry was used to construct the structure’s unique exterior walls that emphasize the building’s affinity with its surrounding environment. Photo: Iwan Baan.
Cordwood masonry was used to construct the structure’s unique exterior walls that emphasize the building’s affinity with its surrounding environment. Photo: Iwan Baan.
Materials matter
Gang pays close attention to the materials her team specifies, partly with an eye toward environmental impact but also to maintain a building’s local authenticity.
“More and more, we’re trying to find ways to use wood,” she said during a speech at the Art Institute of Chicago in March. The Writers Theatre is framed with laminated wood timbers that rest on “paws”—cedar wedges placed at the beam’s base—created by a crafts shop in Ottawa, Ill., that’s one of only two such artisans in the country doing this kind of work.
In New York, the five-story Richard Gilder Center for Science and Innovation, a 195,000-sf addition to the American Museum of Natural History scheduled to open in 2020, is designed for more efficient circulation flow with the 10 existing buildings that surround it. The sculpted walls of the center’s Exhibition Hall will be formed using shotcrete, similar to what’s used in subway construction, says Wolf.
Studio Gang is also working on an office building in Chicago for the Natural Resources Defense Fund that can meet the tough performance standards of the Living Building Challenge. That means avoiding materials with chemicals banned on the Challenge’s ever-expanding Red List, which Gang says is “the new frontier” for AEC firms.
Bringing human scale to skyscrapers
Gang once referred to tall buildings as “vertical social fabric.” And her firm has put that idea to work at two signature high-rise towers in Chicago: Aqua and Vista.
The 82-story Aqua tower, built in 2010, has more than 700 tenants. Each apartment opens up to a balcony whose dramatic contoured shape makes it easier for tenants to see and communicate with neighbors. That contour also “confuses the wind,” says Gang, making the balconies more comfortable.
The 95-story, 1,186-foot-tall Vista building, scheduled for completion in 2020, reflects the geometric properties of a “frustrum,” found in gemstones and crystals. In layman’s terms, the building’s curtain wall is staggered so each ascending floor is indented by a few inches from the floor below, giving tenants a better view of the outdoors.
Vista will also allow more daylight at street level. The same is true of Studio Gang’s design for 40 Tenth Avenue on New York’s west side, whose “solar carve” form follows the movement of the sun and twists the building away from the High Line below. Gang says this design could provide up to 200 additional hours of daylight for the High Line’s vegetation during growing season.
Can buildings engender trust?
Gang is taking the nexus of buildings, people, and public space to a more overtly societal level at Polis Station, her firm’s ongoing reimaging of police stations away from being “scary fortresses” to centers of gravity and safety for the public they serve.
After conducting conversations and workshops with community leaders, local neighbors, children, public officials, and the police, Studio Gang chose a police station in North Lawndale, Ill.—a town plagued by numerous shootings—for its first “intervention.” The project included helping to raise $35,000 to build a basketball half court on the station’s parking lot. (Parents now say this court is much safer than other courts in the neighborhood.)
Gang envisions a 21st-century police station as a community hub that might include a barbershop, bike shop, food market, and other public spaces “that spark conversations” between the community and the police, toward the ultimate goal of re-establishing mutual trust.
“This is not a utopian fantasy,” she insists. “But it requires engaging the public who live there.”
Executive Editor Robert Cassidy contributed reporting for this article.
Related Stories
Architects | Jun 22, 2023
Keith Hempel named President of LPA Design Studios
LPA Design Studios today announced the promotion of Chief Design Officer Keith Hempel, FAIA, to president of the 58-year-old integrated design firm. Hempel, who joined LPA in 1995, has been an integral part of the firm’s growth, helping to develop an integrated design process that has produced industry-leading results.
Industrial Facilities | Jun 20, 2023
A new study presses for measuring embodied carbon in industrial buildings
The embodied carbon (EC) intensity in core and shell industrial buildings in the U.S. averages 23.0 kilograms per sf, according to a recent analysis of 26 whole building life-cycle assessments. That means a 300,000-sf warehouse would emit 6,890 megatons of carbon over its lifespan, or the equivalent of the carbon emitted by 1,530 gas-powered cars driven for one year. Those sobering estimates come from a new benchmark study, “Embodied Carbon U.S. Industrial Real Estate.”
Virtual Reality | Jun 16, 2023
Can a VR-enabled AEC Firm transform building projects?
With the aid of virtual reality and 3D visualization technologies, designers, consultants, and their clients can envision a place as though the project were in a later stage.
Mechanical Systems | Jun 16, 2023
Cogeneration: An efficient, reliable, sustainable alternative to traditional power generation
Cogeneration is more efficient than traditional power generation, reduces carbon emissions, has high returns on the initial investment, improves reliability, and offers a platform for additional renewable resources and energy storage for a facility. But what is cogeneration? And is it suitable for all facilities?
Office Buildings | Jun 15, 2023
An office building near DFW Airport is now home to two Alphabet companies
A five-minute drive from the Dallas-Fort Worth International Airport, the recently built 2999 Olympus is now home to two Alphabet companies: Verily, a life sciences business, and Wing, a drone delivery company. Verily and Wing occupy the top floor (32,000 sf and 4,000 sf, respectively) of the 10-story building, located in the lakeside, work-life-play development of Cypress Waters.
Transit Facilities | Jun 15, 2023
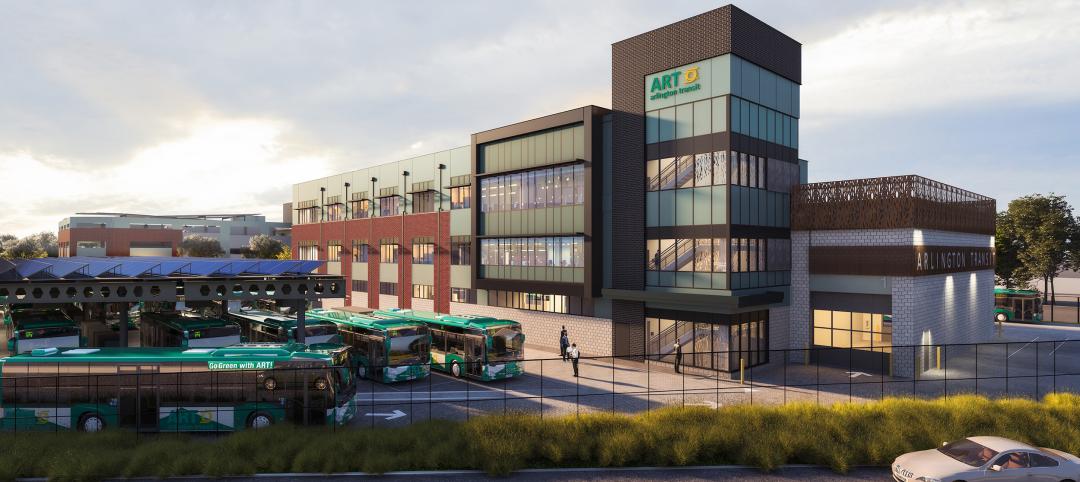
Arlington, Va., transit station will support zero emissions bus fleet
Arlington (Va.) Transit’s new operations and maintenance facility will support a transition of their current bus fleet to Zero Emissions Buses (ZEBs). The facility will reflect a modern industrial design with operational layouts to embrace a functional aesthetic. Intuitive entry points and wayfinding will include biophilic accents.
Urban Planning | Jun 15, 2023
Arizona limits housing projects in Phoenix area over groundwater supply concerns
Arizona will no longer grant certifications for new residential developments in Phoenix, it’s largest city, due to concerns over groundwater supply. The announcement indicates that the Phoenix area, currently the nation’s fastest-growing region in terms of population growth, will not be able to sustain its rapid growth because of limited freshwater resources.
Multifamily Housing | Jun 15, 2023
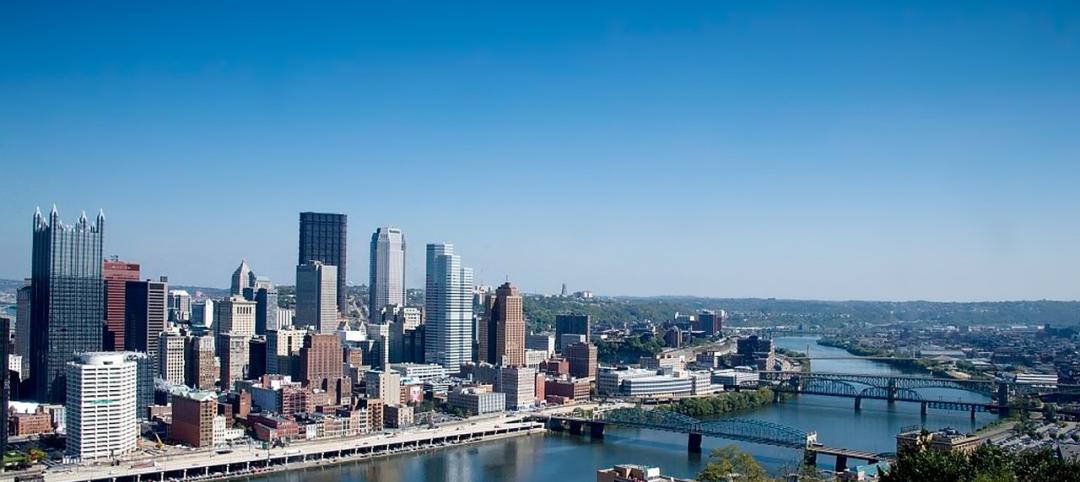
Alliance of Pittsburgh building owners slashes carbon emissions by 45%
The Pittsburgh 2030 District, an alliance of property owners in the Pittsburgh area, says that it has reduced carbon emissions by 44.8% below baseline. Begun in 2012 under the guidance of the Green Building Alliance (GBA), the Pittsburgh 2030 District encompasses more than 86 million sf of space within 556 buildings.
Industry Research | Jun 15, 2023
Exurbs and emerging suburbs having fastest population growth, says Cushman & Wakefield
Recently released county and metro-level population growth data by the U.S. Census Bureau shows that the fastest growing areas are found in exurbs and emerging suburbs.
Healthcare Facilities | Jun 14, 2023
Design considerations for behavioral health patients
The surrounding environment plays a huge role in the mental state of the occupants of a space, especially behavioral health patients whose perception of safety can be heightened. When patients do not feel comfortable in a space, the relationships between patients and therapists are negatively affected.