The butterfly-shaped facility that is the new Rush University Medical Center (RUMC) sits quietly on the Near West Side of Chicago awaiting the official opening of its doors this month. The RUMC facility and its staff are preparing to handle any type of pandemic or chemical, biological, or radiological (CBR) disaster that might hit Chicago.
At a cost of $654 million, the 14-story, 830,000-sf medical center, designed by a Perkins+Will team led by design principal Ralph Johnson, FAIA, LEED AP, is distinguished in its ability to handle disasters.
If such an event were to hit the Chicago area, the emergency response center could offer an unprecedented level of readiness for a mass outbreak of infectious disease, bioterrorist attack, or hazmat incident.
“This is the nation’s first facility designed to provide care for patients involved in chemical, biological, and radiological disasters,” says Dr. Dino Rumoro, RUMC’s chairman of emergency medicine. “We have to be ready for any type of disaster that can hit the city of Chicago.”
The 40,000-sf emergency room includes:
- 60 individual treatment bays that can accommodate up to two patients per bay, doubling the normal patient load
- The ability to control airflow to seal off contagions in parts of the hospital
- Ambulance bays that can be converted into decontamination centers, so that CBR victims could be sprayed down in large groups
Special equipment and a flexible infrastructure allow RUMC to accommodate surge capacity to treat mass casualties beyond the ER. Pillars in the main lobby are equipped with hidden panels that provide access to oxygen and other clinical gases, allowing RUMC to accommodate even more beds in a disaster scenario.
The floors above the emergency room are devoted to the interventional platform, where diagnostic testing, surgical, and interventional services and recovery are located within a short distance of each other. This results in enhanced collaboration between medical specialists, patients, and families. A total of 42 procedure rooms with enlarged operating rooms provide the latest surgical technology.
The new hospital adds 304 individual adult and critical beds on its top five floors, increasing the total number of beds across existing and new facilities to 664, making RUMC one of the largest hospitals in the area.
The hospital is awaiting LEED Gold certification. In addition to using recycled construction materials and considerable water- and energy-saving measures, the hospital has three green roofs—one atop the main tower, another on the ninth floor open to staff, and a third atop the entry pavilion. BD+C
Related Stories
| Nov 27, 2013
Exclusive survey: Revenues increased at nearly half of AEC firms in 2013
Forty-six percent of the respondents to an exclusive BD+C survey of AEC professionals reported that revenues had increased this year compared to 2012, with another 24.2% saying cash flow had stayed the same.
| Nov 27, 2013
Wonder walls: 13 choices for the building envelope
BD+C editors present a roundup of the latest technologies and applications in exterior wall systems, from a tapered metal wall installation in Oklahoma to a textured precast concrete solution in North Carolina.
| Nov 27, 2013
University reconstruction projects: The 5 keys to success
This AIA CES Discovery course discusses the environmental, economic, and market pressures affecting facility planning for universities and colleges, and outlines current approaches to renovations for critical academic spaces.
| Nov 26, 2013
7 ways to make your firm more successful
Like all professional services businesses, AEC firms are challenged to effectively manage people. And even though people can be rather unpredictable, a firm’s success doesn’t have to be. Here are seven ways to make your firm more successful in the face of market variability and uncertainty.
| Nov 26, 2013
Design-build downsized: Applying the design-build method in an era of smaller projects
Any project can benefit from the collaborative spirit and cooperative relationships embodied by design-build. But is there a point of diminishing return where the design-build project delivery model just doesn't make sense for small projects? Design-build expert Lisa Cooley debates the issue.
| Nov 25, 2013
Electronic plan review: Coming soon to a city near you?
With all the effort AEC professionals put into leveraging technology to communicate digitally on projects, it is a shame that there is often one major road block that becomes the paper in their otherwise “paperless” project: the local city planning and permitting department.
| Nov 22, 2013
Kieran Timberlake, PE International develop BIM tool for green building life cycle assessment
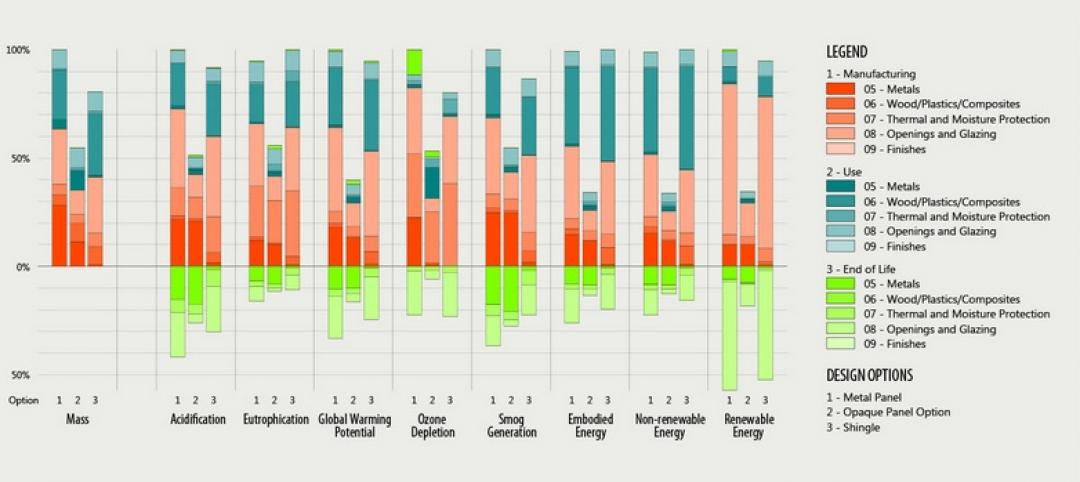
Kieran Timberlake and PE International have developed Tally, an analysis tool to help BIM users keep better score of their projects’ complete environmental footprints.
| Nov 20, 2013
Architecture Billings Index slows in October; project inquiries stay strong
Following three months of accelerating demand for design services, the Architecture Billings Index reflected a somewhat slower pace of growth in October. The October ABI score was 51.6, down from a mark of 54.3 in September.
| Nov 19, 2013
Pediatric design in an adult hospital setting
Freestanding pediatric facilities have operational and physical characteristics that differ from those of adult facilities.
| Nov 18, 2013
6 checkpoints when designing a pediatric healthcare unit
As more time and money is devoted to neonatal and pediatric research, evidence-based design is playing an increasingly crucial role in the development of healthcare facilities for children. Here are six important factors AEC firms should consider when designing pediatric healthcare facilities.