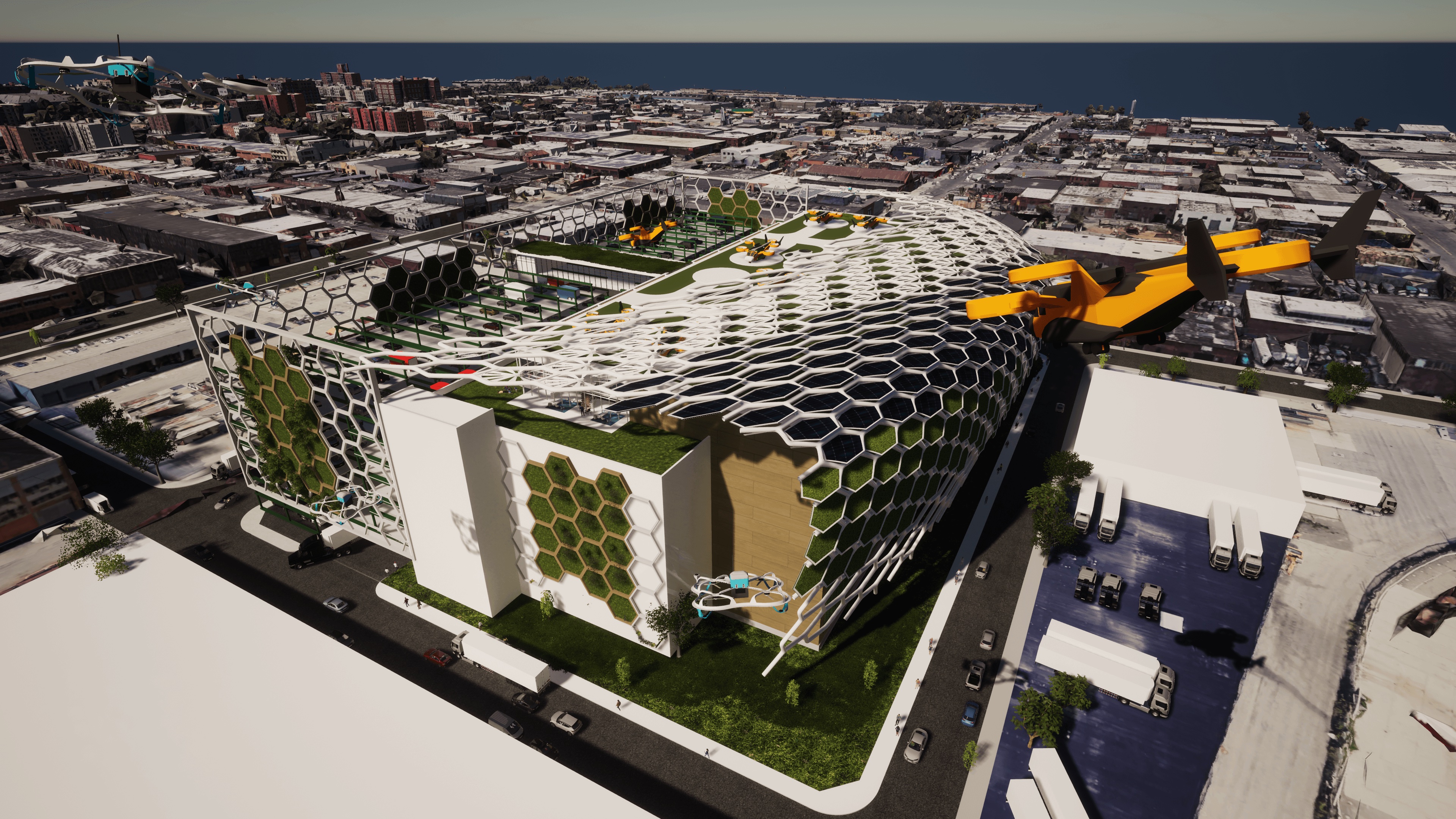
Demand for multistory logistics centers is increasing in cities around the country that are looking to provide “last mile” ecommerce delivery to urban populations while using the least amount of costly land possible.
But vertical logistics centers have their own operational complexities that include inventory and fleet management, vehicular parking, and staying abreast of the latest transportation modes and technologies.
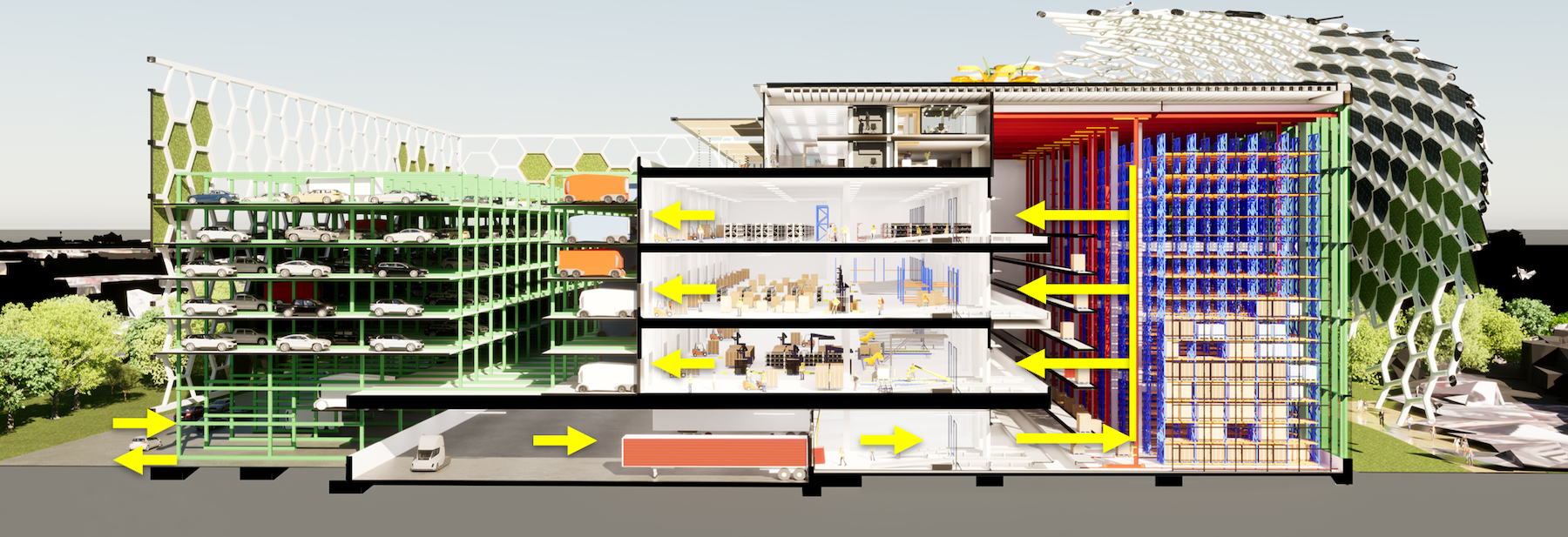
The national design firm Ware Malcomb recently presented a design concept for a Logistics Building of the Future at a conference in Jersey City, N.J., conducted by NAIOP, the Commercial Real Estate Development Association. This concept, which the firm is calling a “thought exercise,” places a premium on technology driven efficiency and coordination. The concept also pays heed to reducing the building’s carbon footprint through a combination of natural and mechanical solutions.
The question being answered by this design concept, says Matt Brady, LEED AP, an Architect and Executive Vice President at Ware Malcomb’s office in Irvine, Calif., is how to fit more products into a facility while realizing the greatest efficiency. “The through-put is the game changer,” he says.
Automation drives efficiency
This hypothetical logistics center is a five-story building (including its roofdeck) that would sit on 4.6. acres in San Francisco. Ware Malcomb collaborated with several industry leaders to devise this concept, including Jones Lang LaSalle, DH Property Holdings (a leading developer of urban infill industrial facilities), Suffolk Construction (for building costs), and Parkmatic, which provides space-controlling automated parking racks.
Brady says computer-driven systems play a big role in the logistics center’s operations: they coordinate arrivals so that trailers can be precision-parked into the facility’s docks; they organize and stage the storage of goods in the building’s tall warehouse so inventory can be retrieved quicker; and in partly automated packing areas, loads of goods are created to be placed into smaller delivery vans, the drivers for which are assigned automatically.
One of the big problems for vertical logistics center in urban settings is finding enough space for parking. Brady notes that in New York, trailer and van drivers sometimes end up parking blocks from existing facilities. Ware Malcomb’s design concept stacks employee vehicles in racks so delivery vans can fit into the center and aren’t idling elsewhere. Brady acknowledges that parking becomes more of a challenge when vehicles are electric and take time to recharge.
Ware Malcomb’s concept is multimodal and assumes electric vehicles and delivery drones. “Flying vehicles aren’t here yet, but warehouses need to be ready for them,” he explains.
A greener distribution center
The design concept also shows options to reduce the logistics center’s carbon footprint. For example, the concept envisions a honeycombed skin that generates wind and cools the building’s exterior surface. The concept also incorporates sustainable features such as agricultural air filtration, wind turbines, angled solar cells, photoreactor algae-filled glass, rainwater collection, and 3D-printed flexible infrastructure.
Brady says the feedback from developers so far has been positive, and at least one developer is interested “in doing something like this.” An ecommerce company has expressed interest in using Ware Malcomb’s design concept as part of a charrette about industrial buildings in general.
Ware Malcomb sees its concept as leading to speculative development, ideally for a single tenant per building so that there’s just one systems operator. Brady says that the point of this exercise is not to get developers to copy the concept as much as it is to prepare them for what might be coming. “Occupiers are evolving fast, and developers need to keep up,” he says.
Brady also believes that while new construction of industrial buildings has been leveling off, demand is a function of the economy. “Based on people we talk to, there’s still a lot of room for ecommerce growth.”
Related Stories
| Apr 2, 2014
8 tips for avoiding thermal bridges in window applications
Aligning thermal breaks and applying air barriers are among the top design and installation tricks recommended by building enclosure experts.
| Apr 2, 2014
Check out the stunning research facility just named 2014 Lab of the Year [slideshow]
NREL's Energy Systems Integration Facility takes top honors in R&D Magazine's 48th annual lab design awards.
| Mar 26, 2014
Callison launches sustainable design tool with 84 proven strategies
Hybrid ventilation, nighttime cooling, and fuel cell technology are among the dozens of sustainable design techniques profiled by Callison on its new website, Matrix.Callison.com.
| Mar 26, 2014
First look: Lockheed Martin opens Advanced Materials and Thermal Sciences Center in Palo Alto
The facility will host advanced R&D in emerging technology areas like 3D printing, energetics, thermal sciences, and nanotechnology.
| Mar 20, 2014
Common EIFS failures, and how to prevent them
Poor workmanship, impact damage, building movement, and incompatible or unsound substrate are among the major culprits of EIFS problems.
| Mar 20, 2014
Fluor defines the future 7D deliverable without losing sight of real results today
A fascinating client story by Fluor SVP Robert Prieto reminds us that sometimes it’s the simplest details that can bring about real results today—and we shouldn’t overlook them, even as we push to change the future state of project facilitation.
| Mar 19, 2014
Frames: the biggest value engineering tip
In every aspect of a metal building, you can tweak the cost by adjusting the finish, panel thickness, and panel profile. These changes might make a few percentage points difference in the cost. Change the framing and you have the opportunity to affect 10-20 percent savings to the metal building portion of the project.
| Mar 12, 2014
14 new ideas for doors and door hardware
From a high-tech classroom lockdown system to an impact-resistant wide-stile door line, BD+C editors present a collection of door and door hardware innovations.
Sponsored | | Mar 10, 2014
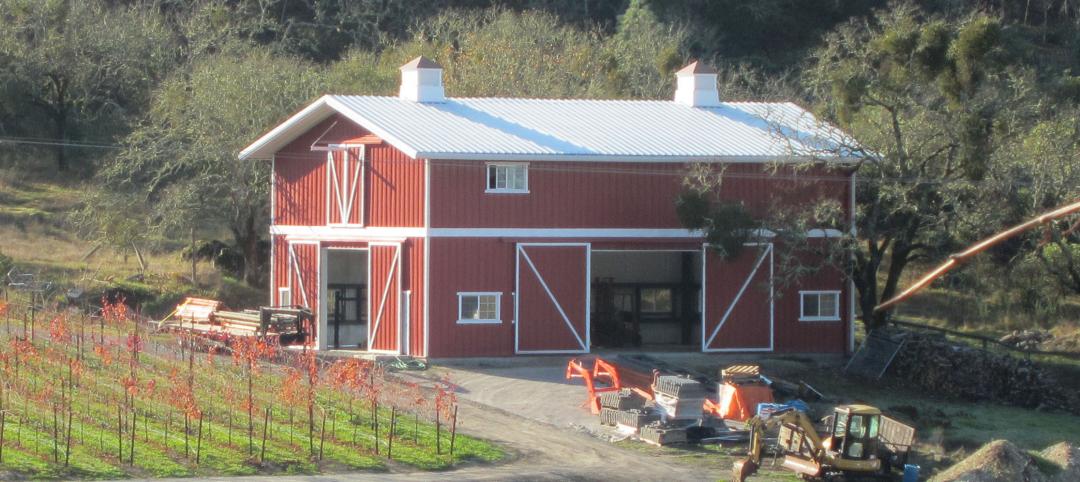
A high-performance barn
Bastoni Vineyards replaces a wooden barn with an efficient metal building used for maintenance, storage, and hosting events.
| Mar 7, 2014
Chicago's 7 most threatened buildings: Guyon Hotel, Jeffrey Theater make the list
The 2014 edition of Preservation Chicago's annual Chicago's 7 list includes an L station house, public school, theater, manufacturing district, power house, and hotel.