All kinds of recycled waste goes into public roads these days, including blast furnace slag, scrap tires, and roofing shingles, according to the Federal Highway Administration.
An estimated 300,000 metric tons of recycled plastic are also used annually as a binder additive for public roads in the U.S. But that’s a drop in the bucket compared to the five trillion pieces of plastic junk currently floating in the oceans, to which eight million metric tons of plastic waste gets added every year.
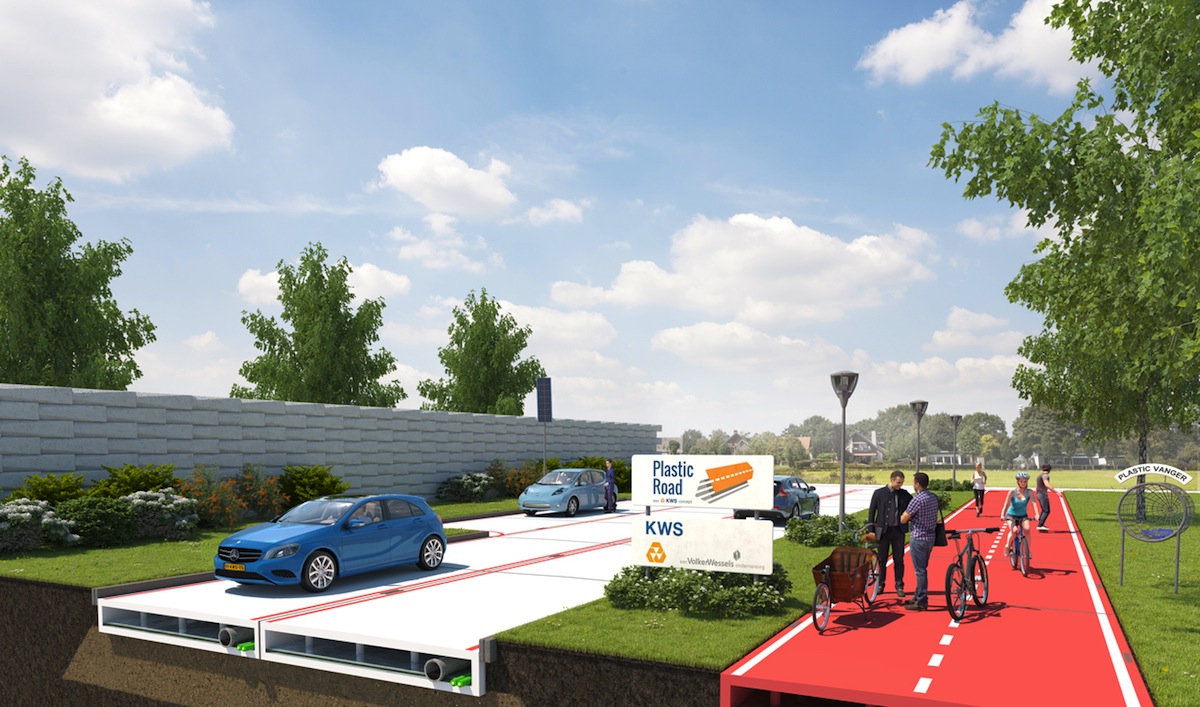
The Netherlands is trying to take this recycling to another level, and is vying to become the first country to pave streets with materials made entirely from plastic waste.
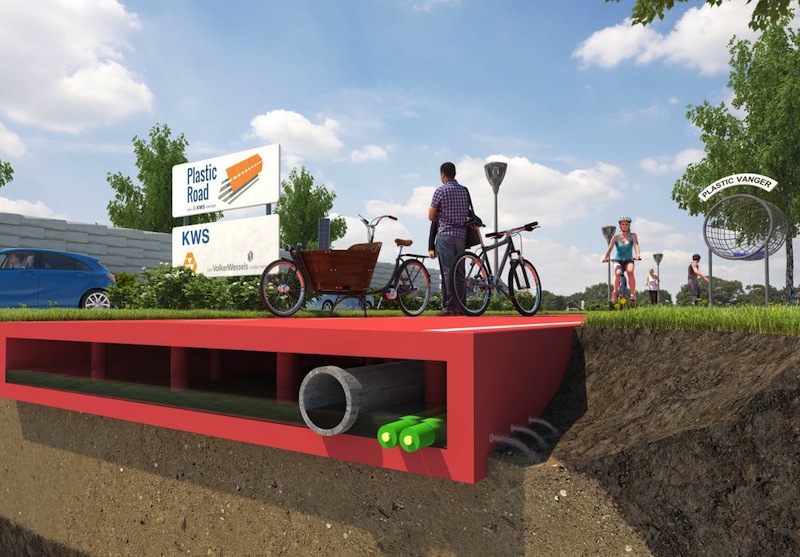
Dutch-based KWS Infra, the roads division of VolkerWessel, is piloting a program to make roads from plastic garbage, including bags and bottles extracted from the ocean, according to Fast Company. This PlasticRoad project, which is still on the drawing board, is part of a larger initiative to rid the seas of its “plastic soup”.
Alex van de Wall, KWS’s innovation manager, says that the plastic being used would include a waste stream that normally doesn’t have high-end recycling applications and would otherwise be burned.
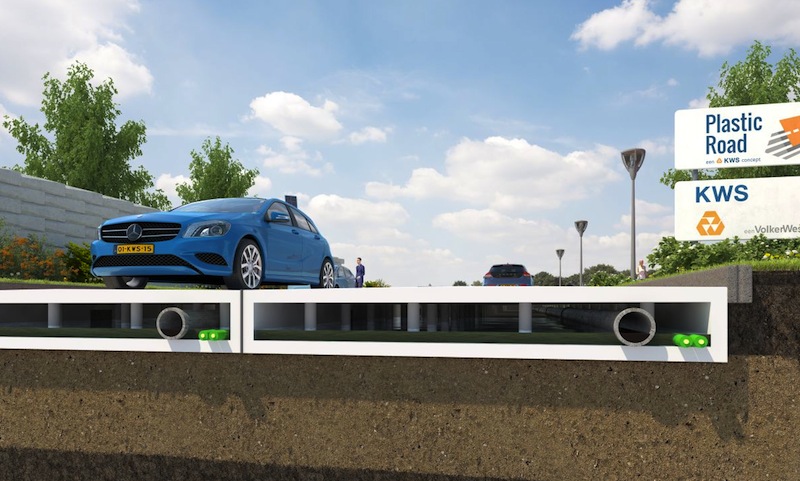

KWS sees a number of advantages to using plastic trash for roads over asphalt or concrete:
• Recycled plastic has a considerable lower carbon footprint than the production of asphalt, which accounts for 2% of global carbon emissions. Plastics can also withstand greater extremes of temperature—between -40 Celsius and 80C.
• Plastic roads could be modularized—i.e., made in factories and then snapped together in the field—so a road could be built quicker than with asphalt. KWS also claims that plastic-made roads would be far more durable and easier to maintain and repair than asphalt roads.
• Plastic could be colored white, which would help keep cities cooler and reduce what van de Wall says is the “heat island” effect caused by asphalt paving. Once this concept is translated into an actual product, “There are many options,” he says.
• When a plastic road wears out, it could be recycled again.
KWS thinks it can overcome some of the problems related to using plastic for roads, such as how the product reacts to changing temperatures and gets very hot. The company plans to test plastic roads in the lab first and then try them out at a “street lab” in Rotterdam.
“We’re very positive towards the developments around PlasticRoad,” said Jaap Peters, from that city council’s engineering department. “Rotterdam is a city that is open to experiments and innovative adaptations in practice.”
KWS is currently looking for plastic supply partners to assess the financial feasibility of its design. And if this concept pans out, the company expects to export the idea to other countries.

Related Stories
Giants 400 | Oct 30, 2017
Top 45 green engineering firms
WSP, AECOM, and Arup top BD+C’s ranking of the nation’s largest green sector engineering and EA firms, as reported in the 2017 Giants 300 Report.
Giants 400 | Oct 30, 2017
Top 130 green architecture firms
Gensler, Stantec, and HOK top BD+C’s ranking of the nation’s largest green sector architecture and AE firms, as reported in the 2017 Giants 300 Report.
Greenbuild Report | Oct 18, 2017
Rebuild, retreat, or resist
Hurricanes Harvey and Irma expose the necessity—and limitations—of resilient design and construction measures.
Sustainability | Oct 16, 2017
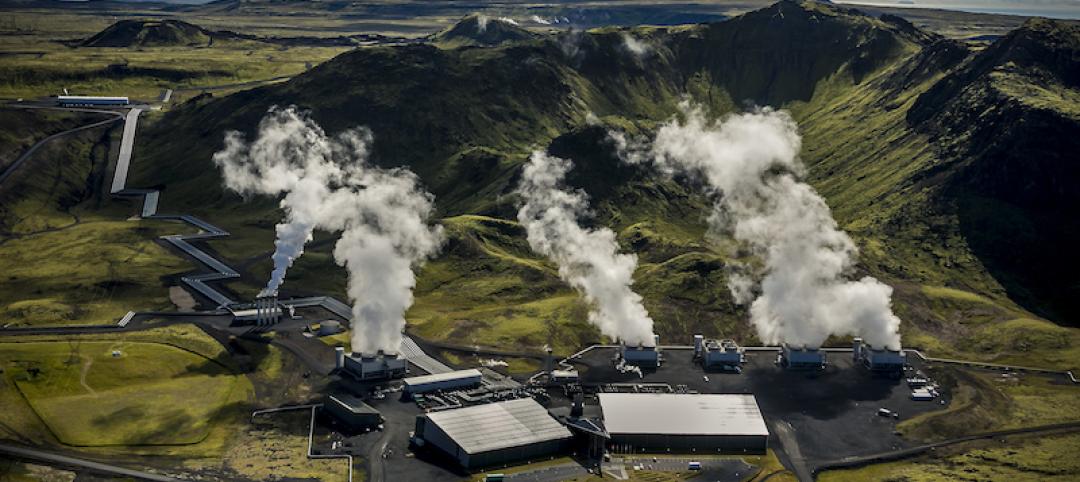
A negative emissions power plant is now operational in Iceland
The geothermal power plant in Hellisheidi, Iceland was outfitted with a Climeworks DAC module.
Sustainability | Oct 9, 2017
New Arizona State University building will reach triple net-zero performance
The science and research complex will include an atrium biome filled with plants and water.
Sustainability | Oct 4, 2017
The solutions to climate change are already at our fingertips
To keep global temperature rise below 2 degrees Celsius of warming, the International Energy Agency (IEA) reports that the global buildings sector will need to decrease its total annual greenhouse gas contribution by 77% by 2050.
Green | Oct 2, 2017
Five strategies to improve energy performance in existing buildings
After performing retro-commissioning and energy audits for more than five million square feet of existing building real estate, we have developed a list of common low/no-cost Energy Conservation Measures (ECMs) that are identified on the majority of projects.
Green | Sep 27, 2017
Wellness gains ground with real estate and property management professionals
Structure Tone survey finds LEED is still a selling point, but interest in resilience practices could be waning.
Codes and Standards | Sep 12, 2017
Washington, D.C. is first LEED Platinum city in the world
All city government buildings are powered by renewables.
Green | Sep 12, 2017
Brooklyn’s Windsor Terrace Library gets a living roof
The roof was funded through a process that allows local residents to decide how City capital dollars are spent in their neighborhoods.