A remarkable number of biopharma companies, under the gun to get their research and products to market quicker, aren't happy with design-build and design-build-bid methods of construction project delivery. However, lean and integrated delivery models are still being adopted warily by this sector, with questions about quality being among the primary barriers.
These are some of the key findings in “Horizons: Life Sciences,” a report released by the AEC and consulting firm CRB, that explores trends and attitudes about processes and manufacturing for the biopharmaceutical industry, based on responses of more than 500 industry leaders to nearly 80 questions.
The report presents a biopharma industry that has been turned upside down by the coronavirus pandemic and the urgency it has fomented to provide solutions to these kinds of health events. This disruption has spurred “a whole new mindset, which casts off our industry’s conservative nature in favor of more innovation, more speed, and more flexibility in the name of more lives saved,” Noel Maestre, CRB’s Vice President of Life Sciences, writes in the report’s executive summary. “We will one day defeat this pandemic, but the waves of change that are overtaking the life sciences are only just gathering momentum.”
GAUGING NEW MODELS FOR COST AND RISK
The report touches on a host of topics that include cell and gene therapy production, the role that technology like AI and blockchain is playing in biopharma research and manufacturing, and how what the report calls “Pharma 4.0”—an incorporation of the state-of-the art operating models—is introducing digitization to the pharmaceutical sector. “Companies that embrace Pharma 4.0 are able to harmonize the flow of data from R&D through manufacturing and distribution, enhance cybersecurity, and improve their quality and regulatory compliance,” the report states.
However, to reach that plateau—what the report calls the next Digital Plant Maturity Model—biopharma companies must find ways to assuage their concerns about cost, risk management, and security, and look realistically at their operational parameters and limitations. For example, two-thirds of respondents were confident that their companies are ready to implement blockchain to secure their supply chains, which CRB thinks is overly optimistic: “What is holding back widespread adoption of blockchain is the lack of computational power.”
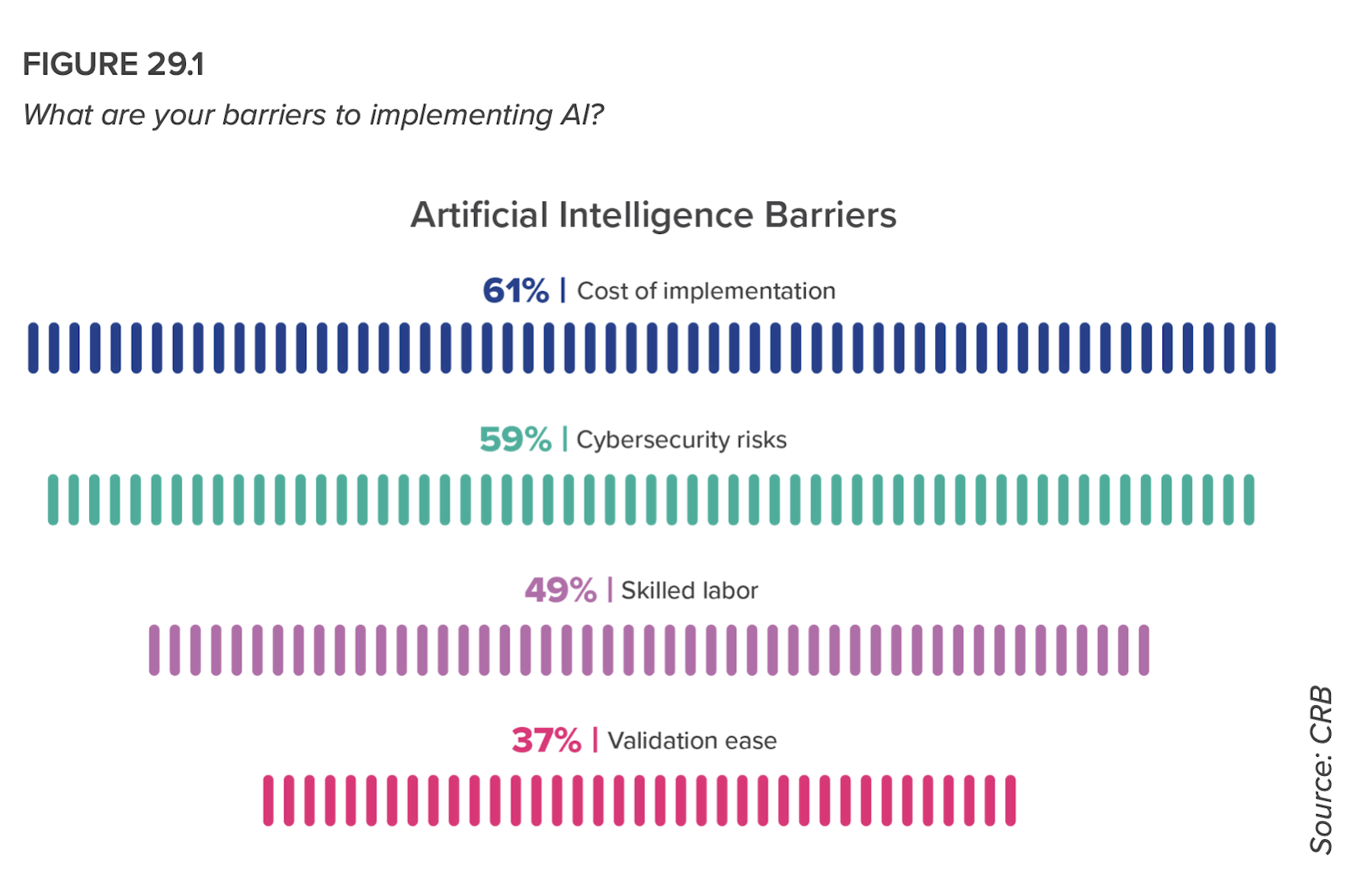
In that same vein, despite acknowledging shortages in skilled data analysts and concerns about cost and cybersecurity, respondents intend to use AI for quality testing (71%), to improve material planning (59%), for predictive analytics (53%), and to improve efficiency (52%).
NOT ENOUGH AEC FIRMS FOR LIFE SCIENCES PROJECTS
A good portion of this 106-page report addresses life sciences-related construction. If digitalization represents level four of the manufacturing process, CRB thinks that most construction companies are at level three, “having moved beyond the data silos that that can exist between design and construction teams.”
CRB’s internal Construction 4.0 initiative is applying Digital twin and augmented reality to the design and construction of biopharma facilities. “AR is a good starting point for incorporating aspects of Pharma 4.0 into the construction process,” the report states. And CRB is “beginning to see the ease with which 3D printing is becoming possible in manufacturing and even construction.”
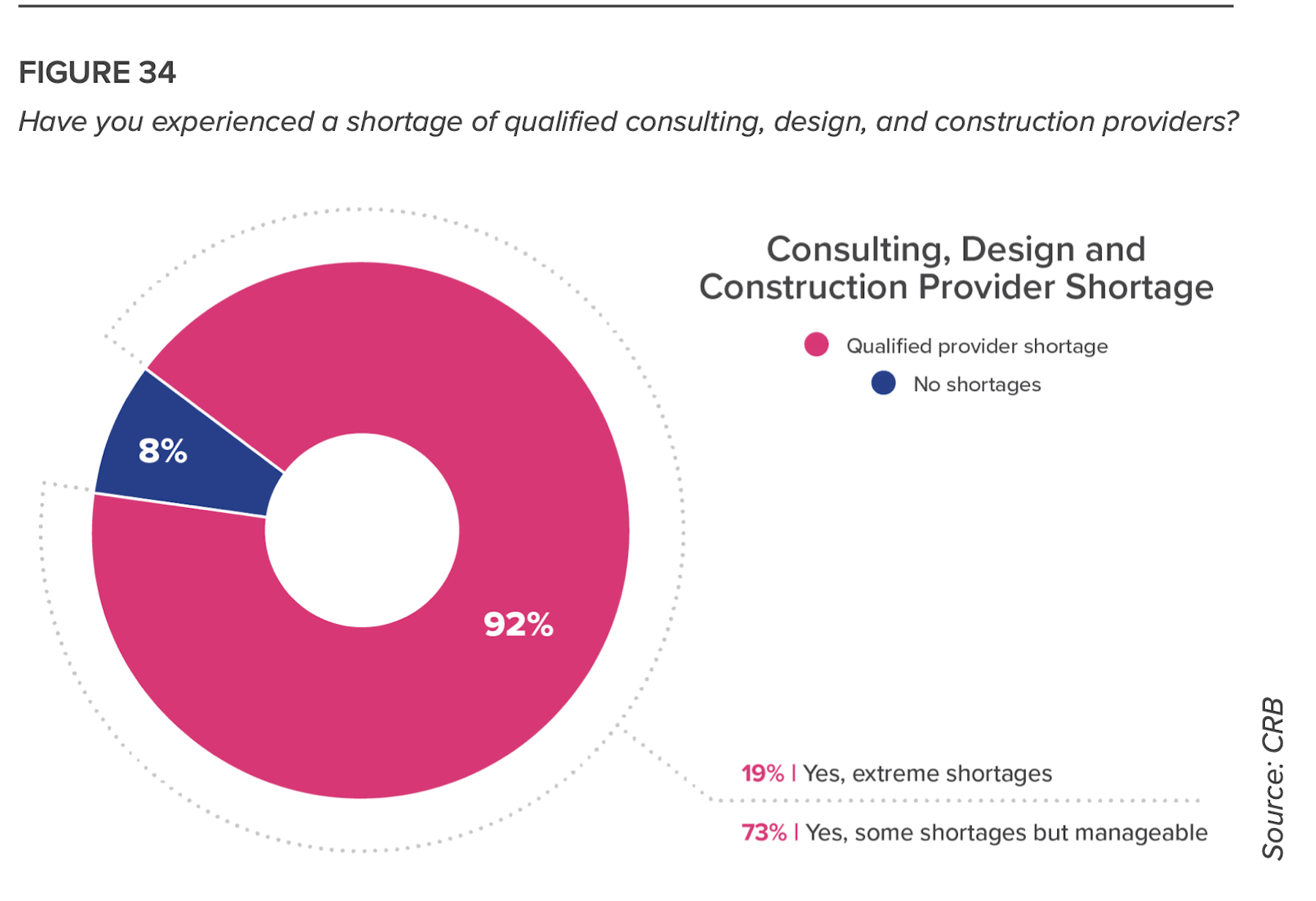
One major problem, however, is impeding a broader involvement in this movement: A sizable number of respondents to this survey cited a shortage of available AEC partners for their building projects. The answer, suggests CRB, is “to find partners capable of keeping schedules on track by establishing a phased project delivery approach.”
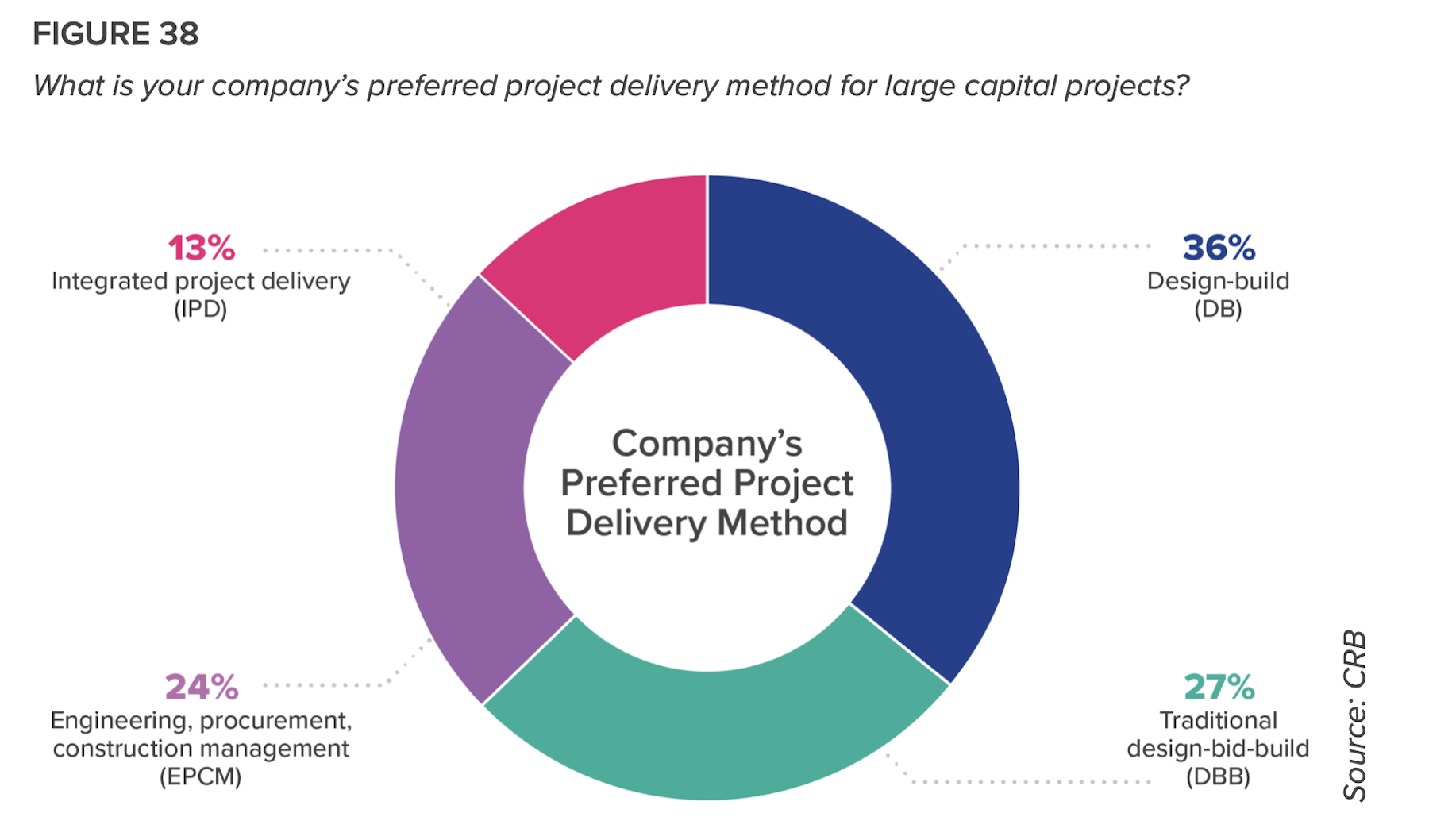
But such approaches have been slow to catch on among biopharma companies. Despite “significant dissatisfaction” with the dominant delivery models, more than 60 percent of respondents continue to favor design-build or design-build-bid. Only 13 percent prefer Integrated Project Delivery, and that drops to just 6 percent among Contract Manufacturing Organizations (CMOs).
CRB infers that many biopharma companies are making delivery choices out of ignorance: just 9 percent of respondents said they were “very familiar” with lean principles. (That number rises to 20 percent among big pharma companies.)
And while 90 percent of respondents said they are open to alternative delivery methods, 60 percent also said that procurement-method constraints were holding them back.
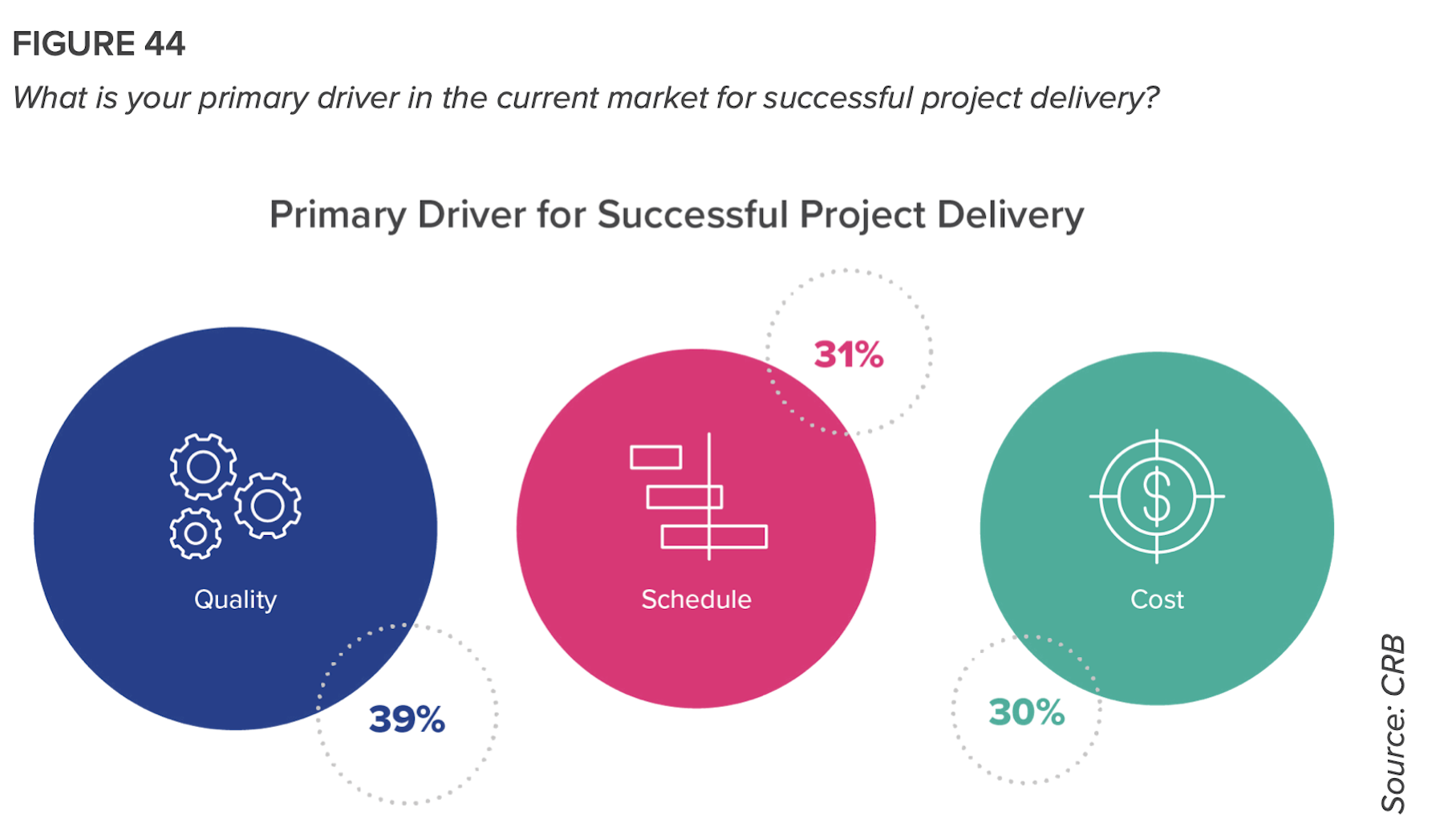
“If it’s a 10-step path to universal acceptance of IPD, we’re probably at about Step 3, and reaching full acceptance won’t likely happen in this decade,” the report states. “But there is movement, and a clear recognition of the shortcomings of the traditional models. The pandemic has opened the gates to welcome a different way of doing things.”
A RELUCTANT EMBRACE OF PREFAB AND MODULAR
The report takes a closer look at the pharma industry’s acceptance of prefabrication, modularization, and off-site manufacturing, and finds it wanting. Only half of respondents think that these alternatives are “moderately valuable” to their projects, and another 48% think they are of slight or no value.
Ninety-three percent of those polled ranked quality as their top adoption concern. More than three-quarters of startup companies listed cost as their main barrier.
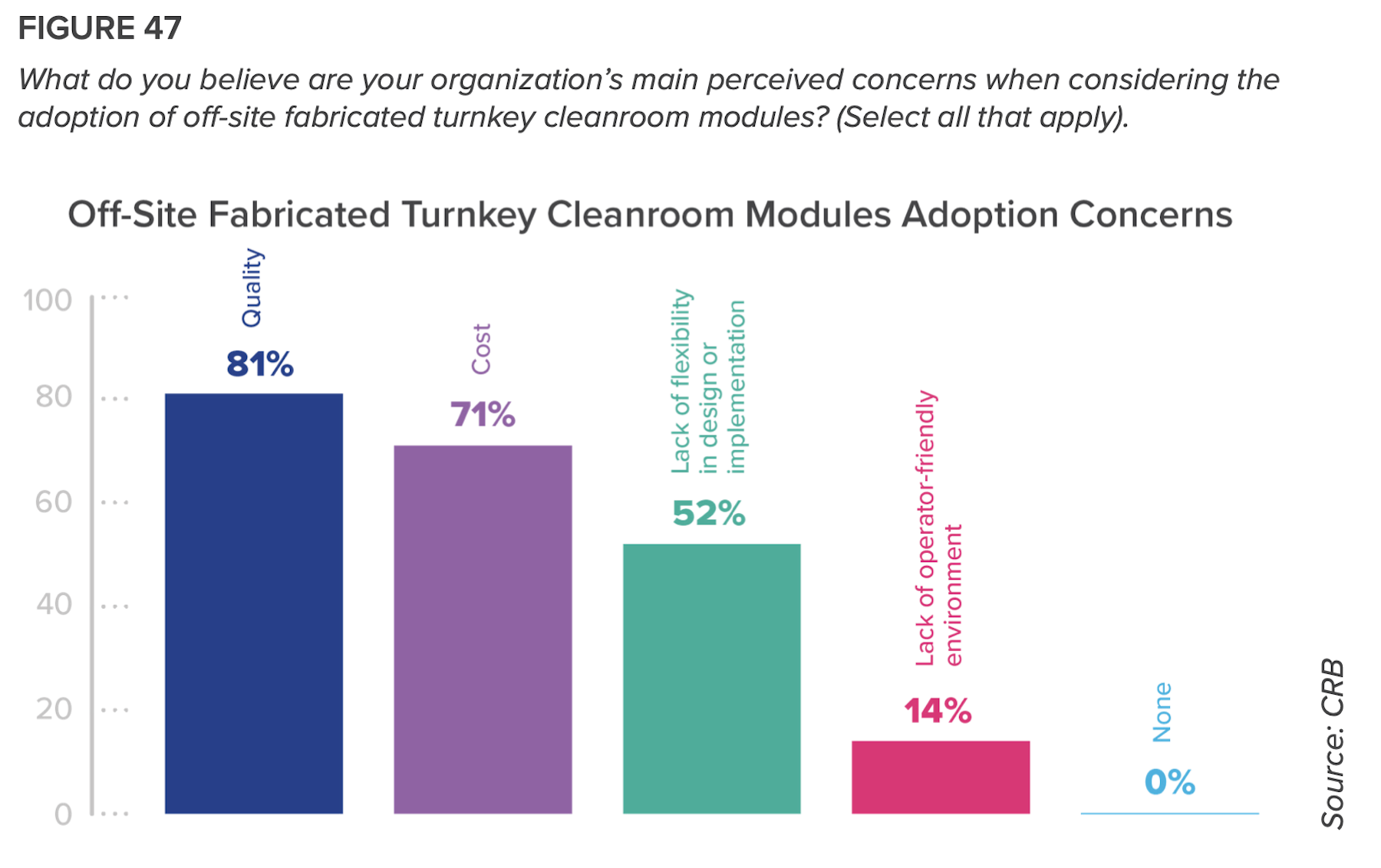
But CRB insists that prefab and modular production “is not just a fad.” Indeed, the survey’s respondents ranked financial modeling the most important among tools needed to achieve greater adoption. “An important component of adoption is to quantify how potential additional costs are recouped,” the report states.
Related Stories
Laboratories | Oct 23, 2024
From sterile to stimulating: The rise of community-centric life sciences campuses
To distinguish their life sciences campuses, developers are partnering with architectural and design firms to reimagine life sciences facilities as vibrant, welcoming destinations. By emphasizing four key elements—wellness, collaboration, biophilic design, and community integration—they are setting their properties apart.
Laboratories | Oct 2, 2024
Trends in scientific research environments: Q&A with Flad's Matt McCord
As part of an ongoing series, Matt McCord, AIA, NCARB, LEED AP BD+C, Associate Principal with Flad Architects, discusses the future of the scientific workplace.
Laboratories | Sep 27, 2024
Traditional lab design doesn't address neurodiverse needs, study finds
A study conducted by ARC, HOK, and the University of the West of Scotland, has revealed that half (48.1%) of all survey respondents who work in laboratory settings identify as neurodivergent.
Laboratories | Sep 26, 2024
BSL conversions: A cost-efficient method to support high-containment research
Some institutions are creating flexible lab spaces that can operate at a BSL-2 and modulate up to a BSL-3 when the need arises. Here are key aspects to consider when accommodating a rapid modulation between BSL-2 and BSL-3 space.
Higher Education | Sep 18, 2024
Modernizing dental schools: The intersection of design and education
Page's John Smith and Jennifer Amster share the how firm's approach to dental education facilities builds on the success of evidence-based design techniques pioneered in the healthcare built environment.
Great Solutions | Jul 23, 2024
41 Great Solutions for architects, engineers, and contractors
AI ChatBots, ambient computing, floating MRIs, low-carbon cement, sunshine on demand, next-generation top-down construction. These and 35 other innovations make up our 2024 Great Solutions Report, which highlights fresh ideas and innovations from leading architecture, engineering, and construction firms.
Laboratories | Jul 3, 2024
New science, old buildings: Renovating for efficiency, flexibility, and connection
What does the research space of the future look like? And can it be housed in older buildings—or does it require new construction?
Mass Timber | Jun 26, 2024
Oregon State University builds a first-of-its-kind mass timber research lab
In Corvallis, Oreg., the Jen-Hsun Huang and Lori Mills Huang Collaborative Innovation Complex at Oregon State University aims to achieve a distinction among the world’s experimental research labs: It will be the first all-mass-timber lab meeting rigorous vibration criteria (2000 micro-inches per second, or MIPS).
Healthcare Facilities | Jun 18, 2024
A healthcare simulation technology consultant can save time, money, and headaches
As the demand for skilled healthcare professionals continues to rise, healthcare simulation is playing an increasingly vital role in the skill development, compliance, and continuing education of the clinical workforce.
Laboratories | May 24, 2024
The Department of Energy breaks ground on the Princeton Plasma Innovation Center
In Princeton, N.J., the U.S. Department of Energy’s Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) has broken ground on the Princeton Plasma Innovation Center (PPIC), a state-of-the-art office and laboratory building. Designed and constructed by SmithGroup, the $109.7 million facility will provide space for research supporting PPPL’s expanded mission into microelectronics, quantum sensors and devices, and sustainability sciences.