Last December, Prince George’s County in Maryland became the first K-12 school district in the nation to partner with the private sector to bundle and finance a six-school delivery program. The public-private consortium included Fengate Capital Management, Gilbane’s development and building companies, designer and architect Stantec, and maintenance services provider Honeywell. JLL was Prince George’s Public School’s financial advisor.
The new schools will be ready for the 2023-24 school year, and add 8,000 new seats across five middle schools and one K-8 school. The school district is expected to save $174 million in deferred maintenance and construction costs.
Financing the construction and renovation of public schools continues to be a major challenge that, in many states, hinges on voters approving bond issues or taxes. For most of America’s 13,000-plus school districts, the private sector is an untapped source for funding.
“At the moment, there is no common definition of a P3 in the U.S., there is no centralized governing body overseeing P3s, and there is an extremely limited breadth of experience in [the] K-12 sector,” states Braisford & Dunlavey, an education planning, development, and management consultant based in Washington, D.C., which has released a free, 40-page guide to K-12 public-private partnerships (P3s).
The guide notes that the National Council of Public-Private Partnerships identifies 18 different legal and financial P3 structures, and each agreement is sui generis to the partnership, or deal. “In K-12, we expect the range of employed structures to be much smaller. Still, each partnership will be unique.”
SEVERAL MOTIVATIONS CITED
The guide cautions that P3s are complex deal structures, and there is no simple pro/con checklist for school districts considering entering into them.
Possible motivations might include accelerating the schedule for delivery of one or more school projects. (That was the primarily factor driving Prince George’s County’s P3.) Reallocating risk and lowering construction costs are two other reasons why P3s might make sense. But school districts must also realize there’s a cost to shifting risk to the private sector in terms of capital lending, legal and development fees, and other compensation.
“P3s aren’t employed for fun,” cautions the guide. “They’re neither simple nor free, and can face a resistant community. If they’re employed, it means there’s a problem that needs solving and it’s best solved with a P3.”
And because K-12 districts typically lack revenue-generating components, the full range of P3s isn’t available to them. “We expect most large-scale projects in K-12 will resemble availability payment agreements/concessionaire agreements, in which the development team designs, builds, finances, operates, and maintains a building that it ‘makes available’ to the district in exchange for availability payments (paid annually, throughout the life of the agreement),” the guide states.
For a P3 to be a viable funding solution, enabling legislation must be in place, the guide states. And for large-scale projects to “pencil out,” the guide recommends that operations and maintenance be key components to most deals.
IS YOUR DISTRICT A GOOD P3 CANDIDATE?
Braisford & Dunlavey states that certain districts fit the profile for considering P3s:
•A large school district facing financially crippling deferred maintenance. “Good news for these projects: Bigger districts tend to have bigger budgets. That can attract developers and other private partners for a large-scale P3. While a smaller project isn’t doomed, it’s less likely.”
•A large school district facing growing enrollment.
•A school district (small or large) with land it can give up, and whose needs it cannot meet on its own. The guide suggests that this type of revenue model is an “easier” P3, but the district still needs to convince the public that this is the best use of the land.
•A school district with a visionary leader who steps up and says, “Enough is enough.” The guide says that projects need champions to navigate approvals, manage stakeholder engagement, and think strategically.
The attributes of any good engagement, according to Braisford & Dunlavey, start with a clear definition of expected outcomes. These pacts also require sufficient time to hash out the deal’s structure and legal details. Stakeholders need to be “true partners” invested in each other’s success, and always honest.
The school district should define the quality of the project’s design and construction, but also be flexible enough to allow its private-sector partners to achieve those parameters.
Related Stories
| Oct 26, 2014
Study asks: Do green schools improve student performance?
A study by DLR Group and Colorado State University attempts to quantify the student performance benefits of green schools.
| Oct 21, 2014
Check out BD+C's GreenZone Environment Education Classroom debuting this week at Greenbuild
At the conclusion of the show, the modular classroom structure will be moved to a permanent location in New Orleans' Lower 9th Ward, where it will serve as a community center and K-12 classroom.
| Oct 16, 2014
Perkins+Will white paper examines alternatives to flame retardant building materials
The white paper includes a list of 193 flame retardants, including 29 discovered in building and household products, 50 found in the indoor environment, and 33 in human blood, milk, and tissues.
Sponsored | | Oct 16, 2014
Mill Brook Elementary School colors outside the lines with creative fire-rated framing solution
Among the building elements contributing to the success of the elementary school’s public learning areas is a fire-rated stairwell that supports the school’s vision for collaboration. HMFH Architects designed the stairwell to be bright and open, reflecting the playful energy of students. SPONSORED CONTENT
| Oct 15, 2014
Harvard launches ‘design-centric’ center for green buildings and cities
The impetus behind Harvard's Center for Green Buildings and Cities is what the design school’s dean, Mohsen Mostafavi, describes as a “rapidly urbanizing global economy,” in which cities are building new structures “on a massive scale.”
| Oct 12, 2014
AIA 2030 commitment: Five years on, are we any closer to net-zero?
This year marks the fifth anniversary of the American Institute of Architects’ effort to have architecture firms voluntarily pledge net-zero energy design for all their buildings by 2030.
| Oct 9, 2014
Regulations, demand will accelerate revenue from zero energy buildings, according to study
A new study by Navigant Research projects that public- and private-sector efforts to lower the carbon footprint of new and renovated commercial and residential structures will boost the annual revenue generated by commercial and residential zero energy buildings over the next 20 years by 122.5%, to $1.4 trillion.
| Sep 29, 2014
Living Building vs. LEED Platinum: Comparing the first costs and savings
Skanska USA's Steve Clem breaks down the costs and benefits of various ultra-green building standards and practices.
| Sep 24, 2014
Architecture billings see continued strength, led by institutional sector
On the heels of recording its strongest pace of growth since 2007, there continues to be an increasing level of demand for design services signaled in the latest Architecture Billings Index.
| Sep 22, 2014
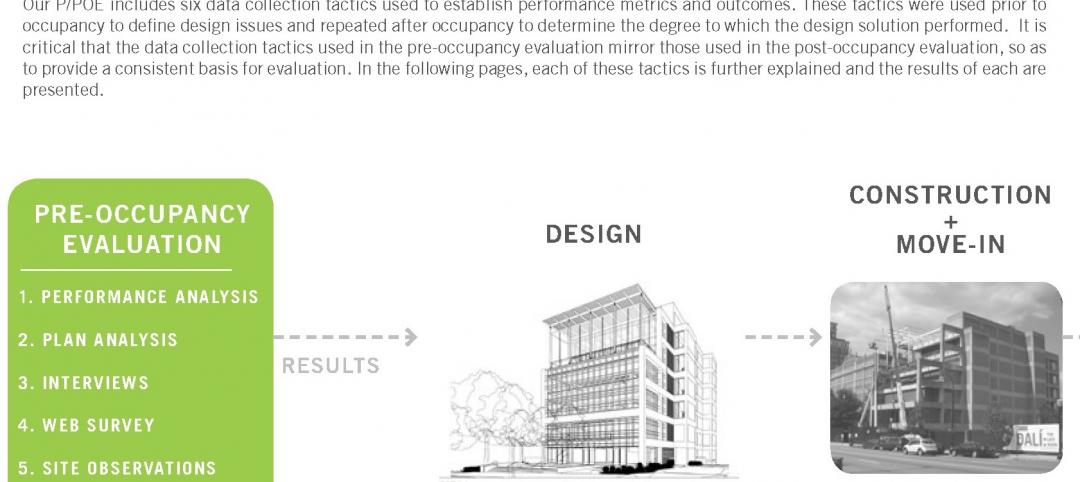
4 keys to effective post-occupancy evaluations
Perkins+Will's Janice Barnes covers the four steps that designers should take to create POEs that provide design direction and measure design effectiveness.