Besides being one of the more famous cases of breaking and entering, what is the one thing Goldilocks is known for? No, not her love of porridge or under-the-covers naps. It is her persnickety nature that shines through most and, as much as we may not want to admit it, we all have a little bit of that Goldilocks mentality in us.
Especially when it comes to shared spaces like offices. For some it’s too hot, for others it’s too cold. It’s too bright, too dark, too loud, or too quiet; in a given office, how many people are actually comfortable with their surrounding environment? In a supposed place of productivity, such as an office, it isn’t just an inconvenience to be uncomfortable; it can quickly become a hindrance to getting work done.
But what’s the solution? We aren’t all as fortunate as our friend Goldilocks and have a few different options to pick from in order to find the one that best suits us. Or are we? Many offices have begun to implement an open office floor plan, meaning there are no assigned seats or workspaces. You can change where you sit and work on a day-to-day or hour by hour basis, meaning if it is too noisy or cold in one area, its possible to just pick up and move to another quieter or warmer area.
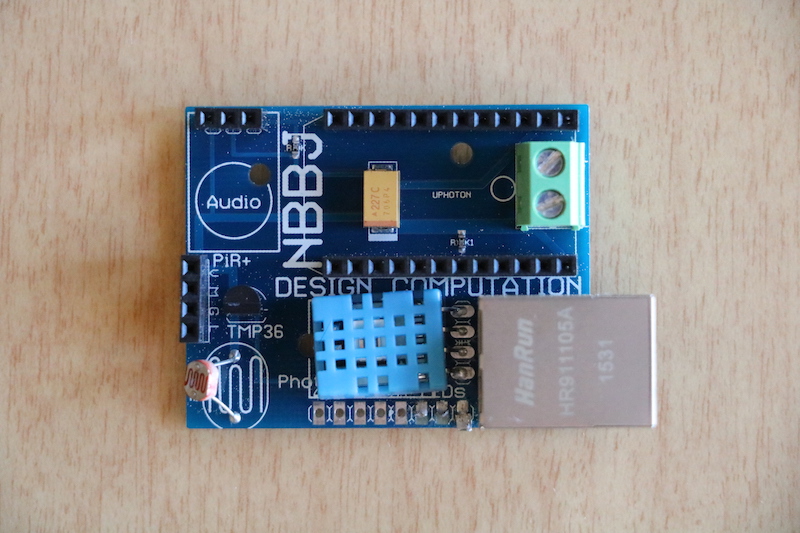
But therein lies the next issue, how do you find that quieter, warmer spot? That’s where Goldilocks comes in. No, not the Goldilocks, but the proprietary sensor technology developed by NBBJ to help employees find the perfect spot in the office, the one that is just right.
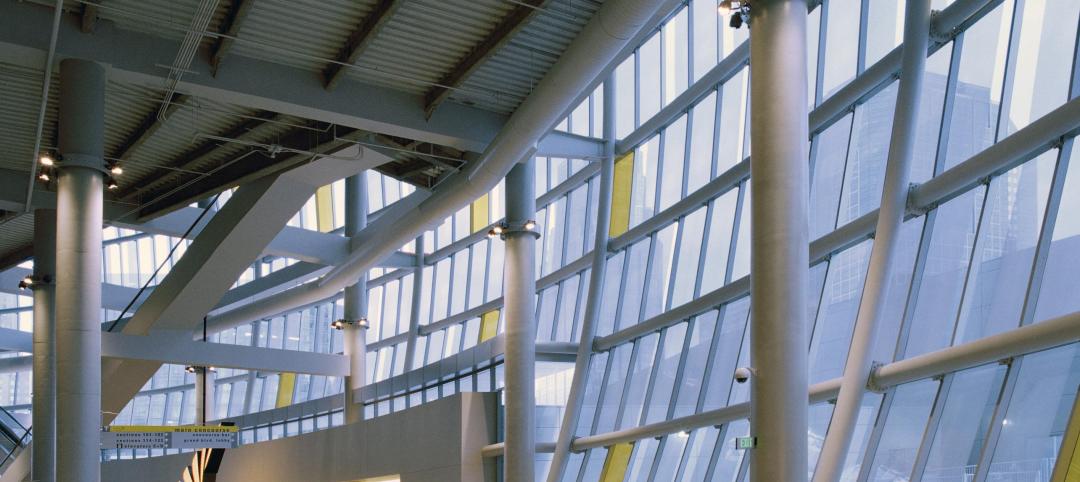
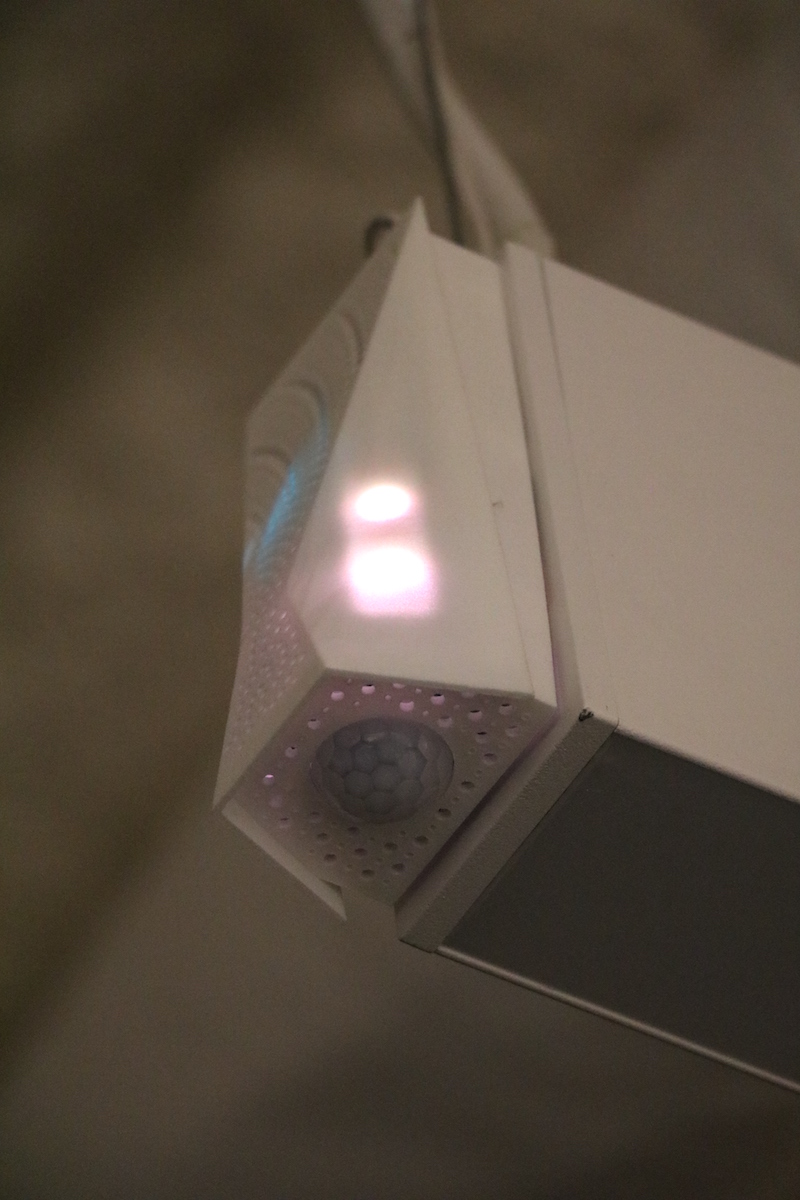
Inside its 140 Broadway offices in New York City, NBBJ installed over 50 sensors to collect data and track light levels, humidity and motion, and sound. According to NBBJ, they are the only company to incorporate sound into a sensor of this type. And considering the fact that noise is the number one complaint in the workplace, this addition of sound sensors seems like one of those why-hasn’t-anyone-done-this-before type additions.
So, where does all of this information the sensors are collecting go? Right to the accompanying app (compatible with Apple or Android smartphones) in real-time. If you get to the office and decide you require a workspace that is bright and warm, simply fire up the app, set the parameters to warm and bright, and you will be shown the best spots in the office that match exactly what you are looking for.
Not only are these sensors a solution for employees to use on a daily basis, but the information gathered, especially the information about sound, can also be used to better design spaces in the future.
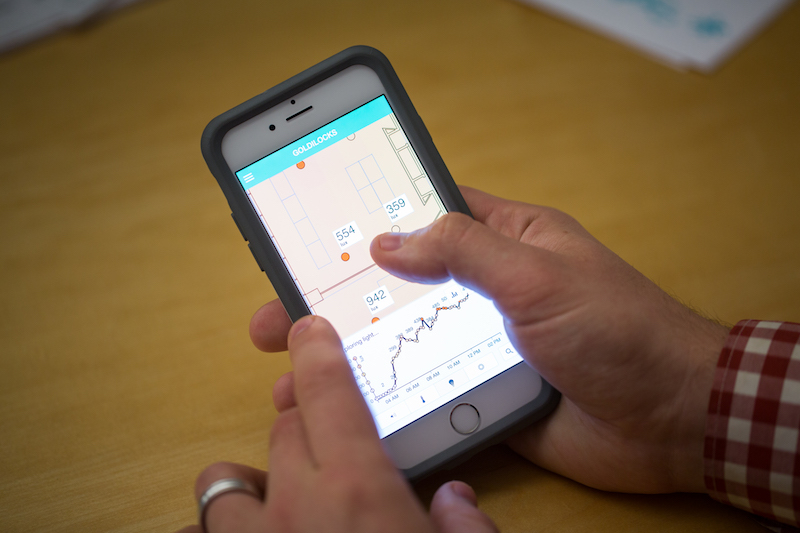 Photo courtesy of NBBJ
Photo courtesy of NBBJ

Related Stories
Engineers | Jun 5, 2023
How to properly assess structural wind damage
Properly assessing wind damage can identify vulnerabilities in a building's design or construction, which could lead to future damage or loss, writes Matt Wagner, SE, Principal and Managing Director with Walter P Moore.
Cladding and Facade Systems | Jun 5, 2023
27 important questions about façade leakage
Walter P Moore’s Darek Brandt discusses the key questions building owners and property managers should be asking to determine the health of their building's façade.
Office Buildings | May 15, 2023
Sixteen-story office tower will use 40% less energy than an average NYC office building
This month marks the completion of a new 16-story office tower that is being promoted as New York City’s most sustainable office structure. That boast is backed by an innovative HVAC system that features geothermal wells, dedicated outdoor air system (DOAS) units, radiant heating and cooling, and a sophisticated control system to ensure that the elements work optimally together.
AEC Tech Innovation | May 12, 2023
Meet Diverge, Hensel Phelps' new ConTech investment company
Thai Nguyen, Director of Innovation with Hensel Phelps, discusses the construction giant's new startup investment platform, Diverge.
University Buildings | May 5, 2023
New health sciences center at St. John’s University will feature geothermal heating, cooling
The recently topped off St. Vincent Health Sciences Center at St. John’s University in New York City will feature impressive green features including geothermal heating and cooling along with an array of rooftop solar panels. The geothermal field consists of 66 wells drilled 499 feet below ground which will help to heat and cool the 70,000 sf structure.
Mass Timber | May 3, 2023
Gensler-designed mid-rise will be Houston’s first mass timber commercial office building
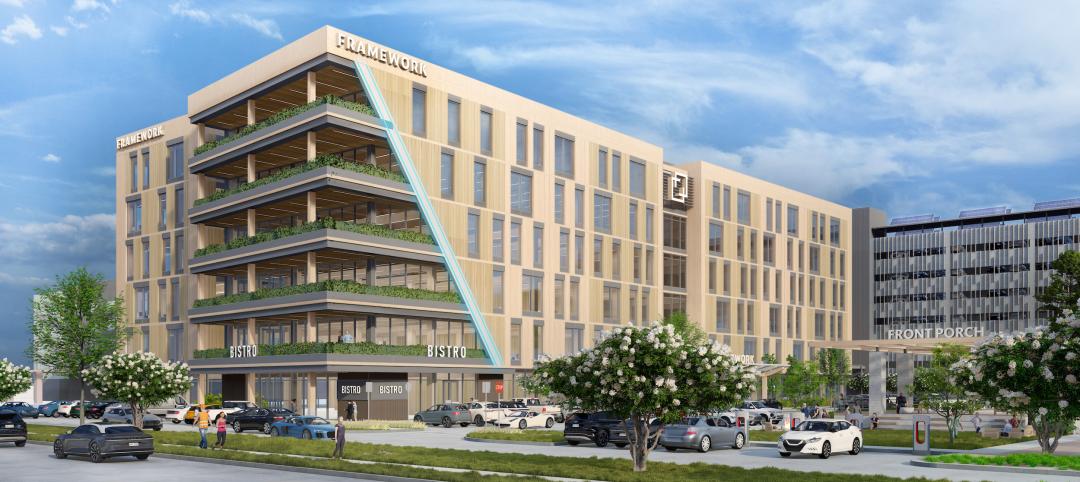
A Houston project plans to achieve two firsts: the city’s first mass timber commercial office project, and the state of Texas’s first commercial office building targeting net zero energy operational carbon upon completion next year. Framework @ Block 10 is owned and managed by Hicks Ventures, a Houston-based development company.
AEC Tech | May 1, 2023
Utilizing computer vision, AI technology for visual jobsite tasks
Burns & McDonnell breaks down three ways computer vision can effectively assist workers on the job site, from project progress to safety measures.
Design Innovation Report | Apr 27, 2023
BD+C's 2023 Design Innovation Report
Building Design+Construction’s Design Innovation Report presents projects, spaces, and initiatives—and the AEC professionals behind them—that push the boundaries of building design. This year, we feature four novel projects and one building science innovation.
Design Innovation Report | Apr 19, 2023
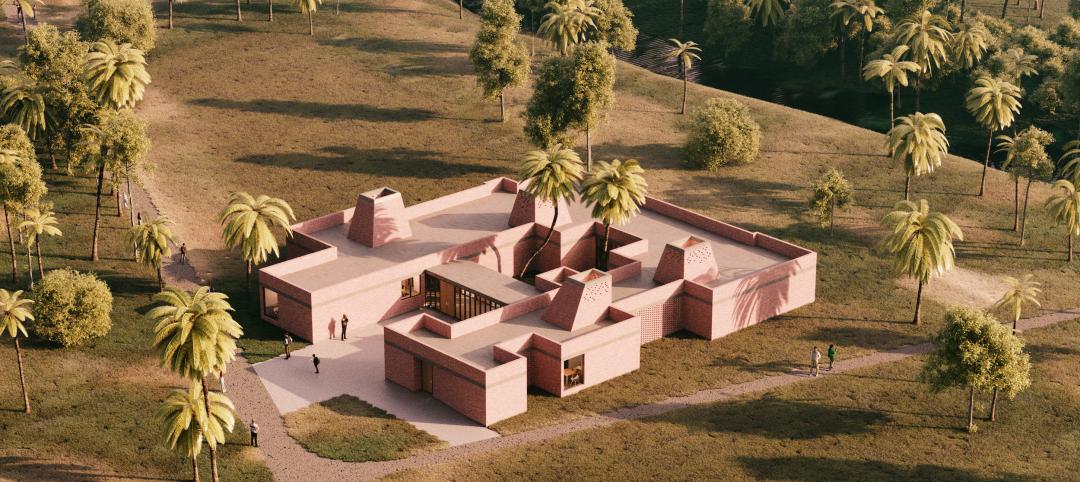
HDR uses artificial intelligence tools to help design a vital health clinic in India
Architects from HDR worked pro bono with iKure, a technology-centric healthcare provider, to build a healthcare clinic in rural India.
3D Printing | Apr 11, 2023
University of Michigan’s DART Laboratory unveils Shell Wall—a concrete wall that’s lightweight and freeform 3D printed
The University of Michigan’s DART Laboratory has unveiled a new product called Shell Wall—which the organization describes as the first lightweight, freeform 3D printed and structurally reinforced concrete wall. The innovative product leverages DART Laboratory’s research and development on the use of 3D-printing technology to build structures that require less concrete.