ASHRAE recently approved publication of its highly anticipated standard to reduce the risk of airborne infectious aerosol transmission in buildings.
ASHRAE Standard 241, Control of Infectious Aerosols establishes minimum requirements to reduce the risk of disease transmission by exposure to infectious aerosols in new buildings, existing buildings, and major renovations. Infectious aerosols are tiny, exhaled particles that can carry pathogens that cause infections or disease.
Infectious aerosols are so small that they can remain in the air for long periods of time. Use of this standard could reduce exposure to the SARS-COVID-2 virus, which causes COVID-19, the flu virus, and other pathogens.
Standard 241 provides requirements for many aspects of air system design, installation, operation, and maintenance. It includes an infection risk management mode (IRMM) that enhances the normal mode of operation via engineering controls to reduce infectious aerosol exposure of occupants. It also provides a Requirements for Use of Filtration and Air Cleaning Technology section that outlines how to draw in additional outdoor air to ventilate a building in an energy-efficient, cost-effective manner.
More on the standard from ASHRAE:
Important aspects of the standard include:
- Infection Risk Management Mode – Requirements of Standard 241 apply during an infection risk management mode (IRMM) that applies during identified periods of elevated risk of disease transmission. AHJs (Authorities Having Jurisdiction) can determine when the enhanced protections of Standard 241 will be required, but its use can also be at the discretion of the owner/operator at other times, for example, during influenza season. This aspect of Standard 241 introduces the concept of resilience – ability to respond to extreme circumstances outside normal conditions - into the realm of indoor air quality control design and operation.
- Requirements for Equivalent Clean Airflow Rate – Other indoor air quality standards, including ASHRAE Standards 62.1, 62.2, specify outdoor airflow rate and filtration requirements to control normal indoor air contaminants. Standard 241 breaks new ground by setting requirements for equivalent clean airflow rate, the flow rate of pathogen free air flow into occupied areas of a building that would have the same effect as the total of outdoor air, filtration of indoor air, and air disinfection by technologies such as germicidal ultraviolet light. This approach allows the user of the standard flexibility to select combinations of technologies to comply with the standard that best satisfy their economic constraints and energy use goals.
- Requirements for Use of Filtration and Air cleaning Technology – Dilution of indoor air contaminants by ventilation with outdoor air can be an energy intensive and expensive way to control indoor air quality. Standard 241 provides extensive requirements for use of filtration and air cleaning to effectively and safely achieve meet equivalent clean airflow requirements efficiently and cost effectively. These include testing requirements to establish performance and to demonstrate that operation does not degrade indoor air quality in other ways, for example by elevating ozone levels.
- Planning and Commissioning – Standard 241 provides assessment and planning requirements culminating in the development of a building readiness plan, a concept carried over from the work of the ASHRAE Epidemic Task Force. It also describes procedures for commissioning systems to determine their installed performance.
The standard is available for presale in the ASHRAE Bookstore.
Related Stories
Codes and Standards | Mar 5, 2015
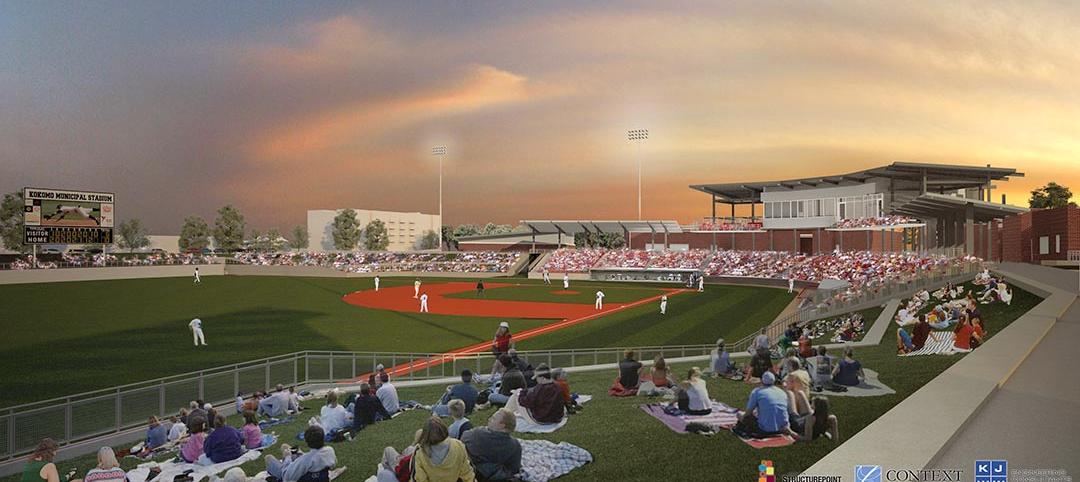
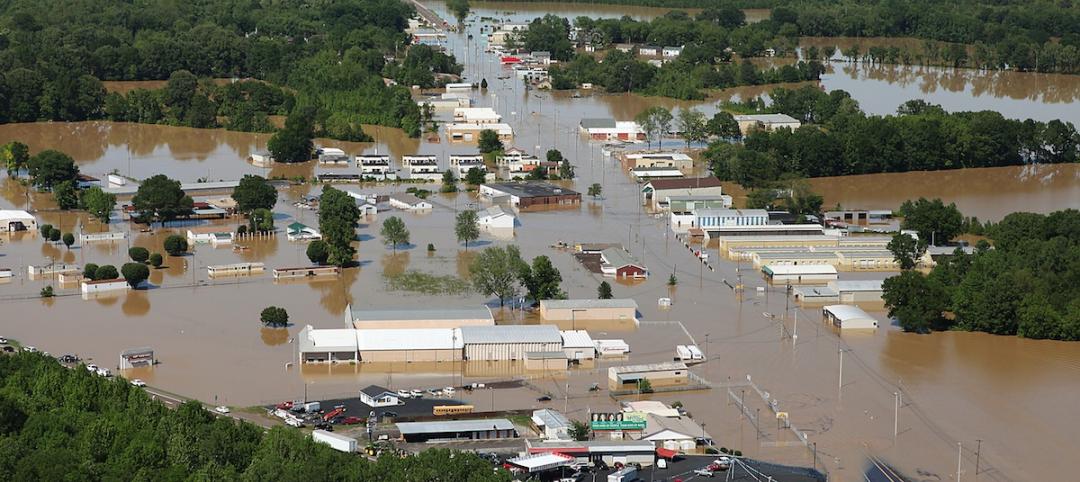
FEMA cuts off funding to Indiana after Kokomo continues building stadium in flood zone
FEMA will withhold funding on $5.5 million worth of projects such as building tornado safe rooms in schools.
Codes and Standards | Mar 5, 2015
Construction problems at prison spur support to quash non-traditional project delivery in Iowa
Iowa lawmakers are investigating construction problems at the Fort Madison prison project and are scrutinizing rules regarding project delivery on state projects.
Codes and Standards | Mar 5, 2015
AEC industry groups look to harmonize green building standards, codes
The USGBC, ASHRAE, ICC, IES, and AIA are collaborating on a single green code.
Codes and Standards | Mar 2, 2015
Nevada moves to suspend prevailing wage rules on school projects
The Nevada Senate approved a bill that would suspend prevailing wage rules on school projects.
Codes and Standards | Feb 22, 2015
Louisiana officials critical of stricter building standards in flood-prone areas
Buildings would have to be built either two or three feet above the base flood elevation for a 100-year flood or above the base elevation for a 500-year flood.
Codes and Standards | Feb 18, 2015
Buildings with rocking steel-braced frames are advantageous in earthquakes
Research at Case Western Reserve University has found that buildings that rock during an earthquake and return to plumb would withstand seismic shaking better than structural designs commonly used today in vulnerable zones of California and elsewhere.
Codes and Standards | Feb 18, 2015
USGBC concerned about developers using LEED registration in marketing
LEED administrators are concerned about a small group of developers or project owners who tout their projects as “LEED pre-certified” and then fail to follow through with certification.
Codes and Standards | Feb 12, 2015
ASHRAE, USGBC, IES consider biomass requirements in green building standard
The proposal would add biomass to approved renewables.
Codes and Standards | Feb 12, 2015
New Appraisal Institute form aids in analysis of green commercial building features
The Institute’s Commercial Green and Energy Efficient Addendum offers a communication tool that lenders can use as part of the scope of work.
Codes and Standards | Feb 8, 2015
ASHRAE, IAQA approve consolidation
Under the consolidation, IAQA will become a part of the ASHRAE organization while maintaining its own brand and Board of Directors.